Memory management in terms of monitoring memory usage is one important thing to do on your Linux system, there are many tools available for monitoring your memory usage that you can find on different Linux distributions. But they work in different ways, in this how to guide, we shall take a look at how to install and use one such tool called smem.
Don’t Miss: 20 Command Line Tools to Monitor Linux Performance
Smem is a command-line memory reporting tool thats gives a user diverse reports on memory usage on a Linux system. There is one unique thing about smem, unlike other traditional memory reporting tools, it reports PSS (Proportional Set Size), a more meaningful representation of memory usage by applications and libraries in a virtual memory setup.
Existing traditional tools focus mainly on reading RSS (Resident Set Size) which is a standard measure to monitor memory usage in a physical memory scheme, but tends to overestimate memory usage by applications.
PSS on the other hand, gives a reasonable measure by determining the “fair-share” of memory used by applications and libraries in a virtual memory scheme.
You can read this guide (about memory RSS and PSS) to understand memory consumption in a Linux system, but let us proceed to looking at some of the features of smem.
Features of Smem Tool
- System overview listing
- Listings and also filtering by process, mappings or user
- Using data from /proc filesystem
- Configurable listing columns from several data sources
- Configurable output units and percentages
- Easy to configure headers and totals in listings
- Using data snapshots from directory mirrors or compressed tar files
- Built-in chart generation mechanism
- Lightweight capture tool used in embedded systems
How to Install Smem – Memory Reporting Tool in Linux
Before you proceed with installation of smem, your system must meet the following requirements:
- modern kernel (> 2.6.27 or so)
- a recent version of Python (2.4 or so)
- optional matplotlib library for generation of charts
Most of the today’s Linux distributions comes with latest Kernel version with Python 2 or 3 support, so the only requirement is to install matplotlib library which is used to generate nice charts.
On RHEL, CentOS and Fedora
First enable EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository and then install as follows:
# yum install smem python-matplotlib python-tk
On Debian and Ubuntu
$ sudo apt-get install smem
On Linux Mint
$ sudo apt-get install smem python-matplotlib python-tk
on Arch Linux
Use this AUR repository.
How to Use Smem – Memory Reporting Tool in Linux
To view a report of memory usage across the whole system, by all system users, run the following command:
$ sudo smem
PID User Command Swap USS PSS RSS 6367 tecmint cat 0 100 145 1784 6368 tecmint cat 0 100 147 1676 2864 tecmint /usr/bin/ck-launch-session 0 144 165 1780 7656 tecmint gnome-pty-helper 0 156 178 1832 5758 tecmint gnome-pty-helper 0 156 179 1916 1441 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty2 0 152 184 2052 1434 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty5 0 156 187 2060 1444 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty3 0 156 187 2060 1432 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty4 0 156 188 2124 1452 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty6 0 164 196 2064 2619 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty1 0 164 196 2136 3544 tecmint sh -c /usr/lib/linuxmint/mi 0 212 224 1540 1504 root acpid -c /etc/acpi/events - 0 220 236 1604 3311 tecmint syndaemon -i 0.5 -K -R 0 252 292 2556 3143 rtkit /usr/lib/rtkit/rtkit-daemon 0 300 326 2548 1588 root cron 0 292 333 2344 1589 avahi avahi-daemon: chroot helpe 0 124 334 1632 1523 root /usr/sbin/irqbalance 0 316 343 2096 585 root upstart-socket-bridge --dae 0 328 351 1820 3033 tecmint /usr/bin/dbus-launch --exit 0 328 360 2160 1346 root upstart-file-bridge --daemo 0 348 371 1776 2607 root /usr/bin/xdm 0 188 378 2368 1635 kernoops /usr/sbin/kerneloops 0 352 386 2684 344 root upstart-udev-bridge --daemo 0 400 427 2132 2960 tecmint /usr/bin/ssh-agent /usr/bin 0 480 485 992 3468 tecmint /bin/dbus-daemon --config-f 0 344 515 3284 1559 avahi avahi-daemon: running [tecm 0 284 517 3108 7289 postfix pickup -l -t unix -u -c 0 288 534 2808 2135 root /usr/lib/postfix/master 0 352 576 2872 2436 postfix qmgr -l -t unix -u 0 360 606 2884 1521 root /lib/systemd/systemd-logind 0 600 650 3276 2222 nobody /usr/sbin/dnsmasq --no-reso 0 604 669 3288 ....
