Bandwhich, formerly known as “what”, is a terminal utility written in Rust programming language, which is used for monitoring current network bandwidth utilization by the process, connection, and remote IP/hostname. It sniffs a specified network interface and tracks IP packet size, cross-referencing it with the /proc filesystem on Linux and lsof on macOS.
Recommended Read: 16 Useful Bandwidth Monitoring Tools to Analyze Network Usage in Linux
Bandwhich is responsive to the terminal window size, shows lesser information if there isn’t much room for it. Also, it will strive to resolve IP addresses to their hostname in the background using reverse DNS.
How to Install Bandwhich in Linux Systems
This Bandwhich utility is a new utility and it is available to install on Arch Linux from the AUR repository using Yay.
Yay is an extremely good AUR helper written in Go, which is used as a Pacman wrapper to search and install packages from the AUR repository and update the entire system.
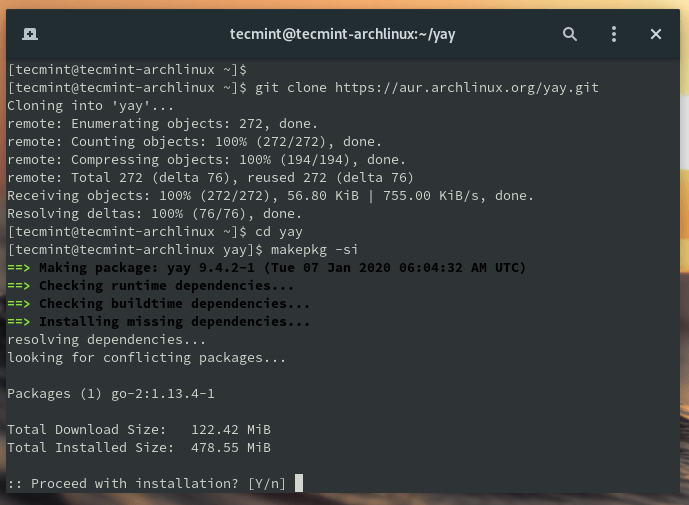
If Yay AUR Helper not installed, you can install it by cloning the git repo and building it using the following commands.
$ git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/yay.git $ cd yay $ makepkg -si
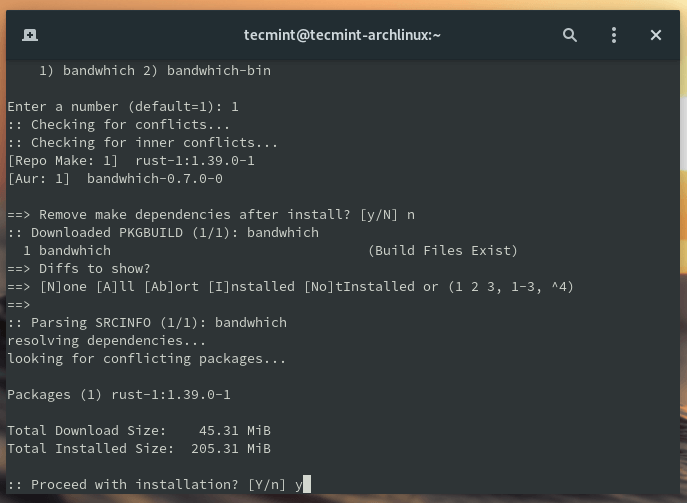
Once Yay installed, you can use it to install Bandwhich as shown.
$ yay -S bandwhich
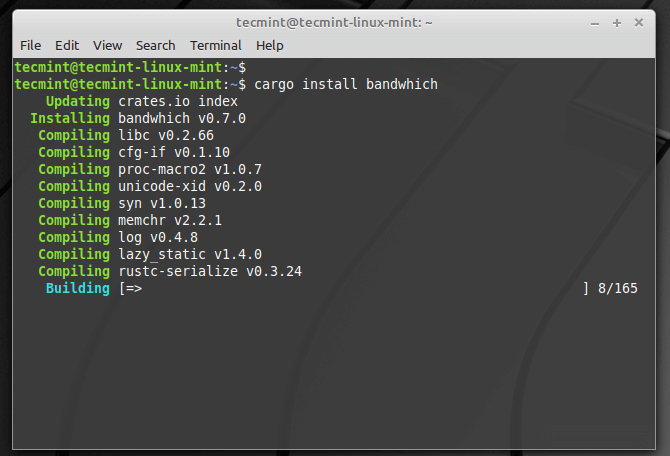
On Other Linux distributions, bandwhich can be installed using the Rust package manager called cargo. To install Cargo on Linux, you need to install Rust programming language.
$ curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
Once Rust installed on the system, you can simply use the cargo command to install Bandwhich in Linux systems.
$ cargo install bandwhich
This installs bandwhich to ~/.cargo/bin/bandwhich but you required root privileges to run it. To fix that, you need to create a symbolic link to the binary as shown.
$ sudo ln -s ~/.cargo/bin/bandwhich /usr/local/bin/
After that, you can able to run bandwhich command, instead of sudo ~/.cargo/bin/bandwhich as shown.
$ sudo bandwhich
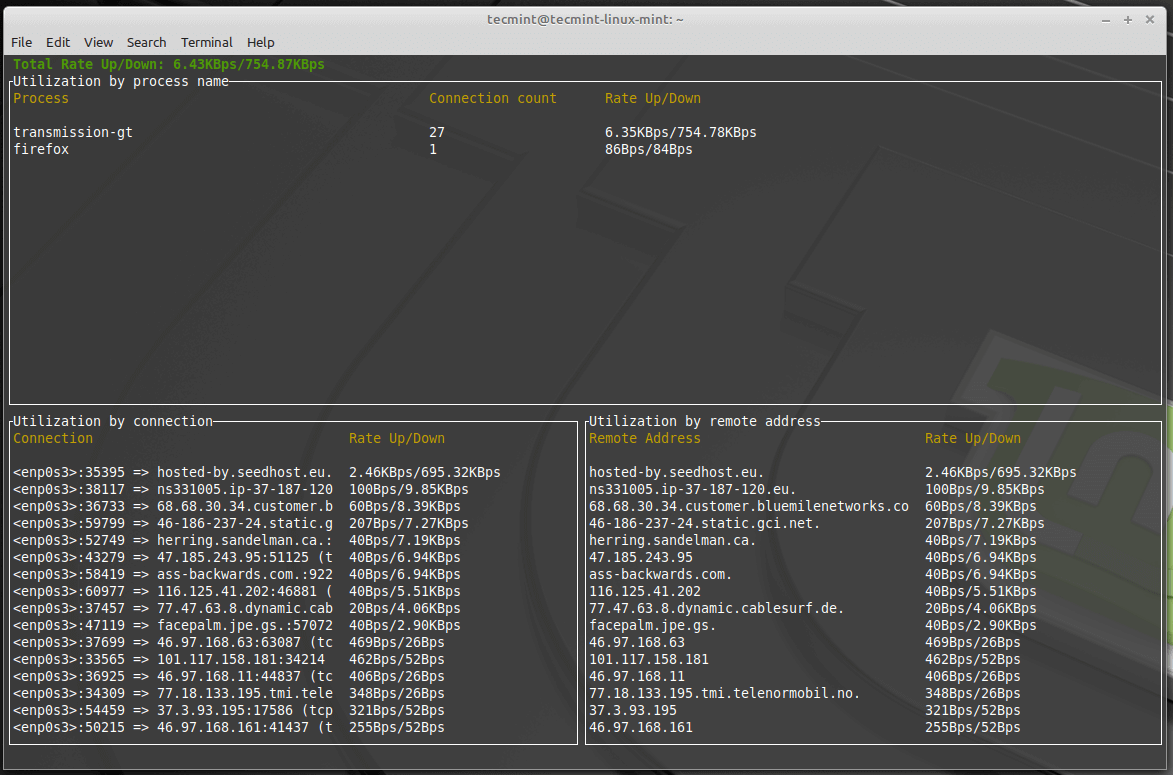
For more usage and options, type:
$ sudo bandwhich --help
That’s It! Bandwhich is a useful command-line utility for displaying current network usage by process, connection and remote IP/hostname in Linux.