This tutorial will guide you on how you can integrate CentOS 7 Desktop to Zentyal 3.4 Primary Domain Controller and benefit a single centralized point of authentication for all your users across your entire network infrastructure with the help of Samba Windows interoperability packages – which includes nmbd – NetBios over IP service and Winbind – services authentication via PAM modules, Kerberos network authentication system client and the graphical version of Authconfig package provided by official CentOS repositories.

Requirements
- Install and Configure Zentyal as a PDC (Primary Domain Controller)
- CentOS 7 Desktop Installation Procedure
Note: The domain name “mydomain.com” used on this tutorial (or other tecmint.com articles) is fictional and resides only on my private network local setup – any resemblance with a true domain name is pure coincidence.
Step 1: Configure Network to reach Zentyal PDC
1. Before starting to install and configure the required services in order to join CentOS 7 Desktop to an Active PDC you need to make sure that your network can reach and get a response from Zentyal PDC or a Windows Active Directory DNS server.
On the first step go to CentOS Network Settings, turn off your interface Wired Connections, add the DNS IPs that points to your Zentyal PDC or Windows AD DNS servers, Apply the settings and turn on your Network Wired Card. Make sure you do all the settings as presented on the below screenshots.
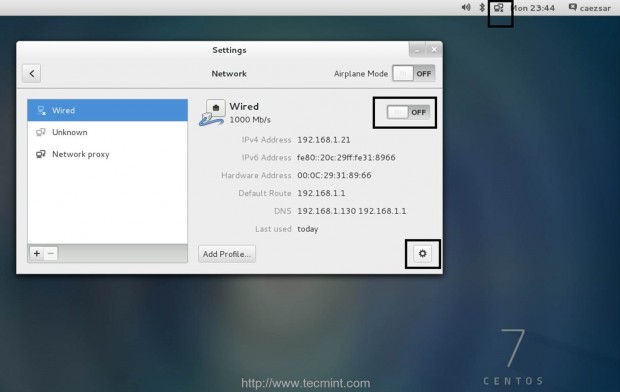
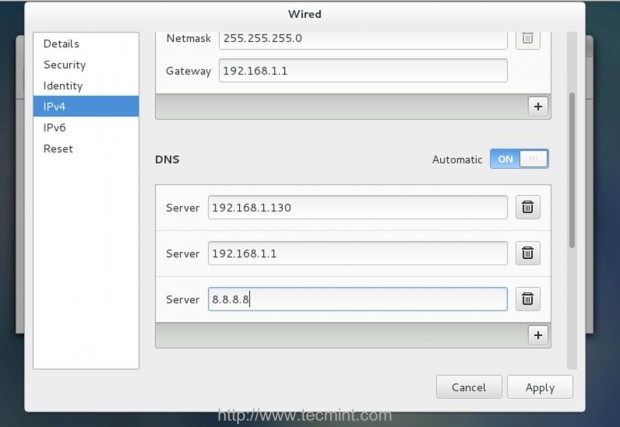
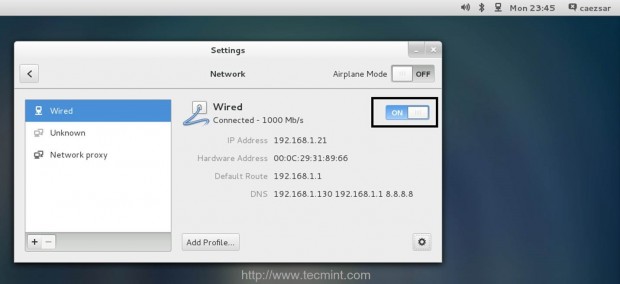
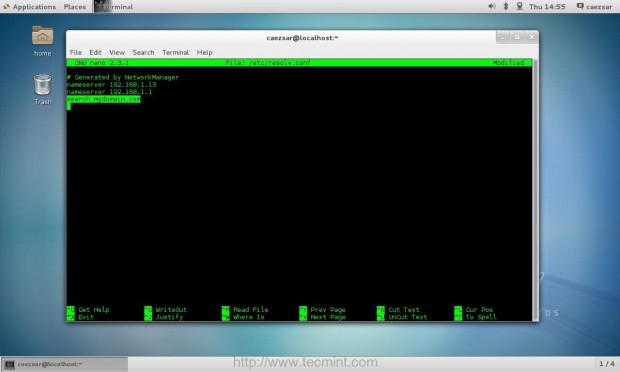
2. If your network has only a single DNS sever that resolves your PDC, you need to ensure that this IP is the first from your DNS servers list. Also open resolv.conf file located in /etc directory with root editing permissions and append the following line at the bottom, after nameserver list.
search your_domain.tld
3. After you have configured CentOS 7 network connections, issue a ping command against your PDC FQDN and make sure it responds accurately with its IP Address.
