When you work with a lot of files on console environment such as moving files or copying files, you may find that your job is tedious. On the GUI environment there is a File Manager. File Manager will help you and speed up your activities associated with the files. You don’t have to remember every syntax / command associated with the files. Just click and drag or press shortcuts to complete your job.

In console environment, you have to remember commands / syntax. Luckily, Linux has a text based File Manager that works on console environment. The name is Midnight Commander (later we call it MC).
What is Midnight Commander
The Midnight Commander website says:
“GNU Midnight Commander is a visual file manager, licensed under GNU General Public License and therefore qualifies as Free Software. It’s a feature rich full-screen text mode application that allows you to copy, move and delete files and whole directory trees, search for files and run commands in the subshell. Internal viewer and editor are included”
How to Install Midnight Commander in Linux
By default, MC is not installed on a Linux machine. So you need to install it first. On Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint you may use this apt-get command:
$ sudo apt-get install mc
On RHEL, CentOS and Fedora, you may use this command:
# yum install mc
After installation is finished, just type “mc” (without quotes) from console to run it.
# mc
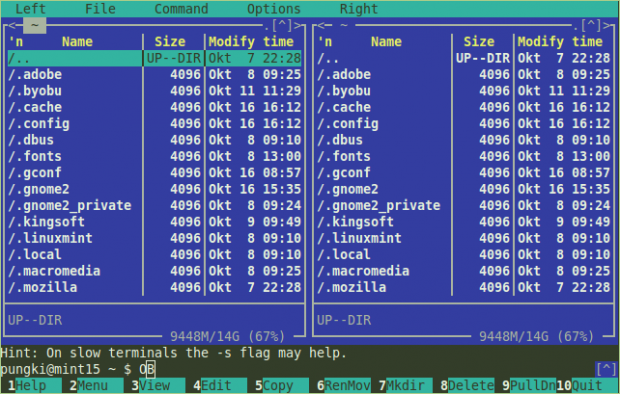
Midnight Commander Features
MC has many features which are useful for a user or a Linux Administrator. Here’s some features that may be useful for daily basis.
Copy, Delete, Rename / Move, Create Directory
MC is divided into two columns. Left column and right column. Those columns are independent window from each other. Each window will represent an active directory. You can switch between window using the Tab button. At the bottom, you will see there are buttons which prefixed by a number. Those numbers represent F1 – F10 buttons.
To copy file(s) from one directory to another, simply highlight the file and press “F5” key. If you want to copy multiple files, you need to press “Insert” button for each file you want to copy.
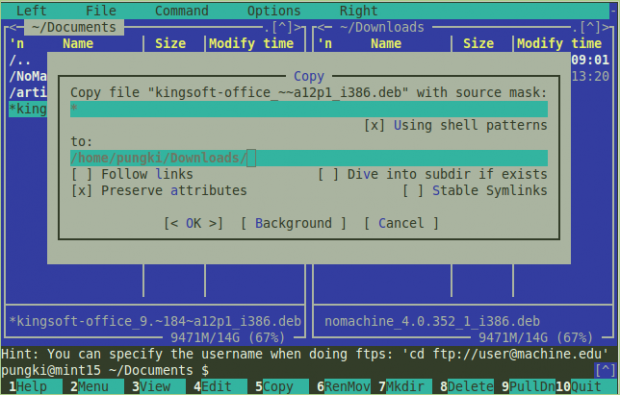
MC will ask your confirmation about destination folder (To), Follow links, Preserves attributes. Generally, you can only focus on the To parameter. Just press OK to commit copy process.
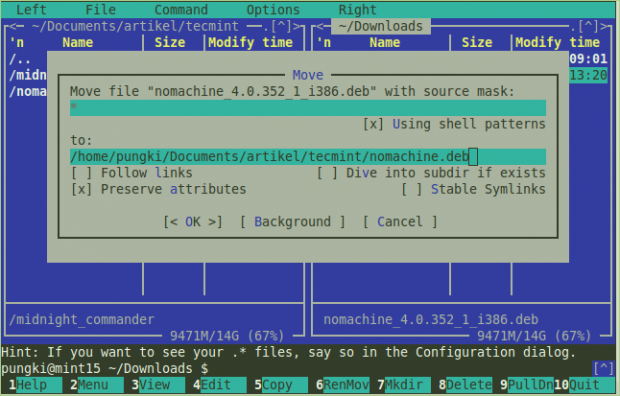
Deleting file(s) is easier. Simply highlight the file(s) and press “F8” key to confirm deletion. Moving file(s) can be done using “F6” key.
