Meltdown is a chip-level security vulnerability that breaks the most fundamental isolation between user programs and the operating system. It allows a program to access the operating system kernel’s and other programs’ private memory areas, and possibly steal sensitive data, such as passwords, crypto-keys and other secrets.
Spectre is a chip-level security flaw that breaks the isolation between different programs. It enables a hacker to trick error-free programs into leaking their sensitive data.
These flaws affect mobile devices, personal computers and cloud systems; depending on the cloud provider’s infrastructure, it might be possible to access/steal data from other customers.
We came across a useful shell script that scans your Linux system to verify whether your kernel has the known correct mitigations in place against Meltdown and Spectre attacks.
spectre-meltdown-checker is a simple shell script to check if your Linux system is vulnerable against the 3 “speculative execution” CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) that were made public early this year. Once you run it, it will inspect your currently running kernel.
Optionally, if you have installed multiple kernels and you’d like to inspect a kernel you’re not running, you can specify a kernel image on the command line.
It will significantly try to detect mitigations, including backported non-vanilla patches, not considering the kernel version number advertised on the system. Note that you should launch this script with root privileges to get accurate information, using the sudo command.
$ git clone https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker.git $ cd spectre-meltdown-checker/ $ sudo ./spectre-meltdown-checker.sh
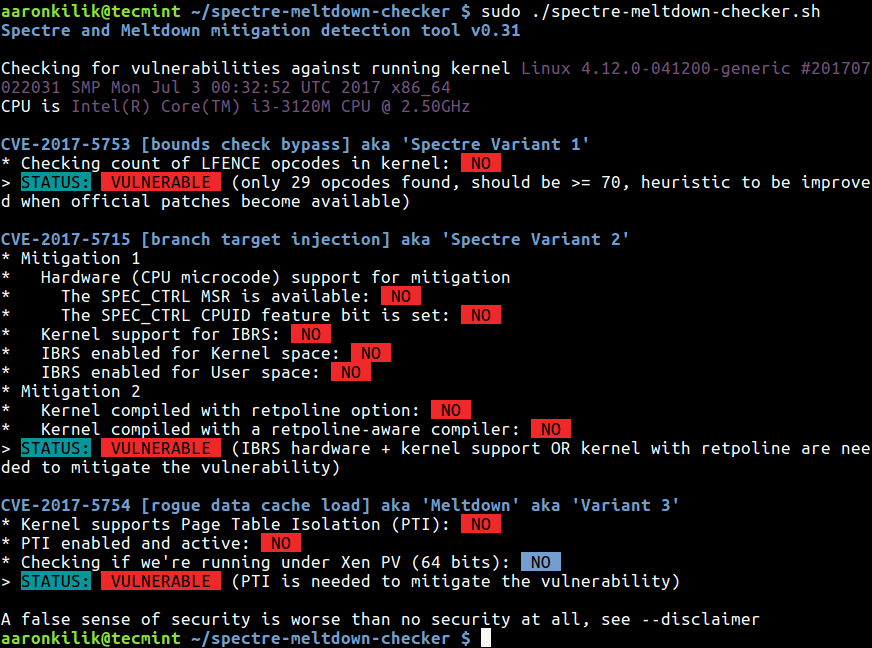
From the results of the above scan, our test kernel is vulnerable to the 3 CVEs. In addition, here are a few important points to note about these processor bugs:
- If your system has a vulnerable processor and runs an unpatched kernel, it is not safe to work with sensitive information without the chance of leaking the information.
- Fortunately, there are software patches against Meltdown and Spectre, with details provided in Meltdown and Spectre research homepage.
The latest Linux kernels have been redesigned to defang these processor security bug. Therefore update your kernel version and reboot the server to apply updates as shown.
$ sudo yum update [On CentOS/RHEL] $ sudo dnf update [On Fedora] $ sudo apt-get update [On Debian/Ubuntu] # pacman -Syu [On Arch Linux]
After reboot make sure to scan again with spectre-meltdown-checker.sh script.
You can find a summary of the CVEs from the spectre-meltdown-checker Github repository.





I am running Ubuntu Mate 17.10 and ran process twice and still get vulnerable in ‘ Spectre Variant 1 and 2 ‘ , shows exactly what you have in example, is this still in the process of being fixed ? , or am I missing something .
@Richard
This means that your system is vulnerable to ‘ Spectre Variant 1 and 2 ‘. Therefore try to update your kernel to one which has a patch for the flaws.
Check out this guide: https://www.tecmint.com/upgrade-kernel-in-ubuntu/ or update your kernel as follows:
$sudo apt update
$sudo apt-cache search linux-image
$sudo apt install – -only-upgrade
Thanks’ for the reply, updated to latest kernel ( 4.14.14 ) still shows vulnerable to ‘ Spectre Variant 1 and 2 ‘ , any thoughts would be appreciated, maybe try some older versions ?
@Richard
Sure, we will try to find out more whether the latest Ubuntu kernel has been patched. Thanks for the feedback.
I am running on an Antergos (Arch Based Distro). I ran the script and 2 of the 3 sectors had vulnerabilities. I went to upgrade and pacman is saying I have nothing to upgrade. How do I resolve this?
For the Fedora/CentOS/RHEL users I created a COPR repository so that the spectre-meltdown-checker can be installed and updated via package manager.
You can find more information at https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/ganto/spectre-meltdown-checker. I’ll try to include this upstream in the next few days.
@ganto
Thanks a lot for the efforts and for sharing this useful information with us. We will definitely check it out and update the article to include this link.