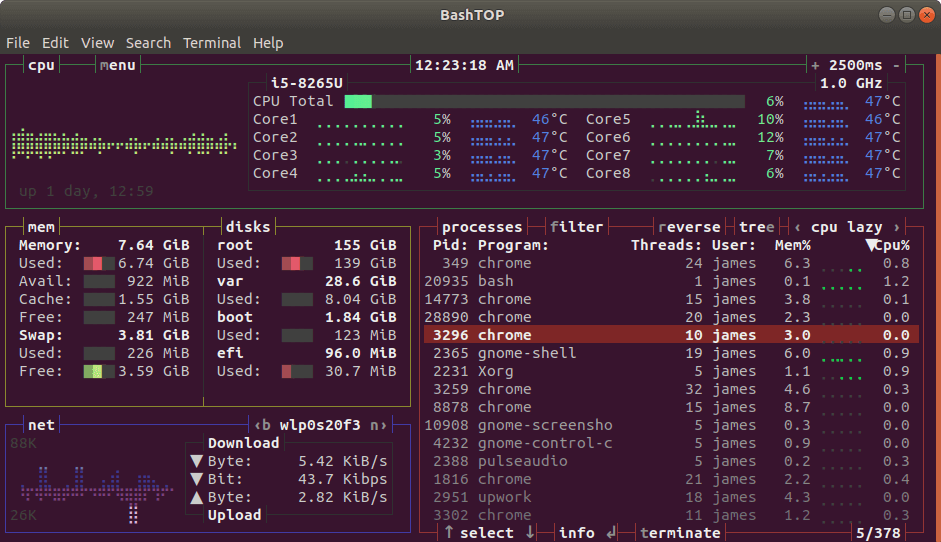
Bashtop is a terminal-based resource monitoring utility in Linux. It’s a nifty command-line tool that intuitively displays statistics for your CPU, memory, running processes, and bandwidth to mention just a few.
It ships with a game-inspired and responsive terminal UI with a customizable menu. Monitoring various system metrics is made easy by the neat arrangement of various display sections.
With Bashtop, you can also sort processes, as well as easily switch between the various sorting options. Additionally, you can send SIGKILL, SIGTERM, and SIGINT to the processes that you want.
Bashtop can be installed on both Linux, macOS, and even FreeBSD. In this guide, you will learn how to install Bashtop on various Linux distributions.
Prerequisites
To successfully install Bashtop, ensure that you have the following dependencies ready in your system.
- Bash 4.4 or later versions
- Git
- GNU Coreutils
- GNU sed, awk, grep and ps command-line tools.
- Lm-sensors – optional – (For gathering CPU temperature statistics).
Installing Bashtop Resource Monitor on Linux
To get started, we will begin with the manual installation of Bashtop. This should work across all distributions:
Manual Installation
To manually install Bashtop, clone the git repository as shown and compile from source using the commands below:
$ git clone https://github.com/aristocratos/bashtop.git $ cd bashtop $ sudo make install
To uninstall Bashtop, run:
$ sudo make uninstall
Install Bashtop in Ubuntu
There are 2 ways of installing Bashtop on Ubuntu: using snap or using the APT package manager.
To install using snap, execute:
$ snap install bashtop
To install using the APT package manager, first append the Bashtop PPA as shown:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:bashtop-monitor/bashtop
Next, update the package list and install Bashtop as shown.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install bashtop
Install Bashtop in Debian
Bashtop is available in Debian’s official repository. To install it, simply run the command:
$ sudo apt install bashtop
Also, you can run the commands shown.
$ git clone https://github.com/aristocratos/bashtop.git $ cd bashtop/ $ cd DEB $ sudo ./build
Install Bashtop in Fedora
To get Bashtop into Fedora, simply run the command:
$ sudo dnf install bashtop
Install Bashtop in CentOS/RHEL 8
For CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 systems, you need to first enable the EPEL repository and later run the command below:
$ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo dnf install bashtop
Install Bashtop on Arch Linux
Bashtop is available in AUR as bashtop-git. To install Bashtop, simply run:
$ sudo pacman -S bashtop
How to Use Bashtop Resource Monitor on Linux
To launch Bashtop, simply run the command below on the terminal.
