Linux memory management is an essential aspect of every System Administrator to improve the performance of a Linux system. It is always a good practice to monitor swap space usage in Linux to ensure that your system operates relative to its memory demands.
Therefore in this article, we are going to look at ways to monitor swap space usage in a Linux system.
Table of Contents
What is Swap space?
Swap space is a restricted amount of physical memory that is allocated for use by the operating system when available memory has been fully utilized. It is memory management that involves swapping sections of memory to and from physical storage.
On most distributions of Linux, it is recommended that you set swap space when installing the operating system. The amount of swap space you can set for your Linux system may depend on the architecture and kernel version.
How Do I Check Swap Space Usage in Linux?
We shall look at different commands and tools that can help you to monitor your swap space usage in your Linux systems as follows:
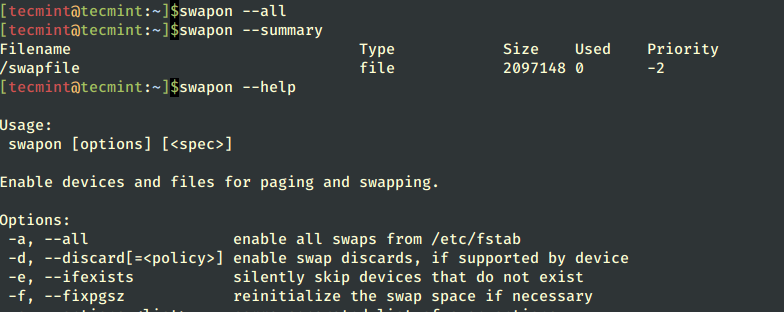
1. Using swapon Command – Check Swap Usage
The swapon command helps you to specify the devices on which paging and swapping will be done and we shall look at a few important options.
To view all devices marked as a swap in the /etc/fstab file you can use the --all option. Though devices that are already working as swap space are skipped.
# swapon --all
If you want to view a summary of swap space usage by device, use the --summary option as follows.
# swapon --summary Filename Type Size Used Priority /dev/sda10 partition 8282108 0 -1
Use --help option to view help information or open the manpage for more usage options.
2. Using /proc/swaps – Measures Swap Space
The /proc filesystem is a very special virtual filesystem in Linux, which is also referred to as a process information pseudo-file system.
It actually does not contain ‘real’ files but runtime system information, for example, system memory, devices mounted, hardware configuration, and many more. Therefore you can also refer to it as a control and information base for the kernel.
To understand more about this filesystem read our article: Understanding /proc File System in Linux.
To check swap usage information, you can view the /proc/swaps file using the cat utility.
# cat /proc/swaps Filename Type Size Used Priority /dev/sda10 partition 8282108 0 -1
3. Using ‘free’ Command – Show Swap Usage
The free command is used to display the amount of free and used system memory. Using the free command with -h option, which displays output in a human-readable format.
# free -h
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 7.7G 4.7G 3.0G 408M 182M 1.8G
-/+ buffers/cache: 2.7G 5.0G
Swap: 7.9G 0B 7.9G
From the output above, you can see that the last line provides information about the system swap space. More usage and examples of free commands can be found at: 10 free Commands to Check Memory Usage in Linux.
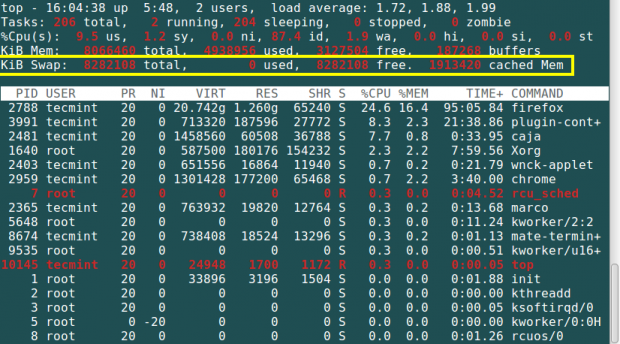
4. Using top Command
The top command displays the processor activity of your Linux system, and tasks managed by the kernel in real-time. To understand how the top command works, read this article: 12 top Commands to Check Linux Process Activity
To check swap space usage with the help of the ‘top’ command run the following command.