When a normal user runs smem, it displays memory usage by process that the user has started, the processes are arranged in order of increasing PSS.
Take a look at the output below on my system for memory usage by processes started by user aaronkilik:
$ smem
PID User Command Swap USS PSS RSS 6367 tecmint cat 0 100 145 1784 6368 tecmint cat 0 100 147 1676 2864 tecmint /usr/bin/ck-launch-session 0 144 166 1780 3544 tecmint sh -c /usr/lib/linuxmint/mi 0 212 224 1540 3311 tecmint syndaemon -i 0.5 -K -R 0 252 292 2556 3033 tecmint /usr/bin/dbus-launch --exit 0 328 360 2160 3468 tecmint /bin/dbus-daemon --config-f 0 344 515 3284 3122 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfsd 0 656 801 5552 3471 tecmint /usr/lib/at-spi2-core/at-sp 0 708 864 5992 3396 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfs-mtp-volu 0 804 914 6204 3208 tecmint /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/i 0 892 1012 6188 3380 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfs-afc-volu 0 820 1024 6396 3034 tecmint //bin/dbus-daemon --fork -- 0 920 1081 3040 3365 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfs-gphoto2- 0 972 1099 6052 3228 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfsd-trash - 0 980 1153 6648 3107 tecmint /usr/lib/dconf/dconf-servic 0 1212 1283 5376 6399 tecmint /opt/google/chrome/chrome - 0 144 1409 10732 3478 tecmint /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/g 0 1724 1820 6320 7365 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfsd-http -- 0 1352 1884 8704 6937 tecmint /opt/libreoffice5.0/program 0 1140 2328 5040 3194 tecmint /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/p 0 1956 2405 14228 6373 tecmint /opt/google/chrome/nacl_hel 0 2324 2541 8908 3313 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfs-udisks2- 0 2460 2754 8736 3464 tecmint /usr/lib/at-spi2-core/at-sp 0 2684 2823 7920 5771 tecmint ssh -p 4521 [email protected] 0 2544 2864 6540 5759 tecmint /bin/bash 0 2416 2923 5640 3541 tecmint /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/mi 0 2584 3008 7248 7657 tecmint bash 0 2516 3055 6028 3127 tecmint /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfsd-fuse /r 0 3024 3126 8032 3205 tecmint mate-screensaver 0 2520 3331 18072 3171 tecmint /usr/lib/mate-panel/notific 0 2860 3495 17140 3030 tecmint x-session-manager 0 4400 4879 17500 3197 tecmint mate-volume-control-applet 0 3860 5226 23736 ...
There are many options to invoke while using smem, for example, to view system wide memory consumption, run the following command:
$ sudo smem -w
Area Used Cache Noncache firmware/hardware 0 0 0 kernel image 0 0 0 kernel dynamic memory 1425320 1291412 133908 userspace memory 2215368 451608 1763760 free memory 4424936 4424936 0
To view memory usage on a per-user basis, run the command below:
$ sudo smem -u
User Count Swap USS PSS RSS rtkit 1 0 300 326 2548 kernoops 1 0 352 385 2684 avahi 2 0 408 851 4740 postfix 2 0 648 1140 5692 messagebus 1 0 1012 1173 3320 syslog 1 0 1396 1419 3232 www-data 2 0 5100 6572 13580 mpd 1 0 7416 8302 12896 nobody 2 0 4024 11305 24728 root 39 0 323876 353418 496520 tecmint 64 0 1652888 1815699 2763112
You can also report memory usage by mappings as follows:
$ sudo smem -m
Map PIDs AVGPSS PSS /dev/fb0 1 0 0 /home/tecmint/.cache/fontconfig/7ef2298f 18 0 0 /home/tecmint/.cache/fontconfig/c57959a1 18 0 0 /home/tecmint/.local/share/mime/mime.cac 15 0 0 /opt/google/chrome/chrome_material_100_p 9 0 0 /opt/google/chrome/chrome_material_200_p 9 0 0 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gconv/gconv-mo 41 0 0 /usr/share/icons/Mint-X-Teal/icon-theme. 15 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/0c9eb80ebd1c36541e 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/0d8c3b2ac0904cb8a5 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/1ac9eb803944fde146 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/3830d5c3ddfd5cd38a 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/385c0604a188198f04 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/4794a0821666d79190 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/56cf4f4769d0f4abc8 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/767a8244fc0220cfb5 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/8801497958630a81b7 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/99e8ed0e538f840c56 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/b9d506c9ac06c20b43 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/c05880de57d1f5e948 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/dc05db6664285cc2f1 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/e13b20fdb08344e0e6 20 0 0 /var/cache/fontconfig/e7071f4a29fa870f43 20 0 0 ....
