Data replication is the process of copying your data across multiple servers to improve data availability and enhance the reliability and performance of an application. In MySQL replication, data is copied from a database from the master server to other nodes in real-time to ensure consistency of data and also to provide backup and redundancy.
In this guide, we demonstrate how you can set up MySQL (Master-Slave) replication in RHEL-based distributions such as CentOS, Fedora, Rocky Linux, and AlmaLinux.
MySQL Replication Setup
So, here is our MySQL replication lab setup.
MySQL Master - 10.128.0.14 MySQL Slave - 10.128.15.211
Let’s get started…
Step 1: Install MySQL on Master and Slave Server
We will start off by installing the MySQL database on both the master and slave servers.
$ sudo dnf install @mysql
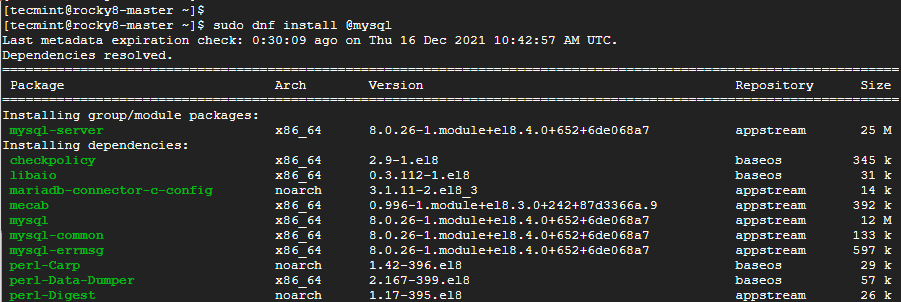
Once the installation is complete, make a point to start the database server.
$ sudo systemctl start mysqld
Then enable it to start to system startup or upon reboot.
$ sudo systemctl enable mysqld
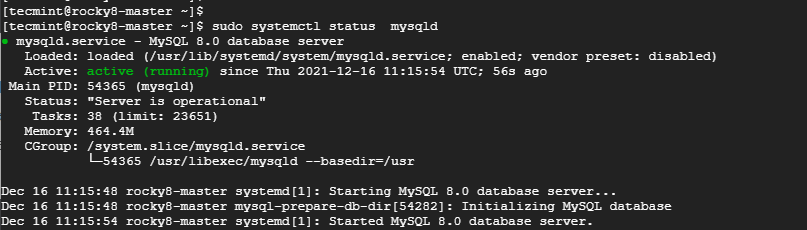
Thereafter, confirm that the MySQL database server is running as shown:
$ sudo systemctl status mysqld
Step 2: Secure MySQL on Master and Slave Server
The next step is to secure the MySQL database on both the master and slave servers. This is because the default settings are insecure and present some loopholes which can easily be exploited by hackers.
So, to harden MySQL, run the command:
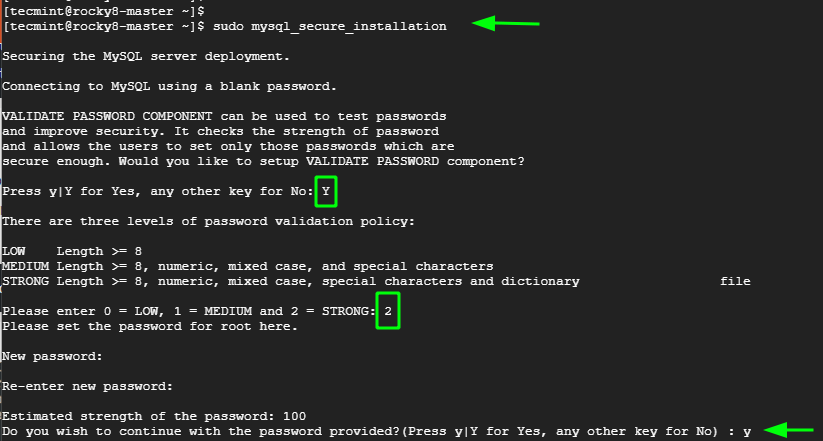
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
First, you will be required to set the MySQL root password. Be sure to provide a strong root password, preferably with more than 8 characters which are a mix of uppercase, lowercase, special and numeric characters.