# top
5. Using atop Command
The atop command is a system monitor that reports about activities of various processes. But importantly it also shows information about free and used memory space.
# atop
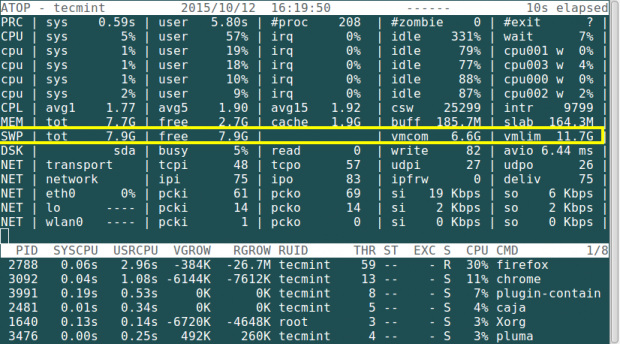
To know more about how to install and use atop command in Linux, read this article: Monitor Logging Activity of Linux System Processes
6. Using htop Command
The htop command is used to view processes in an interactive mode and also displays information about memory usage.
# htop
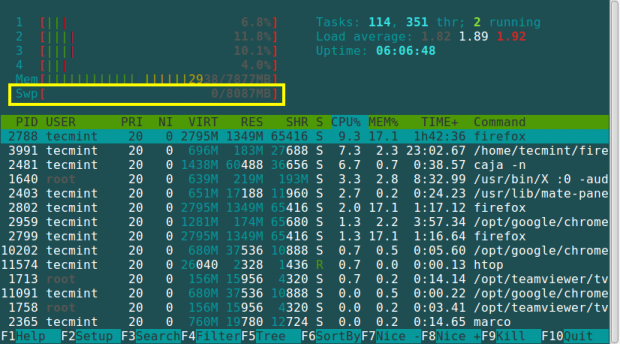
For more information regarding the installation and usage of the htop command, read this article: Htop – Interactive Linux Process Monitoring
7. Using the Glances Command
This is a cross-platform system monitoring tool that displays information about running processes, cpu load, storage space usage, memory usage, swap space usage, and many more.
# glances
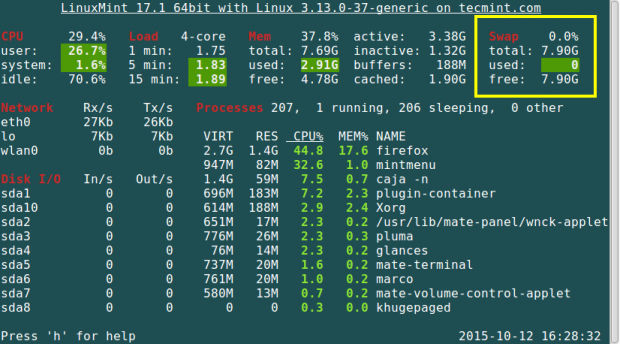
For more information regarding the installation and usage of the glances command, read this article: Glances – An Advanced Real-Time Linux System Monitoring Tool
8. Using the vmstat Command
The vmstat command is used to display information about virtual memory statistics, information about running processes, memory usage, CPU activity, paging, etc.
To install vmstat on your Linux system, run:
$ sudo apt install vmstat [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install vmstat [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/vmstat [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add vmstat [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S vmstat [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install vmstat [On OpenSUSE]
After vmstat installation, run:
# vmstat
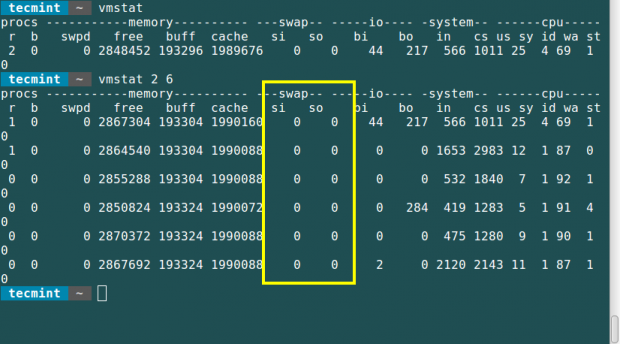
You need to take note of the following in the swap field from the output of this command.