There are also options for filtering smem output and we shall look at two examples here.
To filter output by username, invoke the -u or --userfilter="regex" option as below:
$ sudo smem -u
User Count Swap USS PSS RSS rtkit 1 0 300 326 2548 kernoops 1 0 352 385 2684 avahi 2 0 408 851 4740 postfix 2 0 648 1140 5692 messagebus 1 0 1012 1173 3320 syslog 1 0 1400 1423 3236 www-data 2 0 5100 6572 13580 mpd 1 0 7416 8302 12896 nobody 2 0 4024 11305 24728 root 39 0 323804 353374 496552 tecmint 64 0 1708900 1871766 2819212
To filter output by process name, invoke the -P or --processfilter="regex" option as follows:
$ sudo smem --processfilter="firefox"
PID User Command Swap USS PSS RSS 9212 root sudo smem --processfilter=f 0 1172 1434 4856 9213 root /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/sm 0 7368 7793 11984 4424 tecmint /usr/lib/firefox/firefox 0 931732 937590 961504
Output formatting can be very important, and there are options to help you format memory reports and we shall take a look at few examples below.
To show desired columns in the report, use -c or --columns option as follows:
$ sudo smem -c "name user pss rss"
Name User PSS RSS cat tecmint 145 1784 cat tecmint 147 1676 ck-launch-sessi tecmint 165 1780 gnome-pty-helpe tecmint 178 1832 gnome-pty-helpe tecmint 179 1916 getty root 184 2052 getty root 187 2060 getty root 187 2060 getty root 188 2124 getty root 196 2064 getty root 196 2136 sh tecmint 224 1540 acpid root 236 1604 syndaemon tecmint 296 2560 rtkit-daemon rtkit 326 2548 cron root 333 2344 avahi-daemon avahi 334 1632 irqbalance root 343 2096 upstart-socket- root 351 1820 dbus-launch tecmint 360 2160 upstart-file-br root 371 1776 xdm root 378 2368 kerneloops kernoops 386 2684 upstart-udev-br root 427 2132 ssh-agent tecmint 485 992 ...
You can invoke the -p option to report memory usage in percentages, as in the command below:
$ sudo smem -p
PID User Command Swap USS PSS RSS
6367 tecmint cat 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
6368 tecmint cat 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
9307 tecmint sh -c { sudo /usr/lib/linux 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
2864 tecmint /usr/bin/ck-launch-session 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
3544 tecmint sh -c /usr/lib/linuxmint/mi 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
5758 tecmint gnome-pty-helper 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
7656 tecmint gnome-pty-helper 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
1441 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty2 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
1434 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty5 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
1444 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty3 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
1432 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty4 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
1452 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty6 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
2619 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty1 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
1504 root acpid -c /etc/acpi/events - 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
3311 tecmint syndaemon -i 0.5 -K -R 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
3143 rtkit /usr/lib/rtkit/rtkit-daemon 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
1588 root cron 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
1589 avahi avahi-daemon: chroot helpe 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
1523 root /usr/sbin/irqbalance 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
585 root upstart-socket-bridge --dae 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.02%
3033 tecmint /usr/bin/dbus-launch --exit 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.03%
....
