Brief: In this tutorial, we look at some of the best RDP clients for Linux.
Sometimes, you might be required to remotely access your PC in order to carry out a few tasks. You may want to view a few files, make a few tweaks or run any other tasks.
In most cases, remote desktop connections are used by IT support to provide technical support to far-flung staff members and even by regular desktop users to connect to their remote PCs or share their desktops with their friends.
[ You might also like: Best Tools to Access Remote Linux Desktop ]
There are various RDP clients on the market that are used to facilitate remote desktop connections. This guide will review some of the best RDP clients for Linux.
1. TigerVNC – Virtual Network Computing Server
TigerVNC is a robust and platform-agnostic implementation of VNC (Virtual Network Computing), which is a free and open-source client/server application that allows users to log in to a remote system and interact with the graphical environment.
TigerVNC comes with a simple and intuitive interface that allows you to manually enter the IP address of the remote VNC server and connect to it.
It provides several options when establishing a connection including color and compression levels, encoding levels, and sharing the clipboard with the remote screen. You can also choose only to view the remote screen and not interact with it.
When it comes to security, TigerVNC provides TLS encryption to encrypt traffic send to and from the VNC server. In addition, it offers extensions for advanced authentication methods and listens to port 5900 by default.
Generally, TigerVNC client is quite reliable irrespective of the VNC server you are connecting to. It’s a high-performance and stable client that lets you connect seamlessly to the remote server.
TigerVNC is shipped by default with some Linux distributions such as Fedora. You can download TigerVNC from the GitHub Releases Page.
2. Remmina – Remote Desktop Client for Linux
Written in GTK+, Remmina is a high-performance remote desktop client for Linux systems. In addition to supporting the VNC protocol, it supports other protocols such as RDP, SSH, SPICE, NX, and X2GO.
Remmina is an excellent desktop client that provides a straightforward interface for connecting to remote systems. Prior to establishing a connection, Remmina prompts you to create a user profile that is used to determine the parameters for the remote connection.
You will then be required to select the protocol to use when establishing the connection as well as provide the server’s IP address. All the details are saved in the profile for subsequent connections to the same server.
Under the ‘Preferences’ window, you can find a number of default remote connection settings that can be configured when initiating the remote connection.
You can also define custom hotkeys for repetitive tasks. Other settings you can change include the resolution for the remote desktop and the client’s behavior during the connection among many others.
Unlike TigerVNC, Remmina doesn’t provide a server application. Nonetheless, you can use it to make remote connections to any kind of server.
3. AnyDesk – Remote Desktop Application for Linux
AnyDesk is a fast, lightweight yet powerful remote desktop application that is a perfect alternative for TeamViewer. It’s a cross-platform application that can be installed on both desktop and mobile devices. It supports Windows, Linux, macOS, Android, iOS, and even ARM devices such as Raspberry Pi.
AnyDesk has been widely adopted in various circles such as in the education, government, media, and creative industries. It’s also popular among average PC and desktop lovers and IT professionals in accessing remote devices.
AnyDesk provides interactive remote desktop access. You can use the keyboard and mouse to interact with the graphical display of the remote device. We need to mention that for a remote connection to be successful, both ends need to have AnyDesk installed.
Additionally, you can share your screen to make a presentation remotely, collaborate or even get support from IT support. This is ideal for remote workers such as those working from home.
In terms of security, AnyDesk offers Military-grade TLS 1.2 security, and 256-bit AES encryption to secure any communication exchanged between devices.
4. VNC Connect – Remote Desktop Access Solution
VNC Connect is another remote access software that provides support for both desktop and mobile devices. Just like TigerVNC, it comprises a server and client application for the VNC protocol.
VNC Connect offers high-speed streaming to provide a seamless and responsive remote access experience. In addition, you can customize remote access to suit your personal or organizational needs. For example, you can choose between a Direct (LAN) connection or alternatively opt for a cloud-based connection for your sessions.
Security is at the core of VNC Connect. To ensure total privacy while making connections, it provides end-to-end 128-bit AES encryption as a standard with an option for upgrading to 256-bit AES for enterprise users. As such, you can securely access and manage your devices from anywhere.
VNC Connect is designed for both professional and enterprise use with pricing starting at $3.39 for individuals and small businesses and $4.82 for enterprise environments. You get a 14-day free trial regardless of the plan that you go for.
5. Vinagre – Remote Desktop Viewer for Linux
Vinagre is a remote desktop client designed for the GNOME desktop. Like Remmina, it provides a minimalistic design that is simple, intuitive, and user-friendly. To establish a connection, you simply select a protocol from the pull-down menu and ENTER the IP of the remote server.
Protocols supported by Vinagre include RDP, SSH, VNC as well as SPICE protocols. It runs solely on Linux platforms and does not have clients for mobile platforms. Like Remmina, it does not have a server application of its own. However, its performance is best when paired with a default VNC server designed for the GNOME desktop.