Renaming file in other hand is different. When you press “F6” key, you need to make sure that you add a “New Filename” for the file in To parameter. Here’s a screenshot when you want to Rename a file.
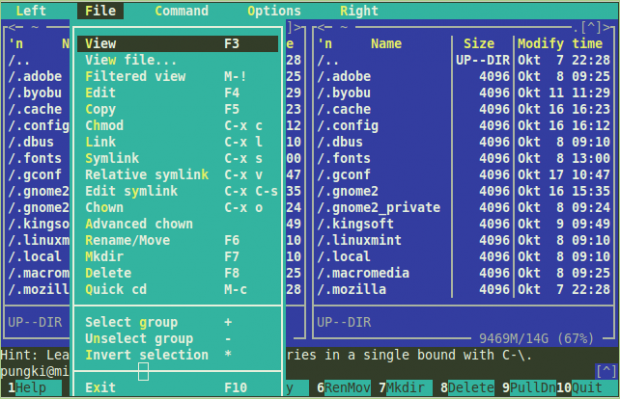
To create a directory, you can press “F7” key. MC will create a new directory in the current directory. For more details about what MC can do with the files, press “F9” > File.
Internal Viewer
In console mode, there are many text editors such as vi, joe, and nano. MC has its own internal viewer. If you want to view the content of a file text, you can highlight the file and press “F3” key. You also can edit the file when you need. Highlight the file and press “F4” to start editing.
When you run the text editor for the first time, MC will ask you to choose default text editor for you. Here’s a sample output:
pungki@mint15 ~ $ Select an editor. To change later, run 'select-editor'. 1. /bin/ed 2. /bin/nano
Then when you press “F4” button to edit a file, MC will use the text editor that you have chosen. If you want to change your default editor, just press “F2” button, choose ‘@’ sign and type ‘select-editor’ (without quotes).
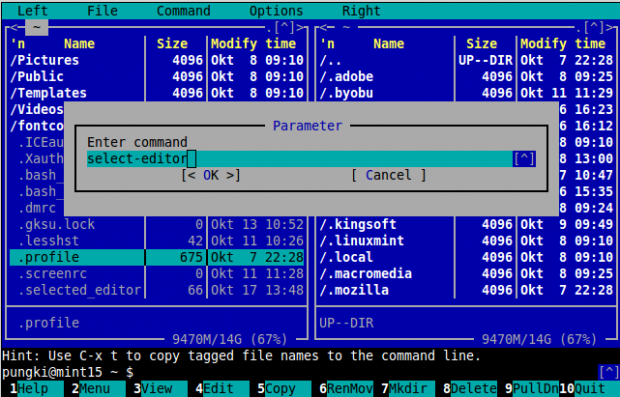
What if you want to use other text editors that are not detected by MC? Let say you want to use Vi text editor. For this case, you can do it another way. In your home directory you will find a “.selected_editor” file. This is a hidden file, so it begins with a dot sign. Edit the file. You will see:
# Generated by /usr/bin/select-editor SELECTED_EDITOR="/usr/bin/vi"
File Pemission
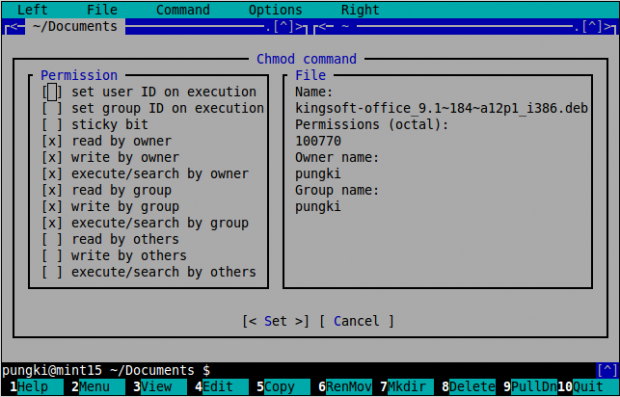
Files and directories have permissions. Permission will manage who can read, write an execute the files and directories. The command to manage it is chmod. You can see how to use chmod in details by typing “man chmod” in the terminal.
