Bat is a cat command clone with advanced syntax highlighting for a large number of programming and markup languages and it also comes with Git integration to show file modifications. Its other features include automatic paging, file concatenation, themes for syntax highlighting, and various styles for presenting output.
Read Also: ccat – Show ‘cat Command’ Output with Syntax Highlighting or Colorizing
In addition, you can also add new syntaxes/language definitions, themes, and set a custom pager. In this article, we will show how to install and use a Bat (cat clone) in Linux.
Read Also: How to Use ‘cat’ and ‘tac’ Commands with Examples in Linux
How to Install Bat (A cat clone) in Linux
On Debian and other Debian-based Linux distributions, you can download the latest .deb package from the release page or use the following the wget command to download and install it as shown.
------------- On 64-bit Systems ------------- $ wget https://github.com/sharkdp/bat/releases/download/v0.15.4/bat_0.15.4_amd64.deb $ sudo dpkg -i bat_0.15.4_amd64.deb ------------- On 32-bit Systems ------------- $ wget https://github.com/sharkdp/bat/releases/download/v0.15.4/bat_0.15.4_i386.deb $ sudo dpkg -i bat_0.15.4_i386.deb
On Arch Linux, you can install it from the Community repository as shown.
$ sudo pacman -S bat
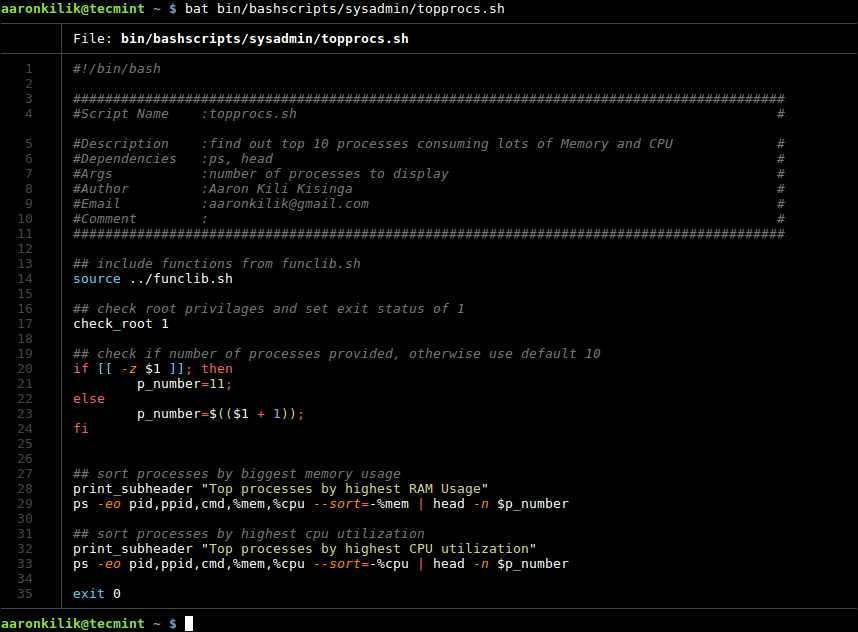
After installing bat, simply run it in the same way you normally run cat command, for example, the following command will display the specified file content with syntax highlighting.
$ bat bin/bashscripts/sysadmin/topprocs.sh
To display multiple files at ones, use the following command.
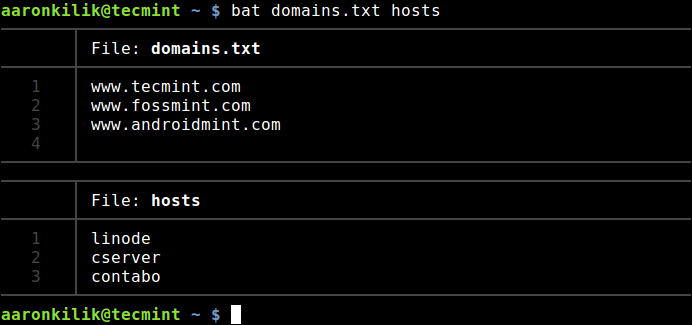
$ bat domains.txt hosts
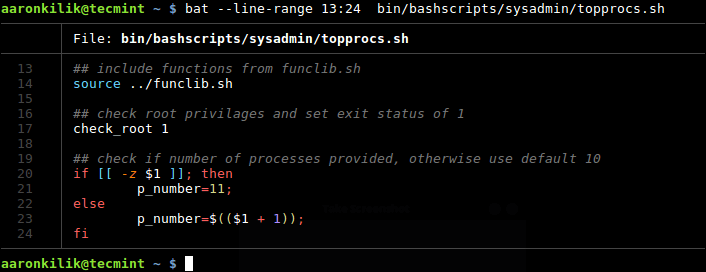
You can only print a specified range of lines (for example print lines 13 to 24 only) for a file or each file, using the --line-range switch as shown.
$ bat --line-range 13:24 bin/bashscripts/sysadmin/topprocs.sh
To show all supported language names and file extensions, use the –list-languages option.
$ bat --list-languages

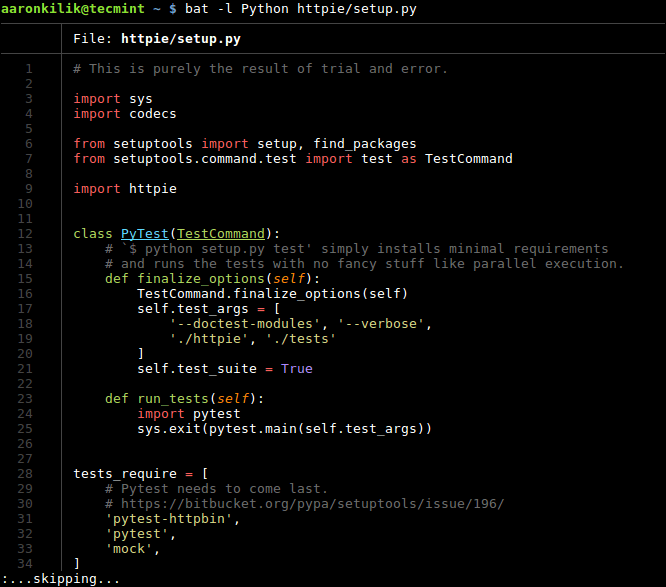
Then explicitly set a language for syntax highlighting using the -l switch.