Vinagre has the ability to sniff a VNS server on a TCP/IP network and tunnel connections via SSH. When connected to a remote server, you have the option of interacting with the graphical components or simply viewing the screen without user interaction.
In addition, you can bookmark an active session for subsequent connections and configure keyboard shortcuts. You can specify the color depth of the remote screen. However, this is not possible whilst in an active session.
Generally, Vinagre is a simple remote desktop client that gets much of the work done with simple tools.
6. TightVNC – Remote Desktop Application
TightVNC is a free and open-source remote desktop software that provides a client/server application for both Windows and Linux. For macOS, it’s available only under a commercial source code license.
It comes with an enhanced Java Viewer that ships with full support for Tight encoding. You can access the Java viewer applet via a built-in HTTP server.
The remote desktop application offers tight encoding with optional JPEG compression. The coding is optimized for slow and medium-speed connections, thus generating less traffic in comparison to traditional VNC encodings. Tight encoding is highly configurable with options for tweaking JPEG image quality and compression levels.
By default, TightVNC tunnels connections via SSH using the existing OpenSSH client installation. This provides much-needed security when connecting with the remote server.
TightVNC works well with other implementations of the VNC protocol. However, it’s always recommended to use TightVNC on both the server and client side to gain the full benefits of remote access.
[ You might also like: How to Install TightVNC to Access Remote Desktops in Linux ]
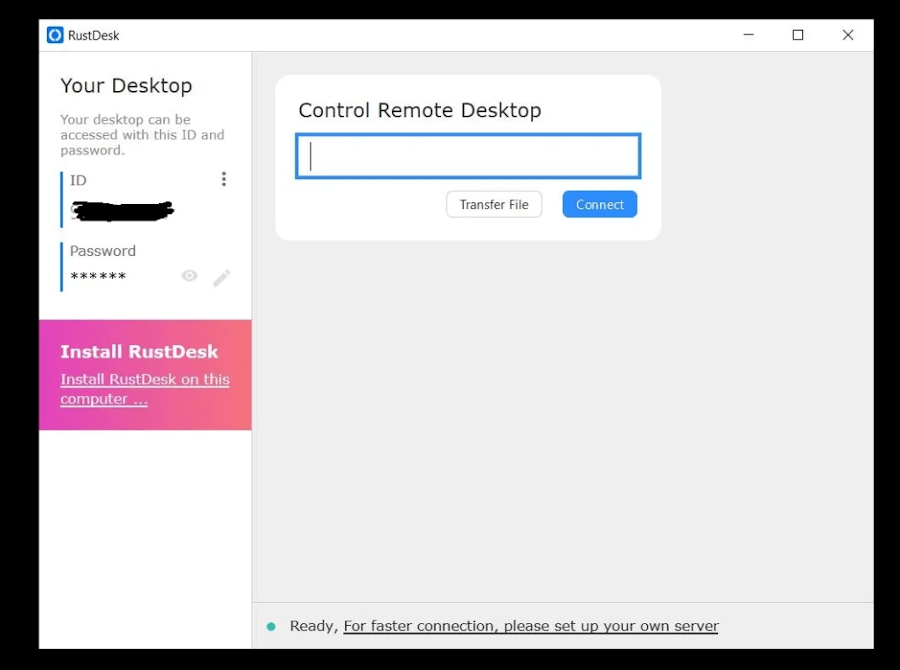
7. RustDesk – Remote Desktop Software
Written in Rust programming language, RustDesk is an open-source remote desktop software that is a perfect alternative to TeamViewer or AnyDesk.
It’s a multi-platform tool that can be installed on Linux, Windows, macOS, and even Android and iOS devices. RustDesk works out of the box without any special configuration. Just like TeamViewer, all you need is the remote client’s ID and Password to establish a remote session.
Apart from allowing remote desktop connections it allows you to easily transfer files from your current device to the remote client and also set up TCP tunneling.
Conclusion
That was a rundown of some of the best RDP clients for Linux. While we admit this is not a complete list of all the RDP clients, these are arguably some of the most reliable and widely used in the Linux community. Thanks for taking the time. Your feedback and suggestions are welcome.




I have been using NoMachine for several years and I think it deserves a mention in this article: – )
JLv
@Jan,
Absolutely, NoMachine is a well-known remote desktop software to access computers remotely from different devices and locations…
Great list!
You can also add to it
Getscreen.me– which works on all major operating systems including Linux. A great alternative to Teamviewer and Anidesk, but much more affordable. There is a free plan as well.Hello.
For me, the problem with RDP on Linux is the use of a *.rdp configuration file in my organization. As far as I know, only Remmina supports these files.
You forgot to mention Rustdesk ;-).
It’s free and probably the best alternative to Teamviewer that I have found, so far.
It runs on all the major operating systems and it’s open source!
https://rustdesk.com/
@Oeystein,
Thanks, included Rustdesk in the article as suggested by you…