# ping pdc_FQDN
4. On the next step, configure your machine hostname as a Fully Qualified Domain Name (use an arbitrary name for your system and append your domain name after the first dot) and verify it by issuing the following commands with root privileges.
# hostnamectl set-hostname hostname.domain.tld # cat /etc/hostname # hostname
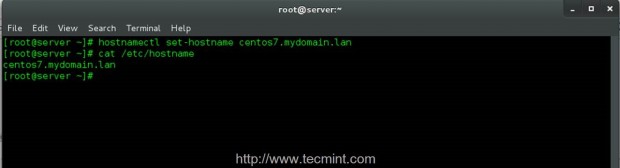
The left system hostname configured on this step, will be the name that will appear on Zentyal PDC or Windows AD on joined Computers names.
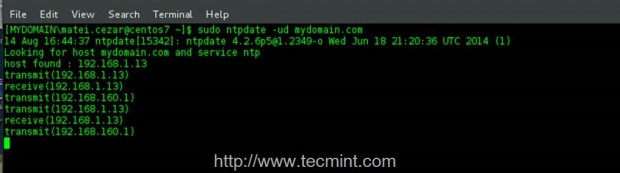
5. The last step that you will need to carry out before installing required packages to join PDC is to ensure that your system time is synchronized with Zentyal PDC. Run the following command with root privileges against your domain to sync time with the server.
$ sudo ntpdate -ud domain.tld
Step 2: Install and Samba, Kerberos and Authconfig-gtk and Configure Kerberos Client
6. All of the packages mentioned above are maintained and offered by official CentOS repositories, so there’s no need to add supplementary repos such as Epel, Elrepo or others.
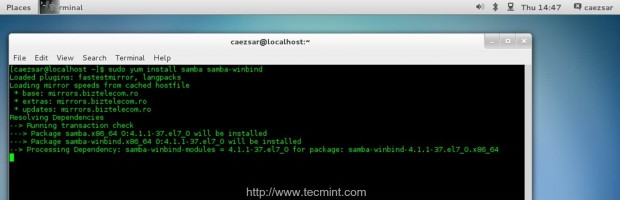
Samba and Winbind provides the needed tools that allows CentOS 7 to integrate and become a member with fully rights on Zentyal PDC Infrastructure or a Windows AD Server. Issue the following command to install Samba and Winbind packages.
$ sudo yum install samba samba-winbind
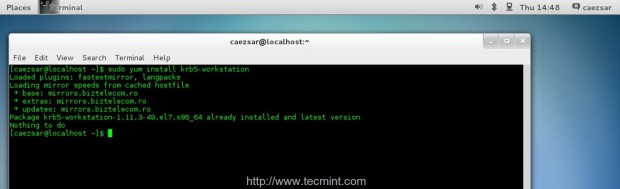
7. Next install the Kerberos Workstation Client, which provides a strong cryptographic network authentication based on a Key Distribution Center (KDC) trusted by all network systems, by issuing the following command.
$ sudo yum install krb5-workstation
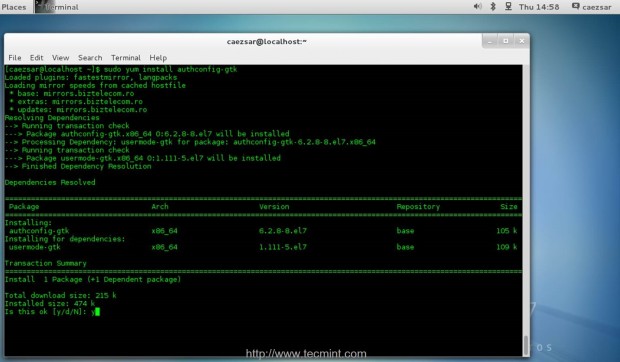
8. The last package that you need to install is Authconfig-gtk, which provides a Graphical Interface that manipulates Samba files in order to authenticate to a Primary Domain Controller. Use the following command to install this tool.