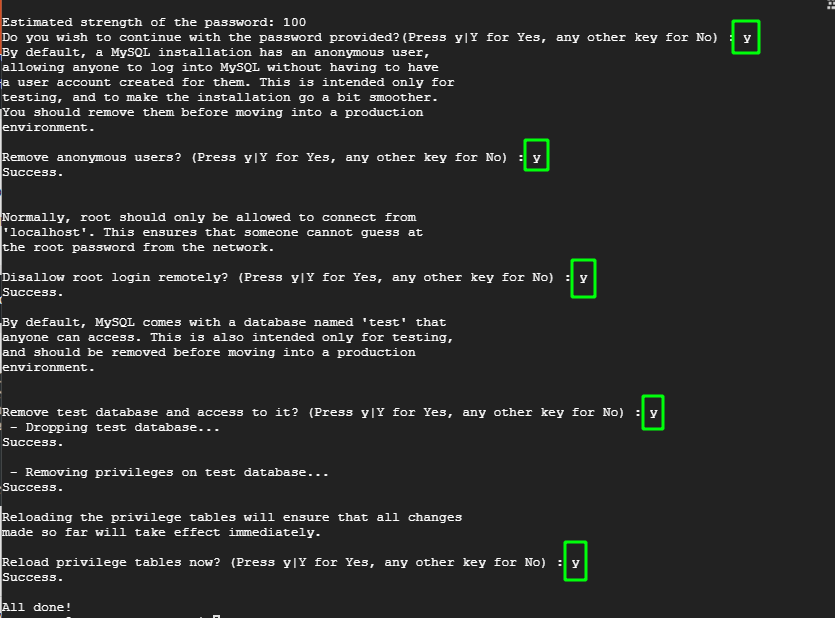
For the remaining prompts, type in 'Y' to tweak the database server to the recommended settings.
Once you have finished installing and hardening MySQL on the master and slave node, the next is to configure the master node.
Step 3: Configure the Master Node (Server)
The next step is to configure the Master node and grant the slave node access to it. First, we need to edit the mysql-server.cnf configuration file.
$ sudo vim /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
Add the following lines under the [mysqld] section.
bind-address = 10.128.0.14 server-id = 1 log_bin = mysql-bin
Once done, save the changes and exit. Then restart the MySQL server.
$ sudo sysemctl restart mysqld
Next, log into MySQL shell.
$ sudo mysql -u root -p
Execute the following commands to create a database user that will be used to bind the master and slave for replication.
mysql> CREATE USER 'replica'@'10.128.15.211' IDENTIFIED BY 'P@ssword321'; mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.*TO 'replica'@'10.128.15.211';
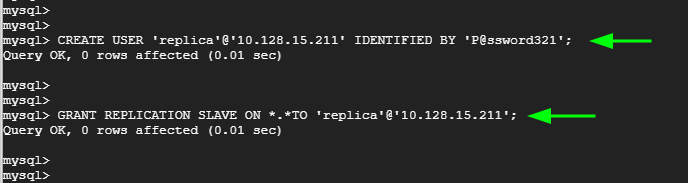
Apply the changes and exit the MySQL server.
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; mysql> EXIT;
Verify the status of the master.
mysql> SHOW MASTER STATUS\G
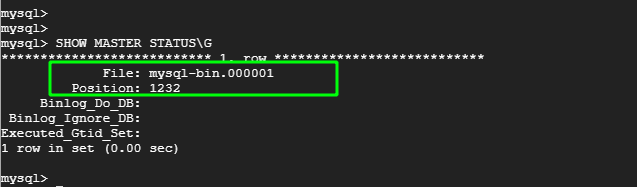
Take note of the Filename and Position. You will need this later on when setting up the slave for replication. In our case, we have the filename as mysql-bin.000001 and Position 1232.
Step 4: Configure the Slave Node (Server)
Now, head back to the Slave node. Once again, edit the mysql-server.cnf configuration file.