The command below will show totals at the end of each column of the output:
$ sudo smem -t
PID User Command Swap USS PSS RSS
6367 tecmint cat 0 100 139 1784
6368 tecmint cat 0 100 141 1676
9307 tecmint sh -c { sudo /usr/lib/linux 0 96 158 1508
2864 tecmint /usr/bin/ck-launch-session 0 144 163 1780
3544 tecmint sh -c /usr/lib/linuxmint/mi 0 108 170 1540
5758 tecmint gnome-pty-helper 0 156 176 1916
7656 tecmint gnome-pty-helper 0 156 176 1832
1441 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty2 0 152 181 2052
1434 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty5 0 156 184 2060
1444 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty3 0 156 184 2060
1432 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty4 0 156 185 2124
1452 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty6 0 164 193 2064
2619 root /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty1 0 164 193 2136
1504 root acpid -c /etc/acpi/events - 0 220 232 1604
3311 tecmint syndaemon -i 0.5 -K -R 0 260 298 2564
3143 rtkit /usr/lib/rtkit/rtkit-daemon 0 300 324 2548
1588 root cron 0 292 326 2344
1589 avahi avahi-daemon: chroot helpe 0 124 332 1632
1523 root /usr/sbin/irqbalance 0 316 340 2096
585 root upstart-socket-bridge --dae 0 328 349 1820
3033 tecmint /usr/bin/dbus-launch --exit 0 328 359 2160
1346 root upstart-file-bridge --daemo 0 348 370 1776
2607 root /usr/bin/xdm 0 188 375 2368
1635 kernoops /usr/sbin/kerneloops 0 352 384 2684
344 root upstart-udev-bridge --daemo 0 400 426 2132
.....
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
134 11 0 2171428 2376266 3587972
Further more, there are options for graphical reports that you can also use and we shall dive into them in this sub section.
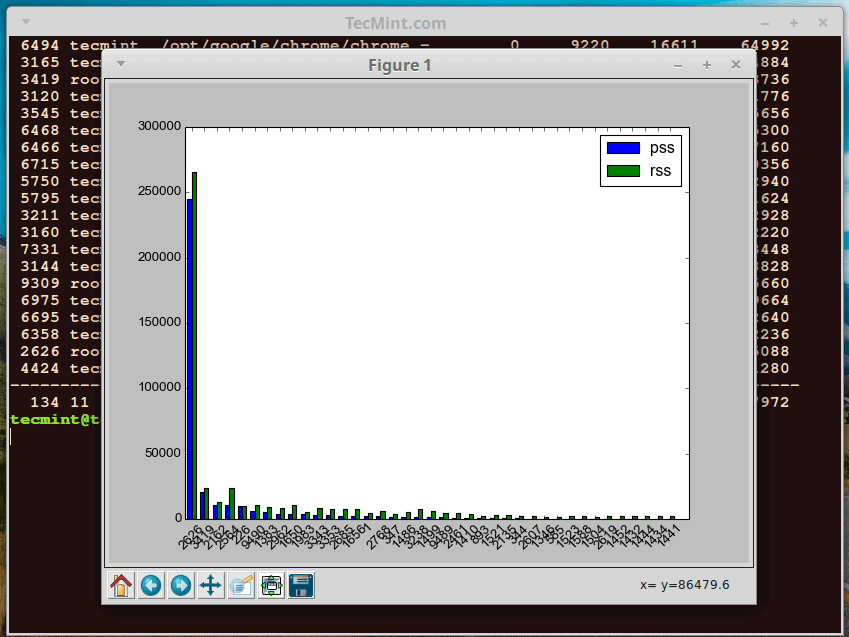
You can produce a bar graph of processes and their PSS and RSS values, in the example below, we produce a bar graph of processes owned by the root user.
