The latest version of CentOS 7.5, a Linux platform based on sources of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.5, has been released in May this year with many bug fixes, new packages & upgrades, such as Microsoft Azure, Samba, Squid, libreoffice, SELinux, systemd and others and support for the 7th generation of Intel Core i3, i5, i7 processors.
It’s highly recommended to go through release notes as well as the upstream technical notes about the changes before an installation or up-gradation.
Download CentOS 7.5 DVD ISO’s
Upgrade CentOS 7.x to CentOS 7.5
CentOS Linux is developed to automatically upgrade to a new major version (CentOS 7.5) by running the following command that will upgrade your system seamlessly from any earlier CentOS 7.x release to 7.5.
# yum udpate
We strongly recommend you to perform a fresh installation rather than upgrading from other major CentOS versions.
In this article, we will show how to install a fresh CentOS 7.5 using the DVD ISO image with a graphical user interface (GUI) on a UEFI based machine.
In order to properly perform the installation of CentOS 7.5 on a UEFI based machine, first enter your motherboard UEFI settings by pressing a special key (F2, F11, F12 depending on motherboard specifications) and assure that QuickBoot/FastBoot and Secure Boot options are disabled.
CentOS 7.5 Installation
1. After you’ve downloaded the image from the above link, burn it to a DVD or create a bootable UEFI compatible USB drive using Rufus utility.
Place the USB/DVD in the appropriate motherboard drive, reboot your machine and instruct the BIOS/UEFI to boot-up from the DVD/USB by pressing a special function key (usually F12, F10 depending on the vendor specifications).
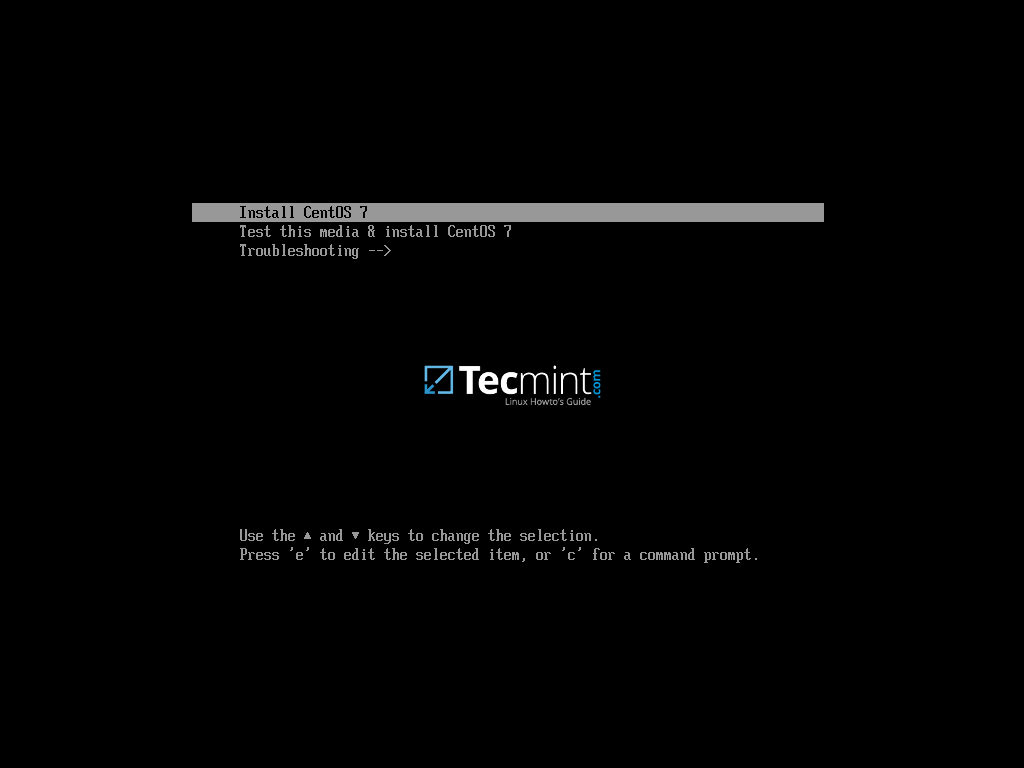
Once the ISO image boots-up, the first screen will appear on your machine output. From the menu select Install CentOS 7 and hit Enter to continue.
