Some of the special directories that a Linux user is bound to work with so many times on a shell command line include the user’s home directory, the current and previous working directories.
Therefore, understanding how to easily access or pinpoint these directories using certain unique methods can be a bonus skill for a new or any Linux user.
In this tips for newbies, we shall look at ways of how a user can identify his/her home, current and previous working directories from the shell using special shell characters and environment variables.
1. Using Specific Shell Characters
There are certain specific characters that are understood by the shell when we are dealing with directories from the command line. The first character we shall look at is the tilde (~): it is used to access the current user’s home directory:
$ echo ~
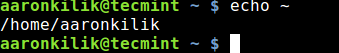
Suggested Read: Learn ‘echo’ Command with This 15-Practical Examples
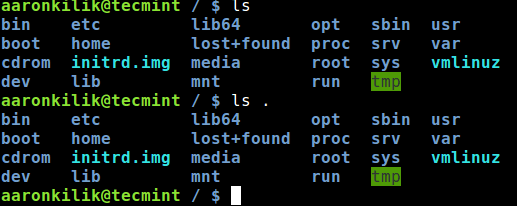
The second is the dot (.) character: it represents the current directory that a user is in, on the command line. In the screen shot below, you can see that the command ls and ls . produce the same out put, listing the contents of the current working directory.
$ ls $ ls .
Suggested Read: Master ‘ls’ Command with This Basic 15-Practical Examples
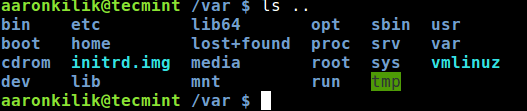
The third special characters are the double dots (..) which represent the directory directly above the current working directory that a user is in.
In the image below, the directory above /var is the root directory (/), so when we use the ls command as follows, the contents of (/) are listed:
$ ls ..
Suggested Read: 7 Quirky ‘ls’ Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know
2. Using Environmental Variables
Apart from the characters above, there are also certain environmental variables meant to work with the directories we are focusing on. In the next section, we shall walk through some of the important environmental variables for identifying directories from the command line.
$HOME: its value is the same as that of the tilde (~) character – the current user’s home directory, you can test that by using the echo command as follows:
$ echo $HOME

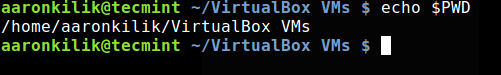
$PWD: in full, it stands for – Print Working Directory (PWD), as the name implies, it prints the absolute path of the current working directory in the shell command line as below:
$ echo $PWD
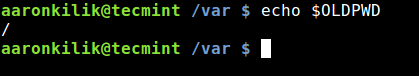
$OLDPWD: it points to the directory a user was in, just before moving to the current working directory. You can access its value as below:
$ echo $OLDPWD
Suggested Read: 15 ‘pwd’ (Print Working Directory) Command Examples in Linux
3. Using Simple cd Commands
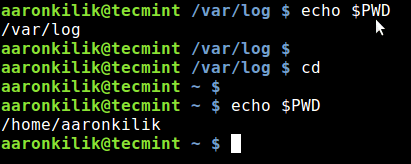
Additionally, you can also run some simple commands to quickly accessing your home directory and previous working directory. For example, when you are in any part of your file system on the command line, typing cd and hitting Enter will move you to your home directory:
$ echo $PWD $ cd $ echo $PWD
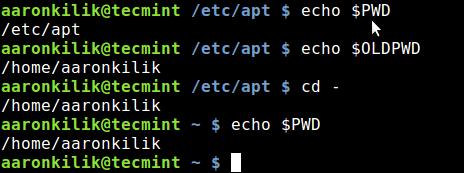
You can also move to the previous working directory using the command cd - command as below:
$ echo $PWD $ echo $OLDPWD $ cd - $ echo $PWD
In this post, we moved through some simple yet useful command line tips for new Linux users to identify certain special directories from within the shell command line.
Do you have any thoughts in terms of Linux tips you want to share with us or questions concerning the subject matter, then use the comment form below to get back to us.




To see all environment variables: env | sort
@Shawn H Corey
Thanks for this helpful tip, and also getting back to us.