The vertical plane shows the PSS and RSS measure of processes and the horizontal plane represents each root user process:
$ sudo smem --userfilter="root" --bar pid -c"pss rss"
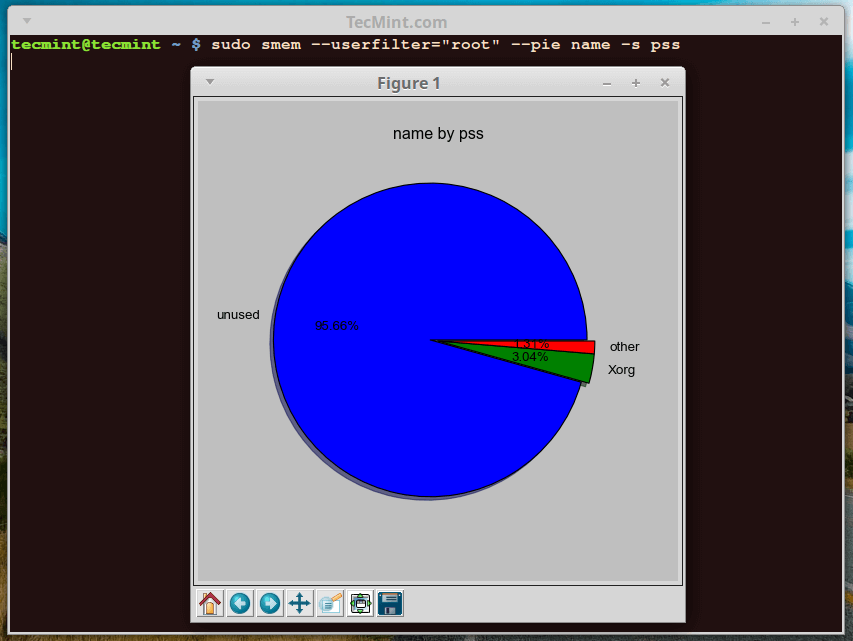
You can also produce a pie chart showing processes and their memory consumption based on PSS or RSS values. The command below outputs a pie chart for processes owned by root user measuring values.
The --pie name means label by name and -s option helps to sort by PSS value.
$ sudo smem --userfilter="root" --pie name -s pss
There are many other known fields apart from PSS and RSS used for labeling charts:
To get help, simply type, smem -h or visit the manual entry page.
We shall stop here with smem, but to understand it better, use it with many other options that you can find in the man page. As usual you can use the comment section below to express any thoughts or concerns.
Reference Links: https://www.selenic.com/smem/


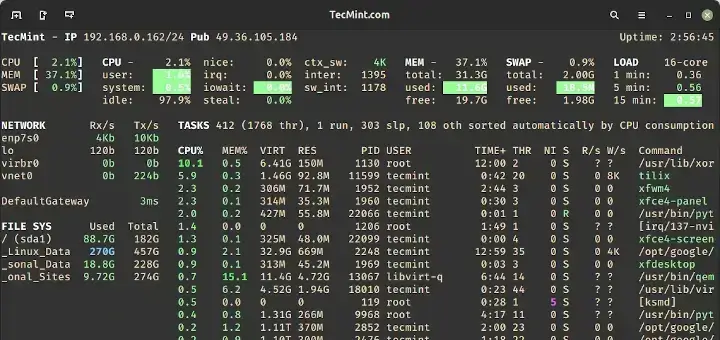
Why I am getting more than 100%?
$ smem -tur -p User Count Swap USS PSS RSS oracle 142 2.67% 13.33% 25.63% 204.15% --------------------------------------------------- 142 2.67% 13.33% 25.63% 204.15%what is rss and pss ? please elaborate if there is more such Abbrv,
@John
RSS(Resident Set Size) is the amount of memory occupied by a process that is held in main memory (RAM) and PSS(Proportional Set Size) is the amount RAM occupied by a process(which is the private memory of that process plus the proportion of shared memory with one or more other processes).
Hi,
I’m using CentOS release 6.7. I have installed and enabled EPEL repo, But getting the following
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, security
Setting up Install Process
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
epel/metalink | 12 kB 00:00
* base: mirror.keystealth.org
* epel: s3-mirror-us-west-2.fedoraproject.org
* extras: mirror.keystealth.org
* updates: mirror.keystealth.org
epel | 4.3 kB 00:00
epel/primary_db | 5.8 MB 00:00
No package python-tk available.
Error: Nothing to do
@Ravi,
I think there’s difference in package names, the old CentOS 6.7 uses tkinter package, so install it using yum as shown:
Thanks Ravi. Its working fine now.
Okay, found it. On Centos it’s sudo yum install tkinter.
@Steve,
On which CentOS version you haven’t found python-tk package, on my CentOS 7 I just did
yum install python-tkand it installed successfully.It’s Oracle Linux 7.2 which is basically CentOS. Weird.
Have you tried installing tkinter package, which is same as python-tk, give it a try and let me know..
What is this python-tk package you’re talking about? Can’t find it. Are you talking about tkinter?