With MC, you only need to select a file then press “F9” > File > Chmod or press “Ctrl-x” and “c“. MC will show to you the current permission of the selected file and show to you more parameters that can be set.
File Owner
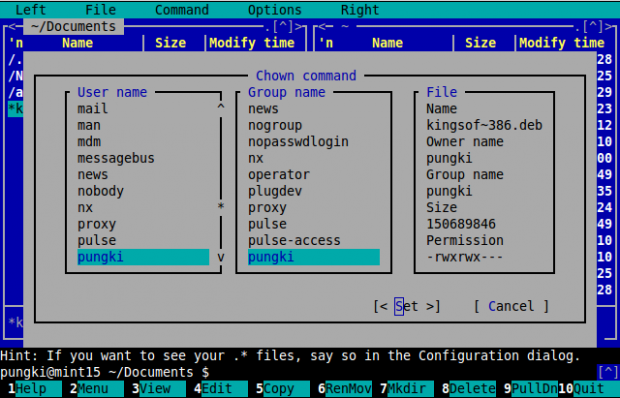
Files and directories also have owner and group owner. The privileges of these owners are managed by chmod command above. The command to manage owner is chown.
As usual, you can see how to use chown in details by typing “man chown” in the terminal. With MC, you only need to select a file then press “F9” > File > Chown or press “Ctrl-x” and “o“. Now you can set owner and group owner from the available list of user name and group name.
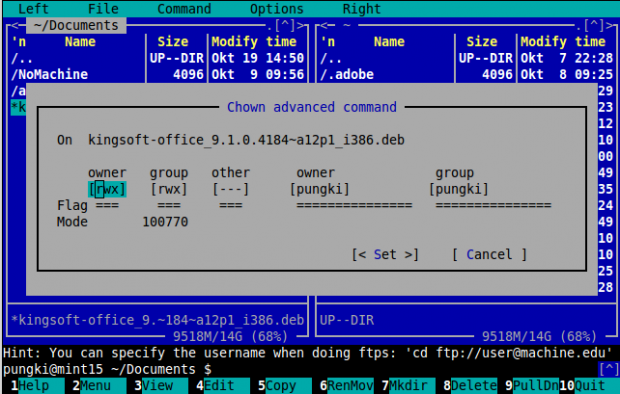
MC also has Advanced Chown. It’s a combination between chmod and chown. You can do 2 different tasks in 1 place. Press “F9” > File > Advanced Chown.
FTP Link
By default, MC will show you 2 column interfaces. Left and right. Those columns are not only for local directory. You can make one of them or both connected to remote computer using FTP link.
In this case, MC will act as a FTP Client. To connect it into FTP service, you need to press “F9” > FTP Link. MC will ask credential of the FTP. The credential format will be like this:
user:password@machine_or_ip_address
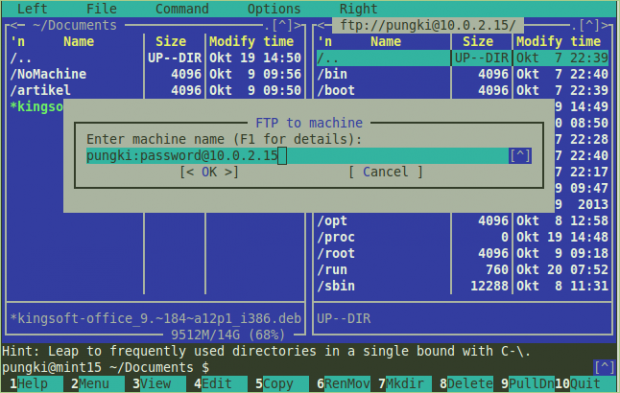
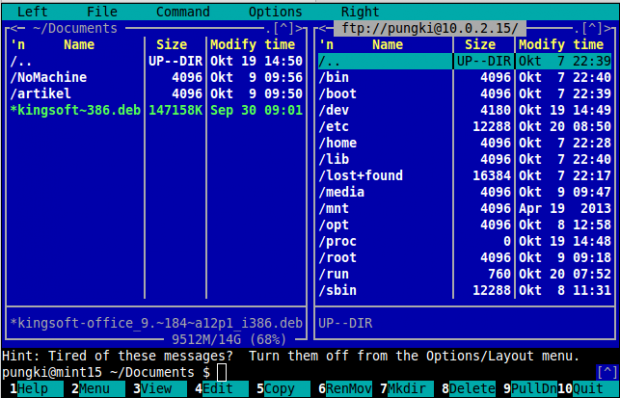
If it’s correct, then the column will show you directories on the remote computer.