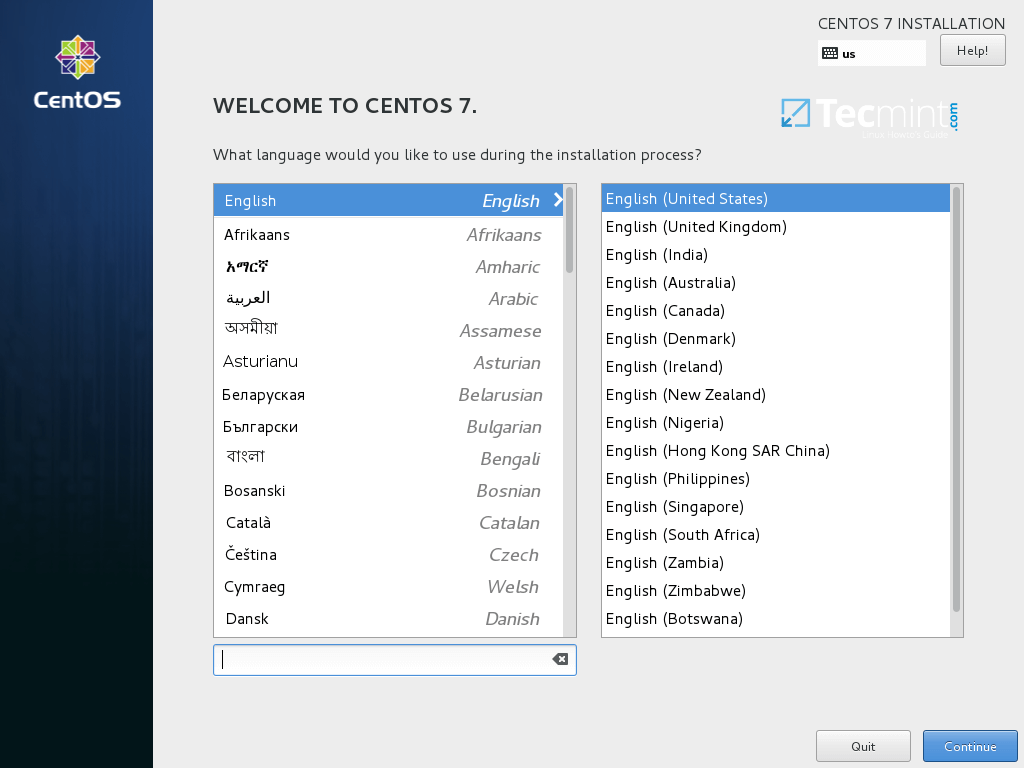
2. After the install ISO image has been loaded into your machine RAM, the welcome screen will appear. Choose the language you want to perform the installation process and press hit on Continue button.