$ sudo yum install authconfig-gtk
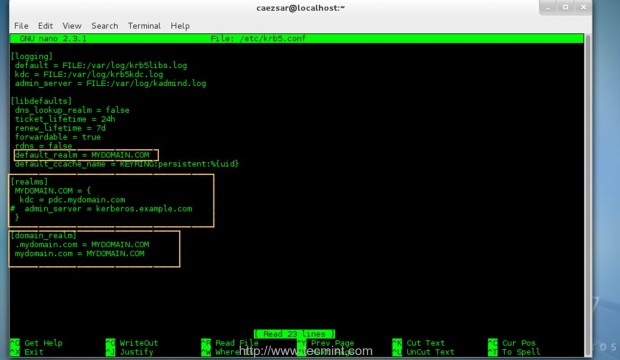
9. After all the required packages had been installed you need to make some changes to Kerberos Client main configuration file. Open /etc/krb5.conf file with your favorite text editor using an account with root privileges and
edit the following lines.
# nano /etc/krb5.conf
Here make sure you replace this lines accordingly – Use uppercase, dots and spaces as suggested in this examples.
[libdefaults]
default_realm = YOUR_DOMAIN.TLD
[realms]
YOUR_DOMAIN.TLD = {
kdc = your_pdc_server_fqdn
}
[domain_realm]
.your_domain.tld = YOUR_DOMAIN.TLD
your_domain.tld = YOUR_DOMAIN.TLD
Step 3: Join CentOS 7 to Zentyal PDC
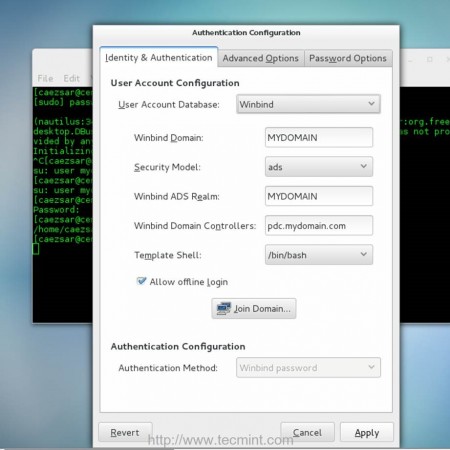
10. After you have made all of the configurations above your system should be ready to become a fully qualified member to Zentyal PDC. Open Authconfig-gtk package with root privileges and make the following adjustments as presented here.
$ sudo authconfig-gtk
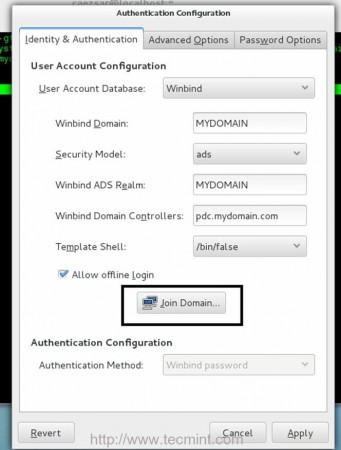
a. On Identity & Authentication tab
- User Account Database = choose Winbind
- Winbind Domain = type YOUR_DOMAIN name
- Security Model = choose ADS
- Winbind ADS Realm = type YOUR_DOMAIN name
- Domain Controllers = type your Zentyal PDC FQDN
- Template Shell = choose /bin/bash
- Allow offline login = checked
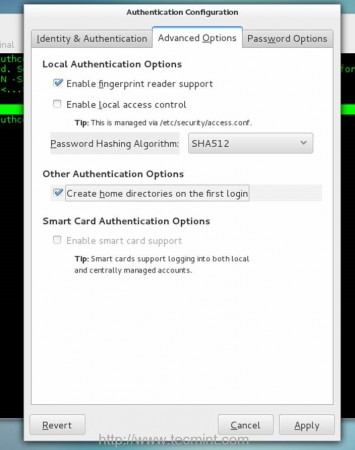
b. Move to Advanced Options tab
- Local Authentication Options = check Enable fingerprint reader support
- Other Authentication Options = check Create home directories on the first login
11. Now, after editing Authentication Configuration tabs with the required values don’t close the window and go back to Identity & Authentication tab. Click on Join Domain button and Save the prompt Alert to proceed further.
