ccat is command line similar to cat command in Linux that displays the content of a file with syntax highlighting for the following programming languages: Javascript, Java, Go, Ruby, C, Python and Json.
To install ccat utility in your Linux distribution, first assure that the wget utility is present in your system. If the wget command line is not installed in the system, issue the below command to install it:
# yum install wget [On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora] # apt-get install wget [On Debian and Ubuntu]
In order to install the latest version of ccat command line via the latest compiled binaries, first download the compressed tarball by issuing the below command. The binary and source code releases archives can be found at the official ccat github webpage.
-------------- On 64-Bit -------------- # wget https://github.com/jingweno/ccat/releases/download/v1.1.0/linux-amd64-1.1.0.tar.gz -------------- On 32-Bit -------------- # wget https://github.com/jingweno/ccat/releases/download/v1.1.0/linux-386-1.1.0.tar.gz
After archive download completes, list the current working directory to show the files, extract the ccat tarball (the linux-amd64-1.x.x Tarball file) and copy the ccat executable binary from the extracted tarball into a Linux executable system path, such as /usr/local/bin/ path, by issuing the below commands.
# ls # tar xfz linux-amd64-1.1.0.tar.gz # ls linux-amd64-1.1.0 # cp linux-amd64-1.1.0/ccat /usr/local/bin/ # ls -al /usr/local/bin/
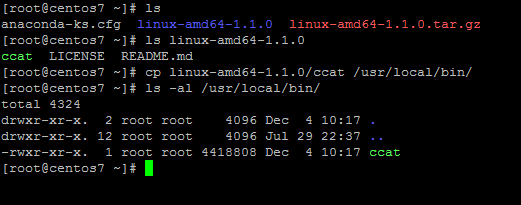
If for some reasons the ccat file from your executable system path has no executable bit set, issue the below command to set executable permissions for all system users.
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/ccat
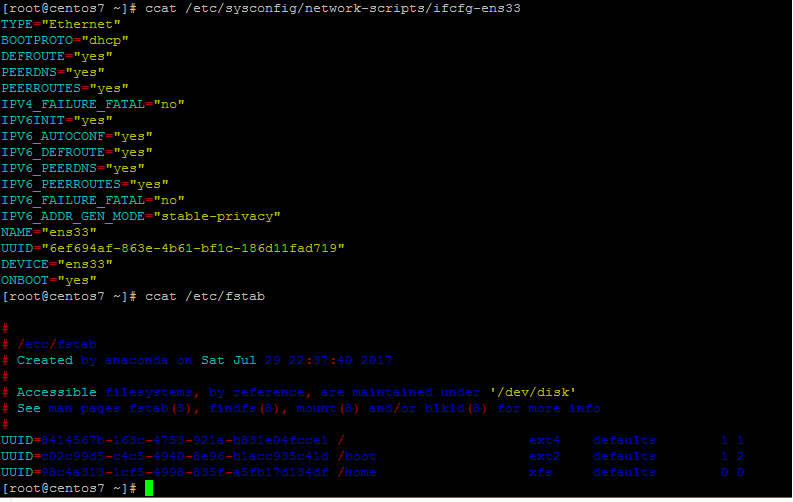
In order to test ccat utility capabilities against a system configuration file, issue the below commands. The content of the displayed files should be highlighted according to file programming language sytnax, as illustrated in the below command examples.
# ccat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 # ccat /etc/fstab
In order to replace cat command with ccat command system wide, add a bash alias for ccat in system bashrc file, log out from the system and log in back again to apply the configuration.
-------------- On CentOS, RHEL & Fedora -------------- # echo "alias cat='/usr/local/bin/ccat'" >> /etc/bashrc # exit -------------- On Debiab & Ubuntu -------------- # echo "alias cat='/usr/local/bin/ccat'" >> /etc/profile # exit
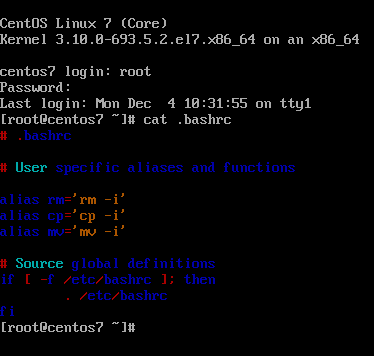
Finally, run cat command against an arbitrary configuration file to test if ccat alias has replaced cat command, as shown in the below example. The output file syntax should be highlighted now.
# cat .bashrc
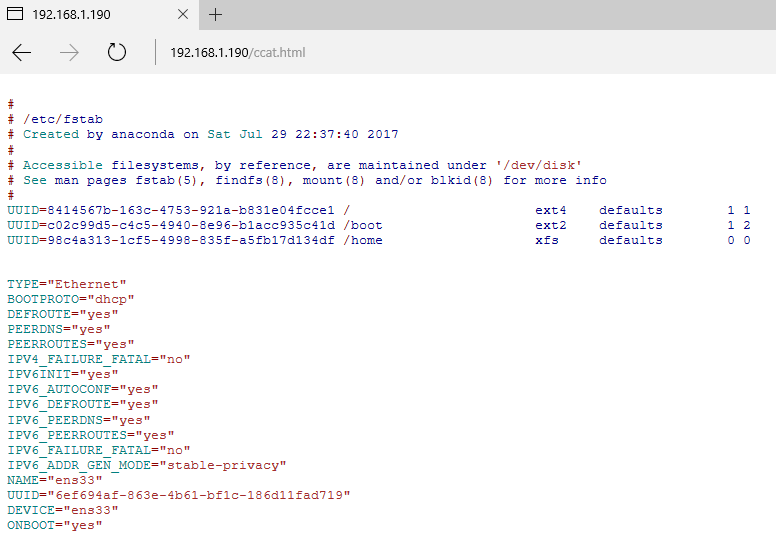
ccat utility can also be used to concatenate multiple files and display the output in HTML format, as illustrated in the below example.
# ccat --html /etc/fstab /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33> /var/www/html/ccat.html
However, you will need a web server installed in your system, such as Apache HTTP server or Nginx, to display the content of the HTML file, as illustrated in the below screenshot.
For other custom configurations and command options visit ccat official github page.




I got to a similar tool with a different route: I mostly use less(1) and that has the
~/.lessfilterfunctionality.That can be used to invoke one of the following
and so the suggested “ccat” would be … existing lesspipe(1)!
There is a typo:
In order to replace cat command with ccat command system wide, add a bash alias for ccat in system *barshrc* file,
I think you mean *bashrc*
@Lujun9972,
Thanks for pointing out typo, I’ve corrected in the article..:)