Brief: In this guide, we will discuss practical examples of sleep commands. After following this guide, Linux programmers will be able to use the sleep command to write robust shell scripts.
Linux programmers and system administrators prefer to write shell scripts to automate simple tasks. However, writing a robust script is not an easy task. We need to handle many corner cases, such as – retry mechanism, debugging, logging, error reporting, etc.
In addition to this, many times, we need to simulate a delay in command execution to test timeout scenarios. Similarly, we need to introduce delays in the script to implement the retry mechanism. The sleep command is a perfect solution to handle such scenarios.
In this guide, we will discuss the usage of the sleep command. As the name suggests, the sleep command is used to delay the next command execution. It causes the calling program to sleep for a specified amount of time.
Table of Contents
So, let’s learn more about sleep commands with practical examples in Linux.
sleep Command Syntax
The syntax of the sleep command is very simple, as it accepts one mandatory parameter with an optional suffix:
$ sleep <NUMBER>[SUFFIX]
It is important to note that, in the above syntax, there isn’t a space between the NUMBER and SUFFIX.
1. How to Delay Linux Command Execution
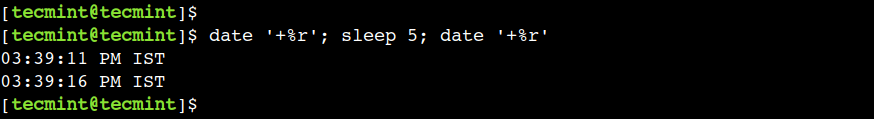
By default, the sleep command waits for a number of seconds. To understand this, let’s print the current time before and after the sleep command:
For example, the following command waits for 5 seconds after printing the current time:
$ date '+%r'; sleep 5; date '+%r'
In this example, we have used a semicolon (;) to separate each command.
2. How to Make a Command to Wait N Minutes
Optionally, the sleep command allows us to specify the time unit using the suffixes. We can use the following suffixes with the sleep command:
s– to specify time units in seconds.m– to specify time units in minutes.h– to specify time units in hours.d– to specify time units in days.
So, let’s use the 'm' suffix to sleep for 1 minute:
$ date '+%r'; sleep 1m; date '+%r'
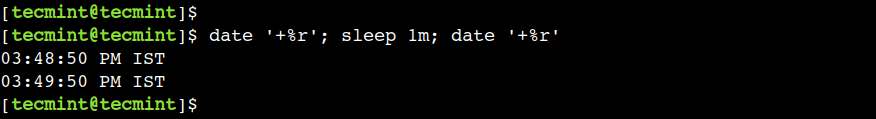
The important point to note that is there shouldn’t be any space between NUMBER and SUFFIX.
3. How to Make Command Sleep for X Minutes and Seconds
We can use multiple suffixes with the sleep command. In such a case, the time duration is calculated by summing up all the values.
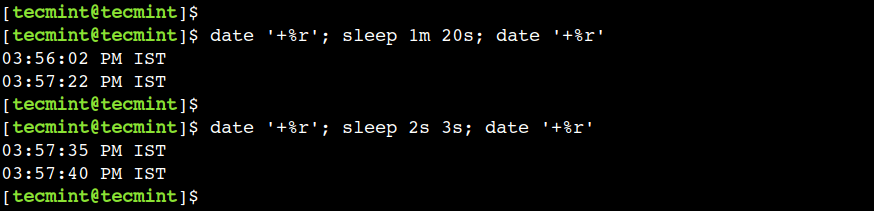
To understand this, let’s use the following command to sleep for 1 minute and 20 seconds:
$ date '+%r'; sleep 1m 20s; date '+%r'
In the above example, we have used two different suffixes. However, we can use the same suffixes as well.
For example, we can use 2s and 3s suffixed to sleep for 5 seconds:
$ date '+%r'; sleep 2s 3s; date '+%r'
4. How to Use Floating Point Numbers With the sleep Command
Additionally, the sleep command also accepts a floating point number as input. We can use this method to sleep for less than a second.
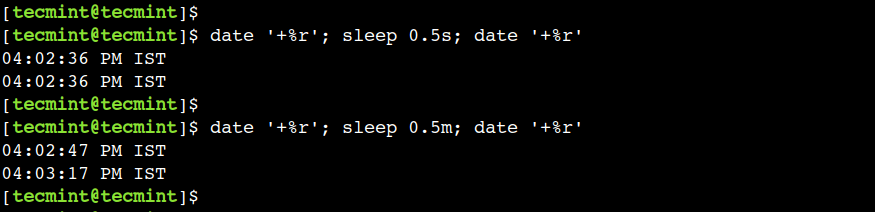
For example, we can use the 0.5s value to sleep for a half second:
$ date '+%r'; sleep 0.5s; date '+%r'
In the above output, we can see that the date command shows the same value for the seconds time unit.
In addition to this, we can use floating values with other suffixes as well. For example, we can use the 0.5m value to sleep for 30 seconds:
$ date '+%r'; sleep 0.5m; date '+%r'
5. How to Simulate Alarm Clock Using sleep Command
In the previous few examples, we saw how to use the sleep command to delay the next command execution. We can use this trick to simulate an alarm clock.
So, let’s use the below command to set alarm after 5 seconds:
$ sleep 5; cvlc alarm.mp3
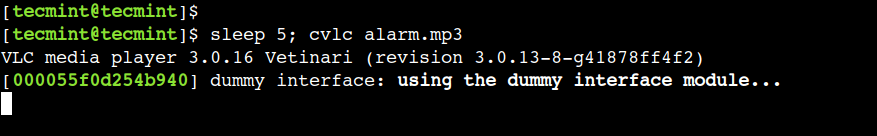
The above command opens the alarm.mp3 file using the VLC media player after waiting for 5 minutes. Just like any other Linux command, we can use the ctrl+c key combination to stop the VLC media player.
In this example, we have used the VLC media player but it is possible to use any other Linux media player or sound utility to achieve the same result.
6. How to Simulate Digital Clock with sleep Command
To simulate a digital clock, we can run the sleep command in an infinite loop after every second. Let’s understand this with an example.
First, let’s write a simple shell script called digital-clock.sh with the following code:
#!/bin/bash while [ 1 ] do clear tput cup 5 30 date '+%r' sleep 1 done
In this script, we have used the tput command to place the cursor at the 5th row and 30th column.
Now, let’s run the script and see the result:
$ chmod +x digital-clock.sh $ ./digital-clock.sh
Finally, we can use the ctrl+c key combination to stop the script execution.
In this guide, we discussed how to use the sleep command to delay the next command execution. Linux programmers can use sleep commands to write robust shell scripts.
Do you know of any other best example of the sleep command in Linux? Let us know your views in the comments below.