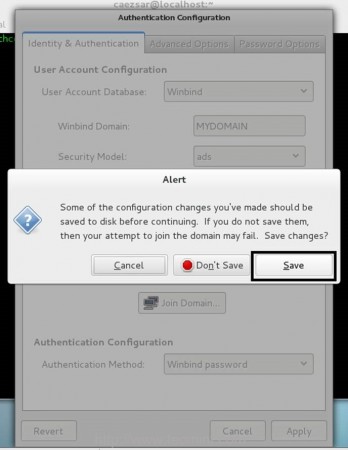
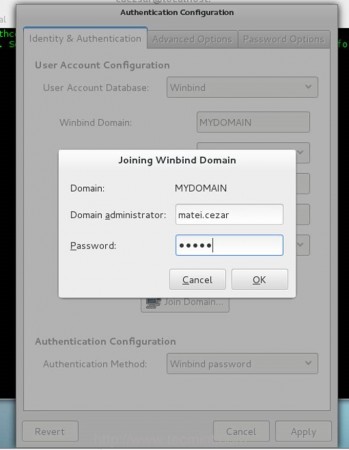
12. If your configuration has been successfully saved, your system will contact the PDC and a new prompt should appear demanding you to enter a domain administrator credentials in order to join the domain.
Enter your domain name administrator user and password, hit on OK button to close the prompt and, then, click on Apply button to apply the final configuration.
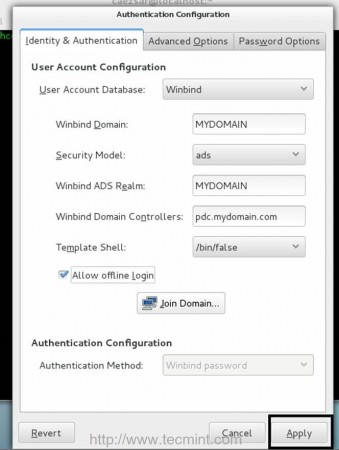
If changes are successfully applied, the Authentication Configuration window should close and a message should appear on Terminal which will inform you that your computer has been integrated into your domain.
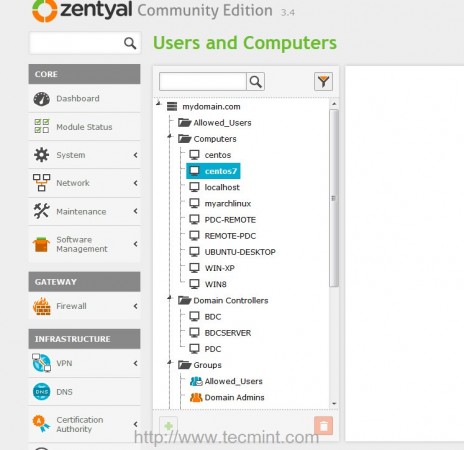
13. In order to verify, if your system has been added to Zentyal PDC, login to Zentyal Web Administrative Tool, go to Users and Computers -> Manage menu and check if your machine hostname appears on Computers list.
Step 4: Login CentOS 7 with PDC Users
14. At this point all the users listed in Zentyal PDC infrastructure should now be able to perform logins to your CentOS machine from a local or remote Terminal or by using the first Login Screen. To login from a Console or a Terminal with an PDC user use the following syntax.