$ bat -l Python httpie/setup.py
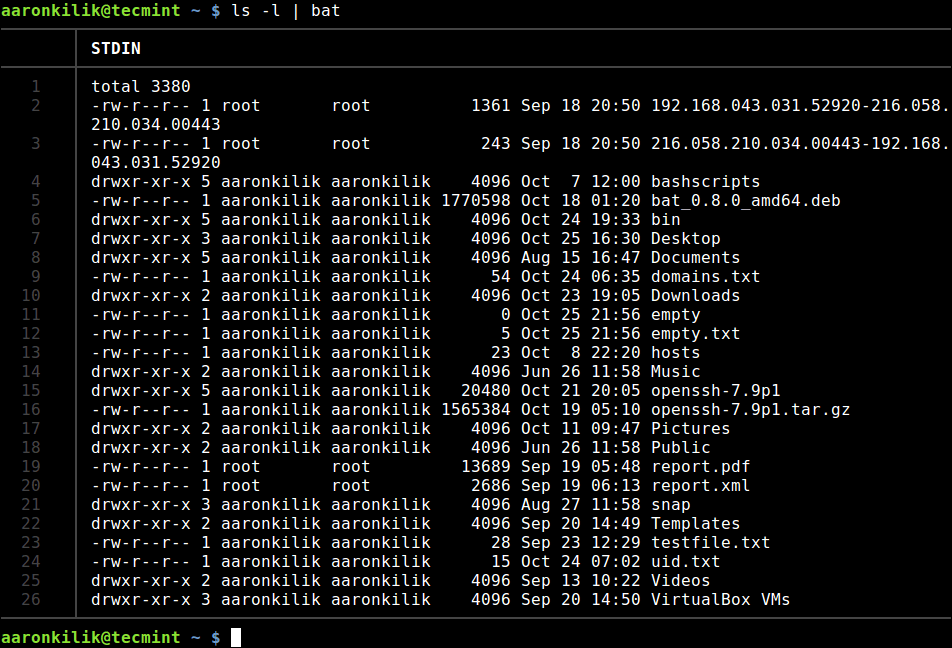
You can also read from stdin as in this example.
$ ls -l | bat
To see a list of available themes for syntax highlighting, use the --list-themes option.
$ bat --list-themes
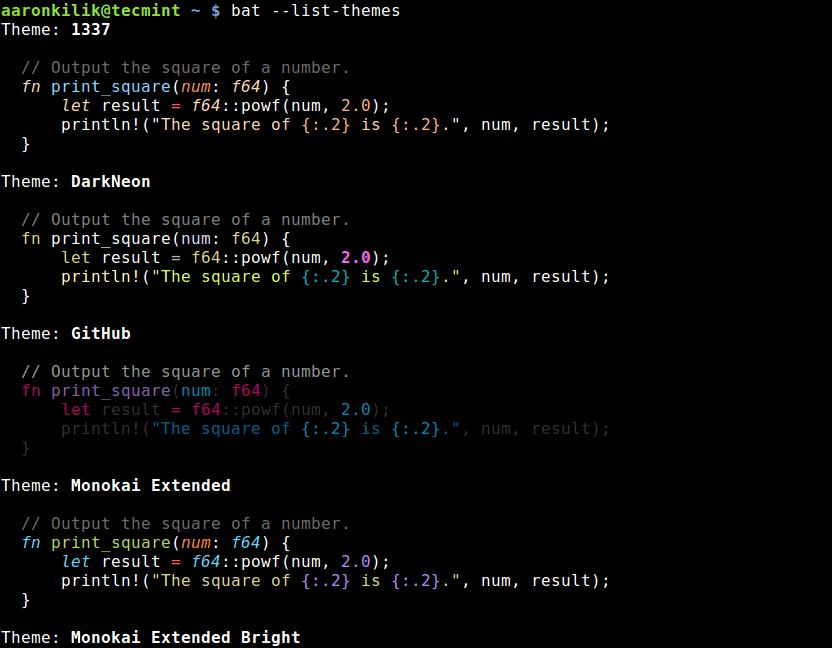
After you have picked a theme to use, enable it with the --theme option.
$ bat --theme=Github
Note that these settings will be lost after a reboot, to make the changes permanent, export the BAT_THEME environment variable in the file ~/.bashrc (user-specific) or /etc/bash.bashrc (system-wide) by adding the following line in it.
export BAT_THEME="Github"
To only show line numbers without any other decorations, use the -n switch.
$ bat -n domains.txt hosts
Bat uses “less” as the default pager. However, you can specify when to use the pager, with the --paging and the possible values include *auto*, never and always.
$ bat –paging always
In addition, you can define the pager using the PAGER or BAT_PAGER (this takes precedence) environment variables, in a similar fashion as the BAT_THEME env variable, as explained above. Setting these variables with empty values disables the pager.
For more information on how to use or customize a bat, type man bat or go to its Github Repository: https://github.com/sharkdp/bat.
Summary
Bat is a user-friendly cat clone with syntax highlighting and git integration. Share your thoughts about it, with us via the feedback form below. If you have come across any similar CLI utilities out there, let us know as well.