$ bashtop
Bashtop Configuration
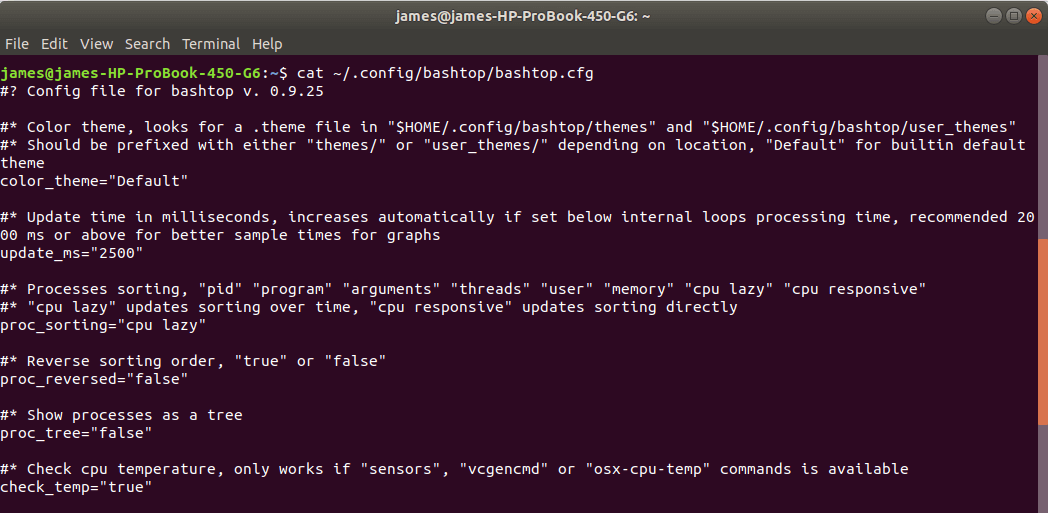
Bashtop’s configuration file is found at ~/.config/bashtop/bashtop.cfg location. You can change the parameters as you deem fit to customize the appearance and output of metrics on the terminal.
Here’s a sample of the default configuration:
To have a peek at the commands & shortcuts, press the ESC key and then select the ‘HELP’ option using the arrow down key.
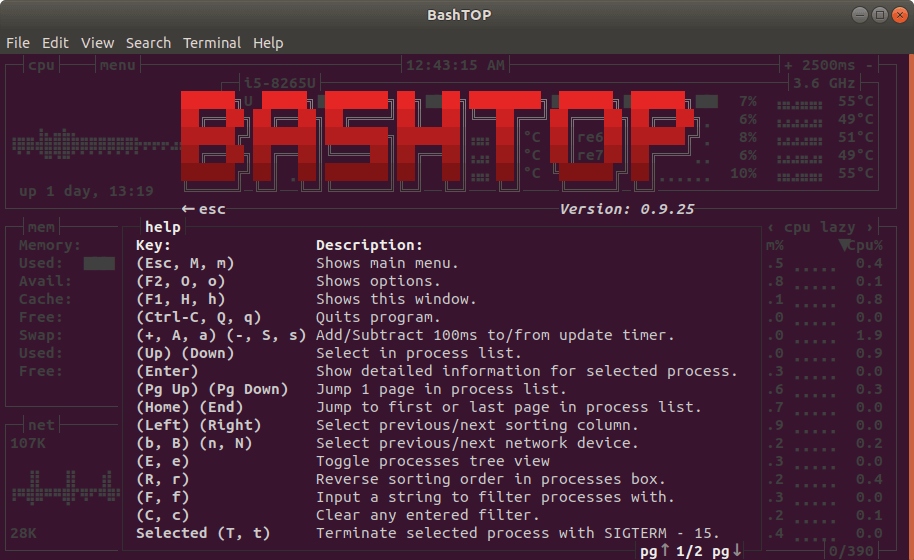
This prints out the menu below with all the command options as shown.
Conclusion
Generally, Bashtop provides an excellent way of keeping an eye on your Linux system resources. However, it’s much slower than top and htop and is a bit resource-intensive. Nevertheless, it’s quite an impressive tool that provides salient information about various system metrics. Give it a try and let us know how it went.




Kubuntu 21.10 kernel 5.13.0-19-generic #19-Ubuntu SMP. KDE 5.22.5. The display is cutting off cpu and temps. On exit says it’s missing python 3 psutil modules. Installed those and it cleaned up some but not perfect.
bashtop IS NOT available on current Debian stable (buster). Trying to install it points to the snap version.