$ sudo vim /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
As before, paste these lines under the [mysqld] section. Change the IP address to correspond to the slave’s IP. Also, assign a different server-id. Here we have assigned it the value of 2.
bind-address = 10.128.15.211 server-id = 2 log_bin = mysql-bin
Save the changes and exit the file. Then restart the database server.
$ sudo systemctl restart mysqld
To configure the Slave node to replicate from the Master node, log in to the Slave’s MySQL server.
$ sudo mysql -u root -p
First and foremost, stop the replication threads:
mysql> STOP SLAVE;
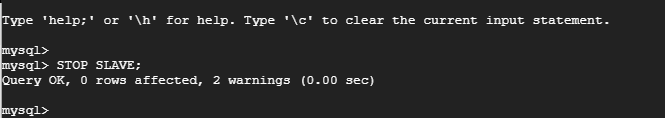
Then execute the following command to configure the slave node to replicate databases from the master.
mysql> CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='10.128.0.14' ,
MASTER_USER='replica' ,
MASTER_PASSWORD='P@ssword321' ,
MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000001' ,
MASTER_LOG_POS=1232;
Note that the MASTER_LOG_FILE and MASTER_LOG_POS flags correspond to the file and Position values from the Master node at the end of Step 1.
The MASTER_HOST, MASTER_USER, and MASTER_PASSWORD correspond to the Master IP address, the replication user, and the replication user’s password respectively.
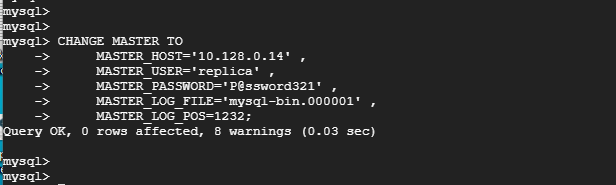
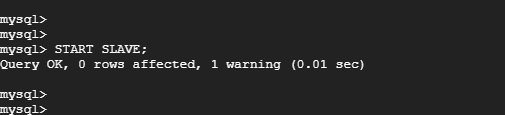
Then start the slave replication threads:
mysql> START SLAVE;
Step 4: Testing MySQL Master-Slave Replication
Now, to test if replication between the master and slave node is working, log in to the MySQL database server on the master node:
$ sudo mysql -u root -p
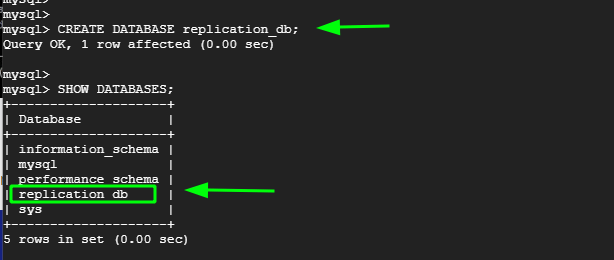
Create a test database. Here, our test database is called replication_db.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE replication_db;
Verify the existence of the database.
mysql> SHOW DATABASES;
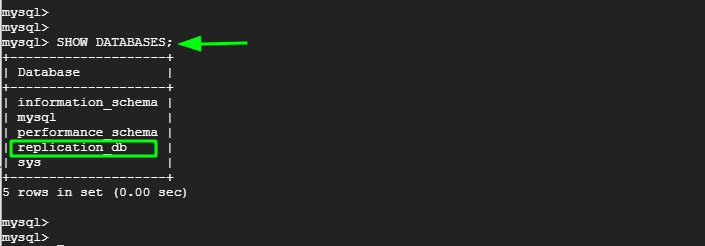
Now, head over to the slave node, log in to the MySQL server and confirm that the replication_db database is present. From the output below, we can see that the database is present. This is confirmation that replication has taken place from the Master to the slave node.
mysql> SHOW DATABASES;
And that’s it, we have successfully demonstrated how you can set up a MySQL master-slave replication model that can replicate databases from the master node to the slave node.





When I tried to add the above lines under
[mysqld]the replication is working fine but my syslog-ng.service is getting stopped.is there any solution for this?
its working fine. thanks for ur help.