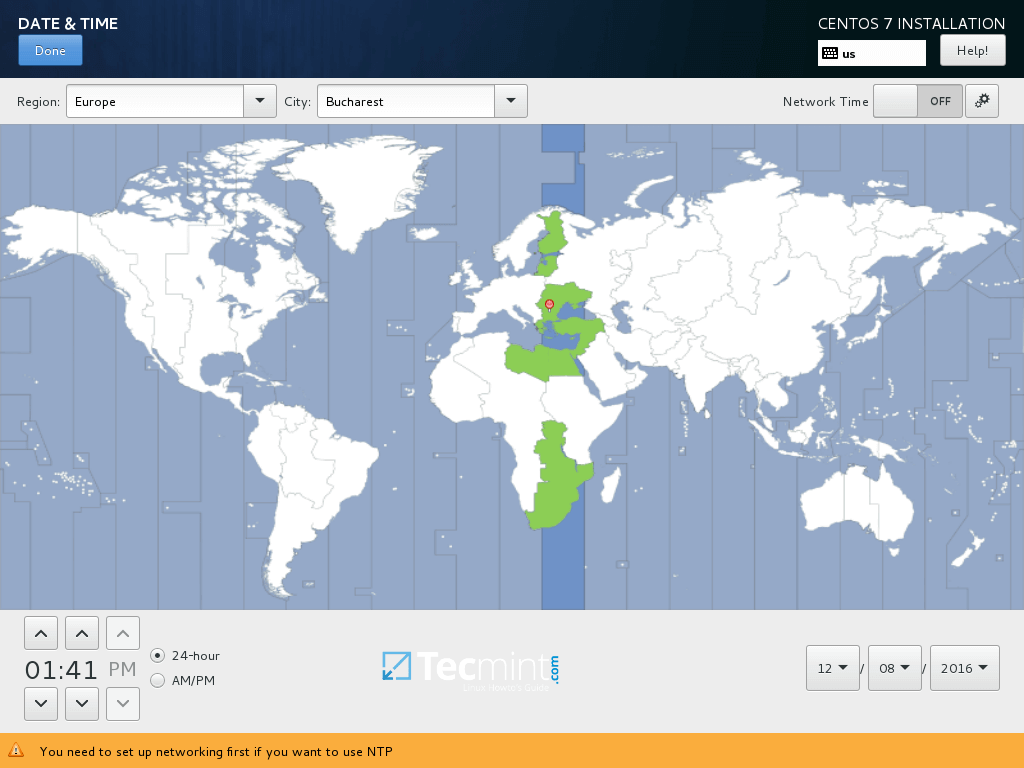
3. On the next screen hit on Date and Time and choose your geographical location from the map. Make sure the date and time are correctly configured and hit on Done button to go back to the main installer screen.
4. On the next step setup the keyboard layout by hitting on Keyboard menu. Choose or add a keyboard layout and hit on Done to continue.