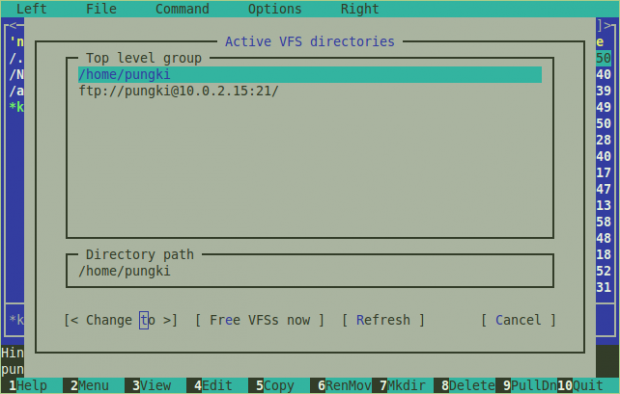
To disconnect your FTP link, you can press “F9” > Command > Active VPS Link. In the Active VFS directories list, you will see your FTP link. Choose your FTP link and press “Free VFSs” now. If you only want to switch to local folder without disconnecting the current FTP link, choose Change to.
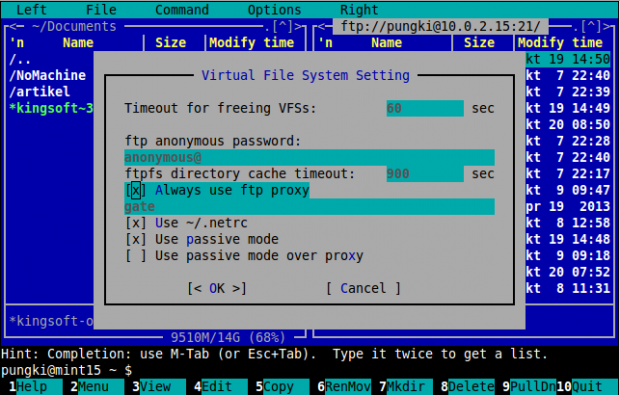
If your network using proxy server, you can configure MC to use FTP proxy. Press “F9” > Options > Virtual FS > Always use ftp proxy.
Leaving Midnight Commander
To leave Midnight Command, press “F9” > File > Exit. Or just press “F10” to quit. There are still a lot of features inside Midnight Commander.
For more details on MC features, please visit Midnight Commander FAQ at:

People interested in such file managers may also like (my) fman.io. It’s available on Linux but has a GUI. It features cool things like jumping to directories very quickly like Sublime Text’s Ctrl+P command, or a Command Palette. It also has a Python-based plugin API.
ctrl+o to switch back to command linx without exiting mc
great awesome tool
Great article! I’d love to see a detailed write-up like this for ranger.
I’m using centos 6, mc is a great awsome tool to manage anything.
In MC on a Linux Mint pc can I display the content of a shared directory from a windows pc in my network? For instance with smb:\\WindowsPC\Shareddocs?
Article worth recommending. After reading it, I often use the MC. Many have explained, which makes the tool is now more user-friendly.
Thank you very much if you found it useful.
Hi, I want to copy .thunderbird from /dev/sdb to /dev/sda is this possible in mc? Or do I have to manually do it somehow?
When I open mc I get the same drive on both sides of the mc window, if I could change one side to the second SSD, then it would be a simple task.
P.S. I am totally new to mc, and I can’t figure out how to get both drives up on the main window. Any help would be fantastic.
Thank you.
@Rodney,
Copy the data from your thunderbird data directory to the other disk or use ImportExportTools from Thunderbird Window to move profiles…
Thank you very much to you and all who answered.
I still have to work out how to do the things suggested, but given time I should break through and get it right.
Rodney Jackson.