- si: Amount of memory swapped in from disk (s).
- so: Amount of memory swapped to disk (s).
Summary
These are easy methods one can use and follow to monitor swap space usage in Linux and hope this article was helpful. In case you need help or want to add any information relating to memory management in Linux systems, please post a comment. Stay connected to Tecmint.




I prefer to create a simple bash script with the content below:
ps ax -o pid,args | grep -v '^ PID'|sed -e 's,^ *,,' > /tmp/ps_ax.output echo -n >/tmp/results for swappid in $(grep -l Swap /proc/[1-9]*/smaps ); do swapusage=0 for x in $( grep Swap $swappid 2>/dev/null |grep -v '\W0 kB'|awk '{print $2}' ); do let swapusage+=$x done pid=$(echo $swappid| cut -d' ' -f3|cut -d'/' -f3) if ( [ $swapusage -ne 0 ] ); then echo -ne "$swapusage kb\t\t" >>/tmp/results egrep "^$pid " /tmp/ps_ax.output |sed -e 's,^[0-9]* ,,' >>/tmp/results fi done echo "top swap using processes which are still running:" sort -nr /tmp/results | head -n 10Result will be the top 10 processes using swap.
@Stanislav,
I tried running the script on my Linux Mint, but getting the following error.
Hi Ravi, seems you have no rights in /tmp, check the permissions:
Here is the output from RedHat 8.7
root@vxltsap001:~# ./swap.sh top swap using processes which are still running: 251000 kb /usr/libexec/packagekitd 126384 kb /opt/commvault/commvault/Base/cvd 68564 kb splunkd -p 8089 restart 48632 kb /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -n 43776 kb /app/code-server/lib/node /app/code-server --bind-addr 0.0.0.0:8443 --user-data-dir /config/data --extensions-dir /config/extensions --disable-telemetry --auth none /config/workspace 30584 kb /opt/commvault/commvault/Base/ClMgrS 24860 kb [splunkd pid=1278354] splunkd -p 8089 restart [process-runner] 17424 kb /usr/bin/docker-proxy -proto tcp -host-ip :: -host-port 8443 -container-ip 172.18.0.2 -container-port 8443 17376 kb /usr/bin/docker-proxy -proto tcp -host-ip :: -host-port 80 -container-ip 172.18.0.3 -container-port 80 17352 kb /usr/bin/docker-proxy -proto tcp -host-ip 0.0.0.0 -host-port 80 -container-ip 172.18.0.3 -container-port 80@Stanislav,
Thanks, yes it seems permission issue, as I am running the script as a sudo user. Could you make the script workable with sudo privileges?
I have no experience with Mint but in Redhat Linux with ordinary users is working as well.
If you want to
topto monitor swap, you should add swap to the menu and sort by it. to do this:fbring up the fields menudto dot swap so it will be seensto sort by swap@Steve
This is splendid! Many thanks for sharing.
Nice artical and nicely explained but i have one query that why to use swap space even if we have lot of free memory?
@Balamukunda
Swap space is used to temporarily hold data moved from the system RAM, which is not actively being used by the system or user especially when RAM is filling up. It is therefore a “backup RAM” of sorts. Even if you have enough RAM, it is still recommended to create a swap space for Linux.
Another reason is that it helps during the hibernation of a computer, where the image of the RAM is captured and saved in the swap area. On restarting the computer, that image is reloaded into RAM, thereby enabling you to work from where you had stopped(point of hibernation).
I hope you find this helpful.
Good stuff, but you forgot to mention likely the best tool to monitor swap usage on Linux: smem.
@Tomas,
Thanks for updating about smem tool, we will try it out and include the tool with examples to this list.
Thanks. That would be really great guys!
Actually ‘smem’ is a Very Heavy option as it loads the Python interpreter & chain.
@Smith,
Yes, you almost right, ‘smem’ is a good alternative tool to ‘free’ for monitoring memory usage in more detailed fashion, actually we are in process creating a separate article on smem by this weekend, till then stay tuned to updates
smem is great tool, thanks for mentioning this!
@nexayg
It’s a great tool indeed, here is a tutorial for using smem: https://www.tecmint.com/smem-linux-memory-usage-per-process-per-user/