The easiest way to determine the type of a file on any operating system is usually to look at its extension (for instance .xml, .sh, .c, .tar etc..). What if a file doesn’t have an extension, how can you determine its type?
Read Also: 7 Ways to Find Out File System Types in Linux
Linux has a useful utility called file which carry out some tests on a specified file and prints the file type once a test is successful. In this short article, we will explain useful file command examples to determine a file type in Linux.
Note: To have all the options described in this article, you should be running file version 5.25 (available in Ubuntu repositories) or newer. CentOS repositories have an older version of file command (file-5.11) which lacks some options.
You can run following command to verify the version of file utility as shown.
$ file -v file-5.33 magic file from /etc/magic:/usr/share/misc/magic
Linux file Command Examples
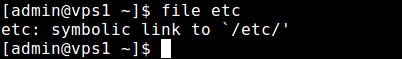
1. The simplest file command is as follows where you just provide a file whose type you want to find out.
$ file etc
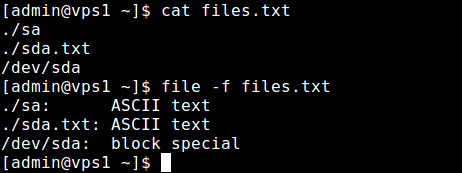
2. You can also pass the names of the files to be examined from a file (one per line), which you can specify using the -f flag as shown.
$ file -f files.list
3. To make file work faster you can exclude a test (valid tests include apptype, ascii, encoding, tokens, cdf, compress, elf, soft and tar) from the list of tests made to determine the file type, use the -e flag as shown.
$ file -e ascii -e compress -e elf etc
4. The -s option causes file to also read block or character special files, for example.
$ file -s /dev/sda /dev/sda: DOS/MBR boot sector, extended partition table (last)
5. Adding the -z options instructs file to look inside compressed files.
$ file -z backup
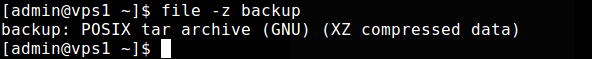
6. If you want to report information about the contents only not the compression, of a compressed file, use the -Z flag.
$ file -Z backup
7. You can tell file command to output mime type strings instead of the more traditional human readable ones, using the -i option.
$ file -i -s /dev/sda /dev/sda: application/octet-stream; charset=binary
8. In addition, you can get a slash-separated list of valid extensions for the file type found by adding the –extension switch.
$ file --extension /dev/sda
For more information and usage options, consult the file command man page.
$ man file
That’s all! file command is a useful Linux utility to determine the type of a file without an extension. In this article, we shared some useful file command examples. If you have any questions or thoughts to share, use the feedback form below to reach us.