By default, all commands executed by Bash on the command line are stored in history buffer or recorded in a file called ~/.bash_history. This means that a system administrator can view a list of commands executed by users on the system or a user can view his/her command history using the history command like so.
$ history
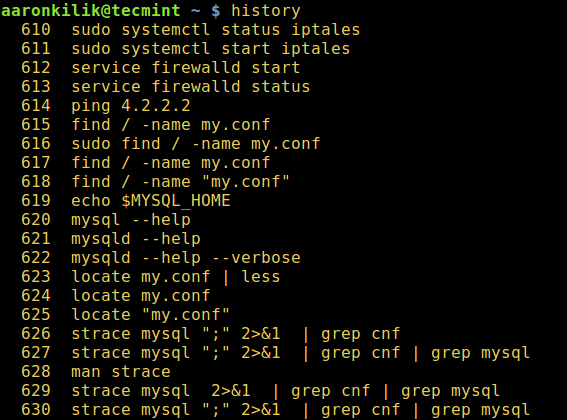
From the output of the history command above, the date and time when a command was executed is not shown. This is the default setting on most if not all Linux distributions.
In this article, we will explain how you can configure time stamp information when each command in the Bash history was executed to be displayed.
The date and time associated with each history entry can be written to the history file, marked with the history comment character by setting the HISTTIMEFORMAT variable.
There are two possible ways of doing this: one does it temporarily while the other makes it permanent.
To set HISTTIMEFORMAT variable temporarily, export it as below on the command line:
$ export HISTTIMEFORMAT='%F %T'
In the export command above, the time stamp format:
%F– expands to full date same, as %Y-%m-%d (year-month-date).%T– expands to time; same as %H:%M:%S (hour:minute:seconds).
Read through the date command man page for additional usage information:
$ man date
Then check your command history as follows:
$ history
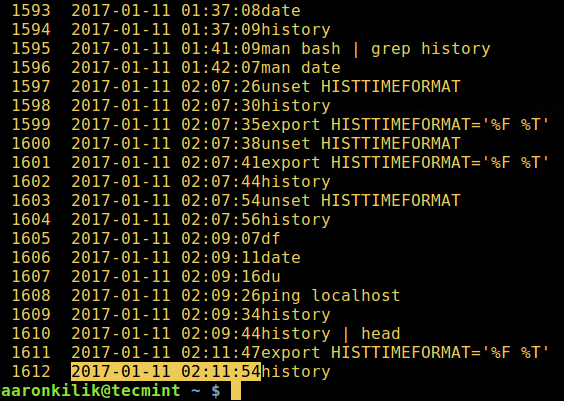
However, if you want to configure this variable permanently, open the file ~/.bashrc with your favorite editor:
$ vi ~/.bashrc
And add the line below in it (you mark it with a comment as your own configuration):
#my config export HISTTIMEFORMAT='%F %T'
Save the file and exit, afterwards, run the command below to effect the changes made to the file:
$ source ~/.bashrc
That’s all! Do share with us any interesting history command tips and tricks or your thoughts about this guide via the comment section below.




In my opinion, it’s a little clearer, like this: export HISTTIMEFORMAT=’%F %T -> ‘
How to stop using history with date and time?
which command i can use?
@Gaspar,
Remove the following line from your
/.bashrcfile to print date and time in history command.I have done it but in history it showing all commands are executed on current date.
This is normally.
New command will have a new time.
how to change date acoording to our choice
Can we set this if we don’t have root privilege on the server? I tried doing it by exporting as shown above .. it didn’t give me any error but it didn’t show the time and date in history
Hello,
Thanks million for your efforts and your great post.
I want to show ip address (of the user that executed the command) in history command. How can i do that?
Second question
when i ssh to my linux machine with putty and suddenly my windows restart (for any reason) there is no history in next ssh
but if i exit from putty with command “exit” in my server history will be saved for next ssh login.
how can i set that each command to be saved even if putty closed abnormal?
Thank you!
@Alexey
Welcome and many thanks for following us.
Modifying bash_history file won’t let you use other options, like re-running some command from history by using ! char at the beginning. IMHO, good, but not ideal
Marek, I have this line: export HISTTIMEFORMAT=”%Y-%m-%d %T ”
in my ~/.bash_profile and all works as expected. I can use !!
@Marek
You actually do not have to modify the bash_history file. This method simply adds the timestamp to a command entry in it, and you can re-run commands as usual.
Just don’t forget to update your actual system time to correlate with your IRL time. Usually the system’s (server) time is not the same as the one where you’re actually working from.
It’s just easier, not that it really matters.
@ThisHosting.Rocks
Useful suggestion, many thanks for adding your thoughts to this post.
Great!
It’s nice to add a space or tab between the date and its command :)
Thanks.
@Faisaal
Yes, that is a good suggestion. Thanks for the feedback.
^^^^^ this
@randy
Good heads up, mistake noted.