In this article, you will learn how to install wget non-interactive network downloader in Linux. Wget is a tool developed by the GNU project used for retrieving or downloading files from web or FTP servers.
The command downloads files that are served with FTP, HTTP or HTTPS protocol. It’s an amalgamation of the words World Wide Web and the word get to form wget. It’s used in Unix/Linux systems to download files and packages on the terminal.
On this page
Install wget on Ubuntu/Debian
To install wget on Ubuntu/Debian distros, log in via SSH as root and run the command.
# apt-get install wget
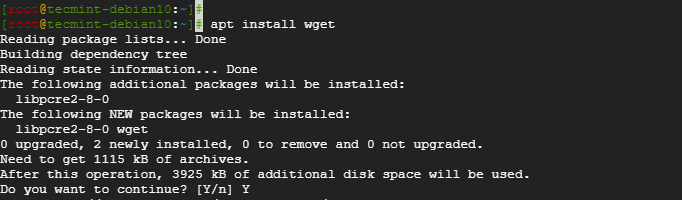
To confirm the installation of the wget tool, run the command.
# dpkg -l | grep wget

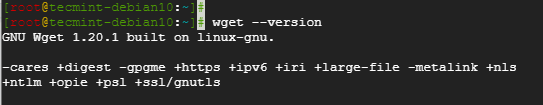
Alternatively, you can check its version by running.
# wget --version
Install wget on RHEL / CentOS / Fedora
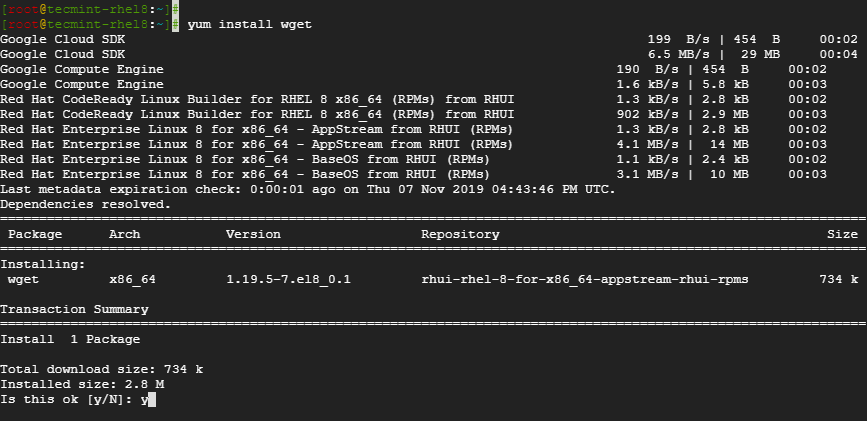
To install wget on RHEL, CentOS and Fedora distros, log in via SSH as root and run the command.
# yum install wget
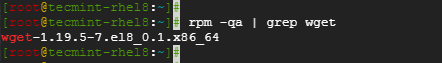
To confirm the installation, run the command.
# rpm -qa | grep wget
Install wget on OpenSUSE
On OpenSUSE, install wget by running.
# zypper install wget
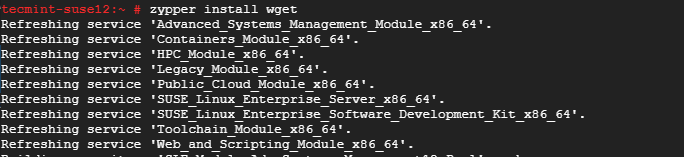
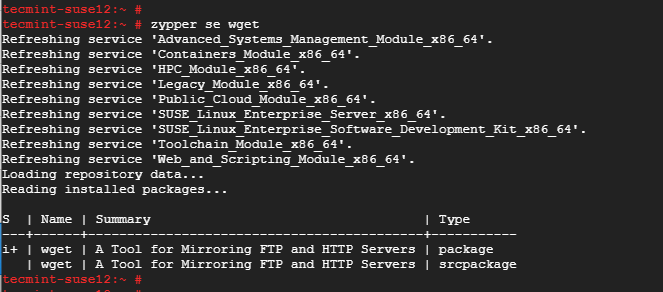
To confirm the installation run.
# zypper se wget
Install wget on ArchLinux
On ArchLinux, install wget by running the command.
# pacman -Sy wget
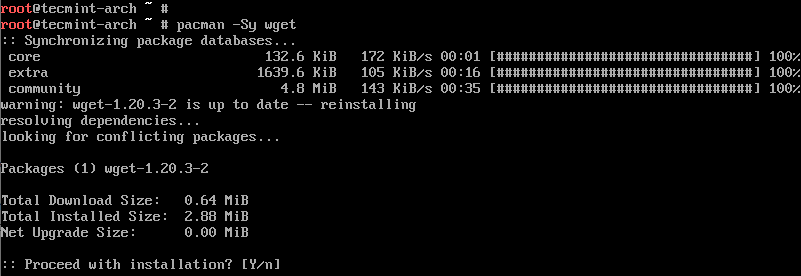
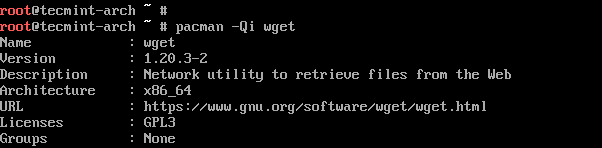
To check if wget is installed and print more information about the tool run.
# pacman -Qi wget
To know more about wget usage and examples, I suggest you read our following articles that explain how you can use wget command-line utility for downloading files from the web.
- 10 Wget (Linux File Downloader) Command Examples in Linux
- How to Limit File Download Speed Using Wget in Linux
- How to Download Files to Specific Directory Using Wget
- How to Rename File While Downloading with Wget in Linux
And with that, we have come to the end of this article. In this tutorial, you learned how to install wget in different Linux distributions.




What is your terminal? It is colorful, is it a special one or you made some arrangements for making it colorful?