$ su - your_domain.tld\\pdc_user
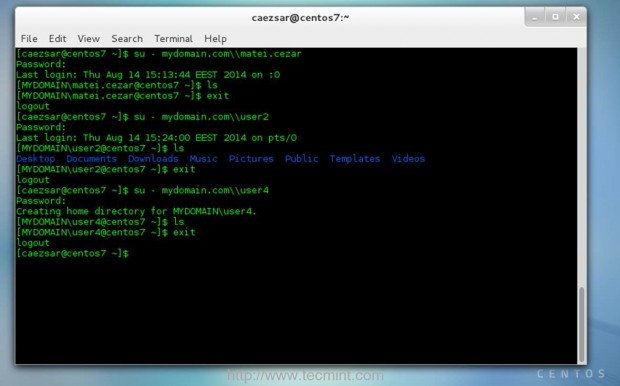
15. The default $HOME for all PDC users is /home/YOUR_DOMAIN/pdc_user.

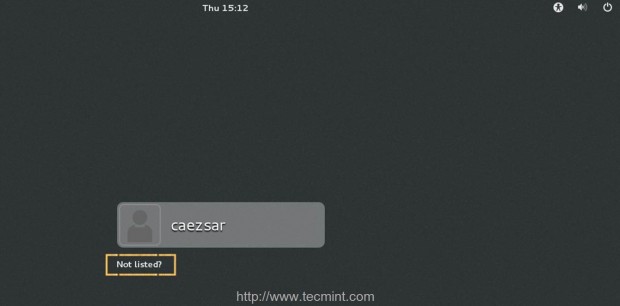
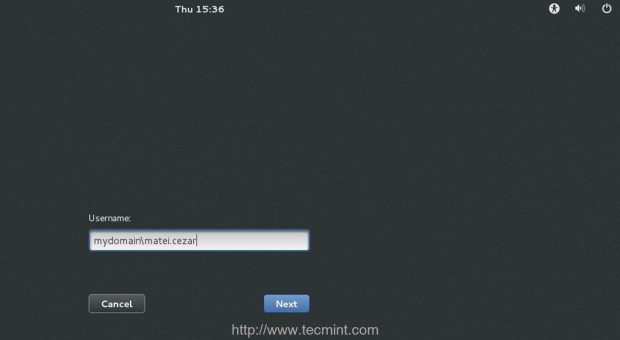
16. In order to perform GUI logins exit to main CentOS 7 Login Screen, click on Not listed? link, supply your PDC user and password in the form of your_domain\pdc_user and you should be able to login onto your machine as a PDC user.
Step 5: Enable PDC Integration System-Wide
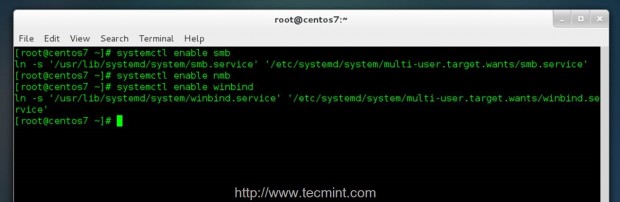
17. To automatically reach and authenticate to Zentyal PDC after every system reboot you need to enable Samba and Winbind daemons system-wide by issuing the following commands with root privileges.
# systemctl enable smb # systemctl enable nmb # systemctl enable winbind
That’s all, it takes for your machine to become a Zentyal PDC member. Although this procedure has been mainly focused on integrating CentOS 7 to Zentyal PDC, the same steps are also required to be completed in order to use Windows Server Active Directory authentication and domain integration.







Hi, with this steps my Linux desktop will receive gpo that I created for Windows client?
Windos gpo doesn’t apply to linux systems.
Hi, is it using the same way if we want to connect centos 7 machine into windows AD? what the different is in /etc/krb5.conf windows AD does not have kdc setting
The procedure for adding CentOS 7 to a Windows ADDC is basically the same as the one explained here for Zentyal. No extra steps needed.
do we need to follow the same guide for Windows DC as well??
@Raj,
The instructions would be different for Windows DC, I hope the following Zentyal documentation will help you out in joining Windows Client to Zentyal.
https://wiki.zentyal.org/wiki/En/4.0/Users,_Computers_and_File_Sharing#Joining_a_Windows.C2.AE_client_to_the_domain
@Raj: If you are planning to use windows server as an Additional Domain Controller, use the same steps as for a typical DC ( install AD Domain Services, Promote it to a DC, then the option Add a domain controller to an existing domain, specify your domain name and domain admin credentials and your’re done!
Thanks, I have been using all of these tutorials a lot, very helpful.
Do you have any How-To’s on joining Centos 7 to an existing samba DC to act as a BDC then another tutorial to show how to convert the Centos7 BDC to a PDC?