5. Next, add or configure the language support for your system and hit Done to move to the new step.
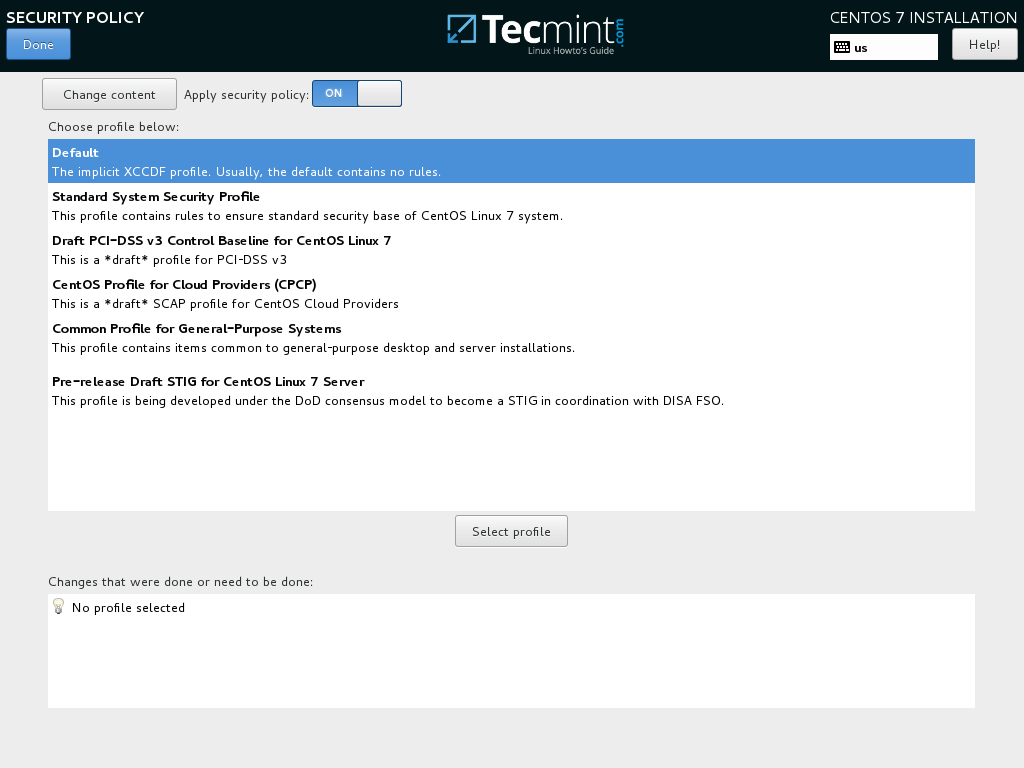
6. In this step you can setup your system Security Policy by choosing a security profile from the list.
Set the desired security profile by hitting on Select profile button and Apply security policy button to ON. When you finish click on Done button to continue with the installation process.
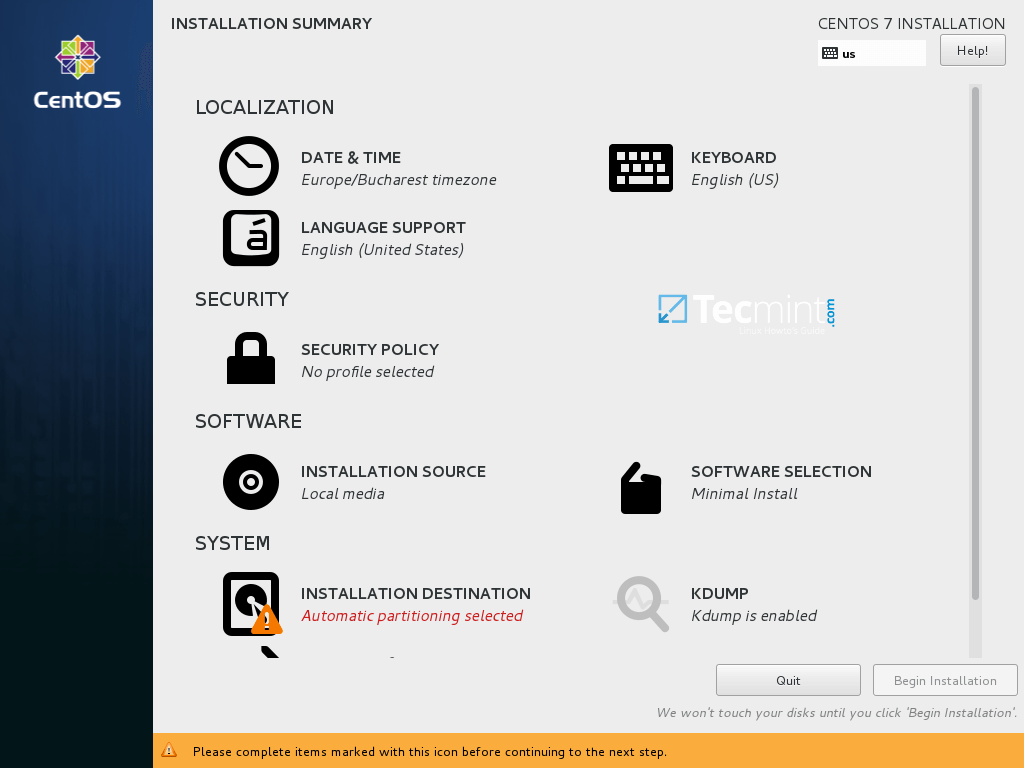
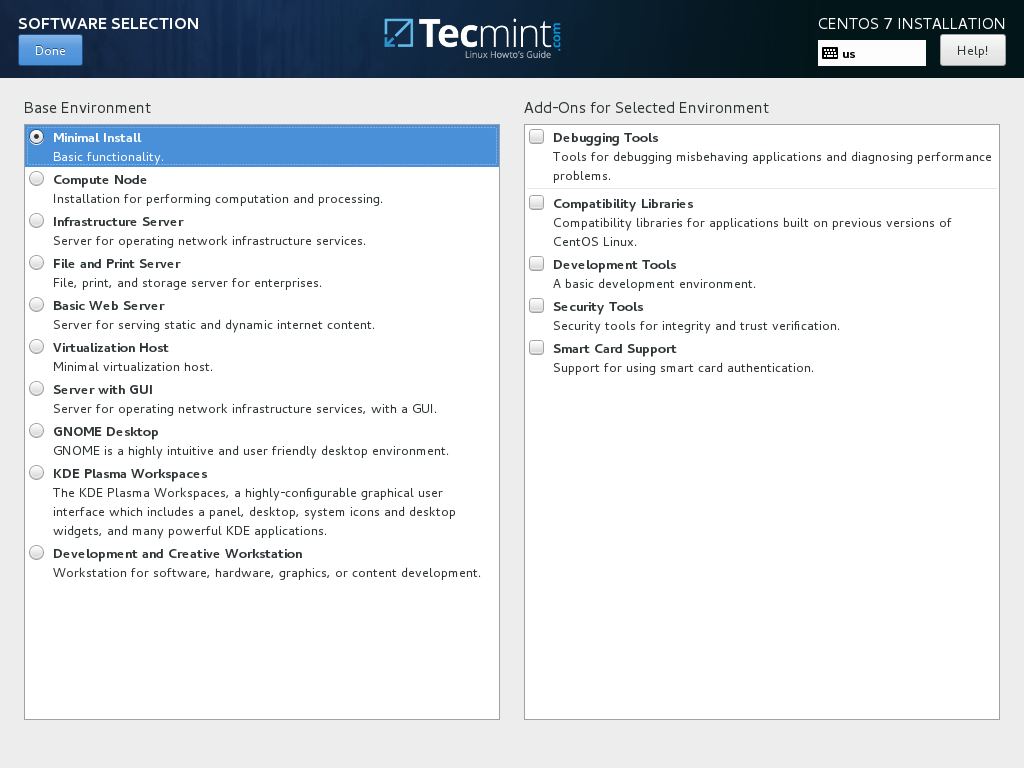
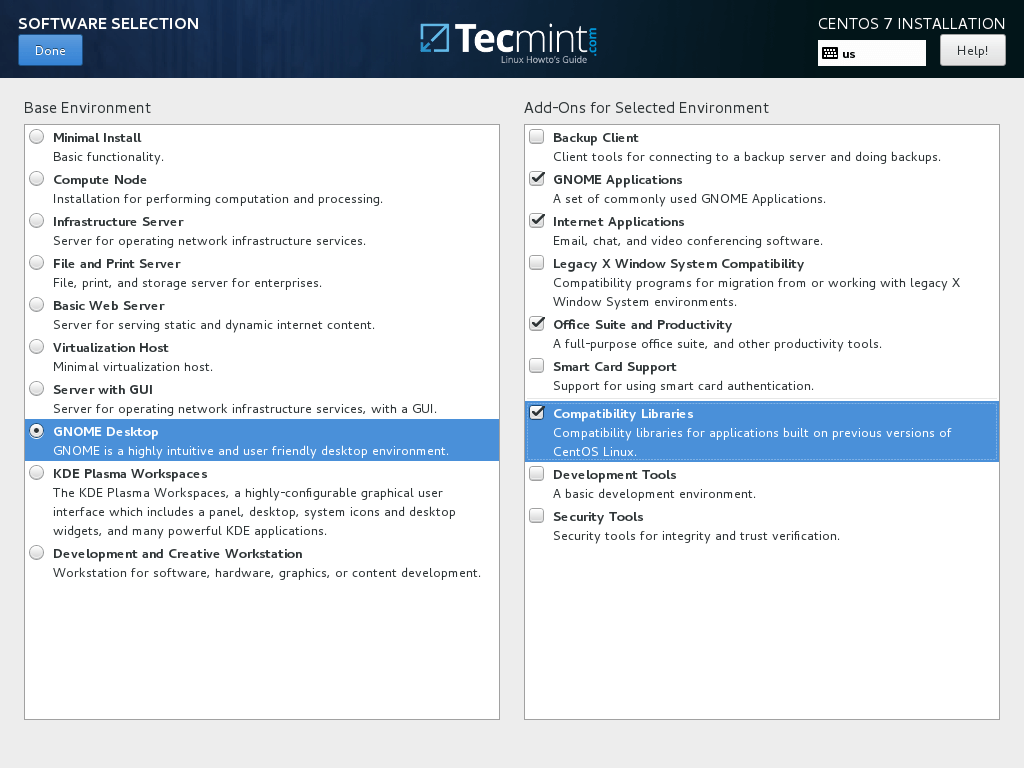
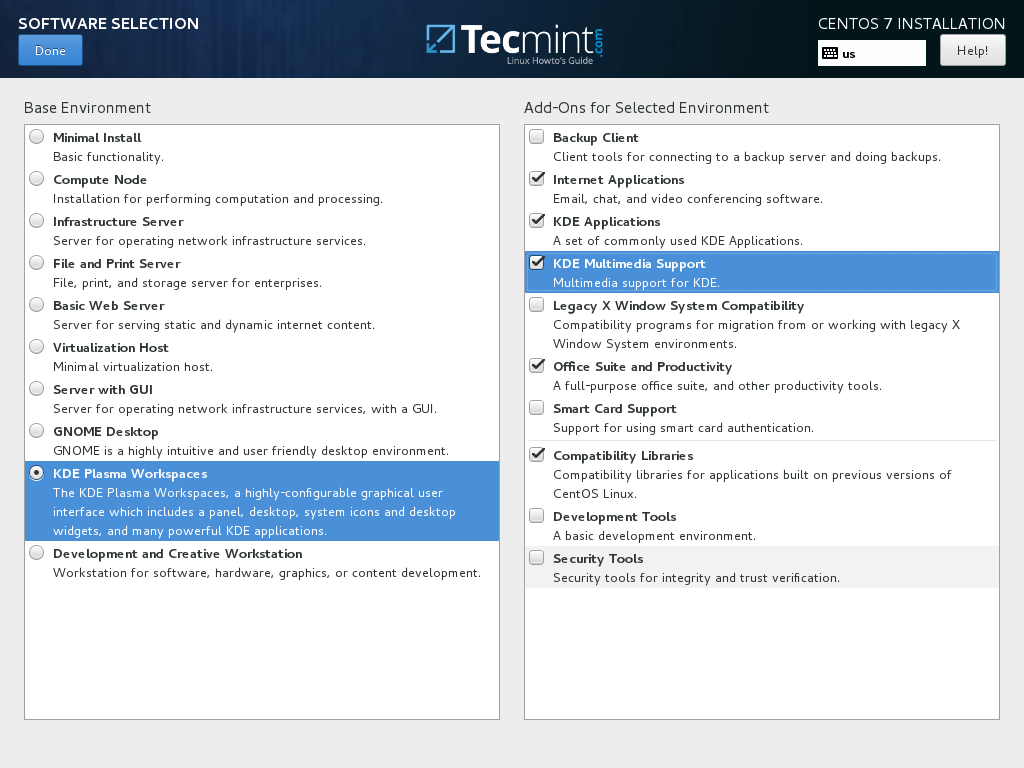
7. On the next step you can configure your base machine environment by hitting on Software Selection button.
From the left list you can opt to install a desktop environment (Gnome, KDE Plasma or Creative Workstation) or choose a server custom installation type (Web server, Compute Node, Virtualization host, Infrastructure server, Server with a graphical interface or File and Print Server) or perform a minimal installation.
In order to subsequently customize your system, select Minimal Install with Compatibility Libraries add-ons and hit on Done button to continue.
For a full Gnome or KDE Desktop environment use the below screenshots as a guide.
8. Assuming that you want to install a Graphical User Interface for your server, choose Server with GUI item from the left plane and check the proper Add-ons from the right plane depending on what kind of services the server will provide to your network clients.
The range of services you can choose from is diversified, from Backup, DNS or e-mail services to File and Storage services, FTP, HA or Monitoring tools. Choose only the services that are crucial for your network infrastructure.

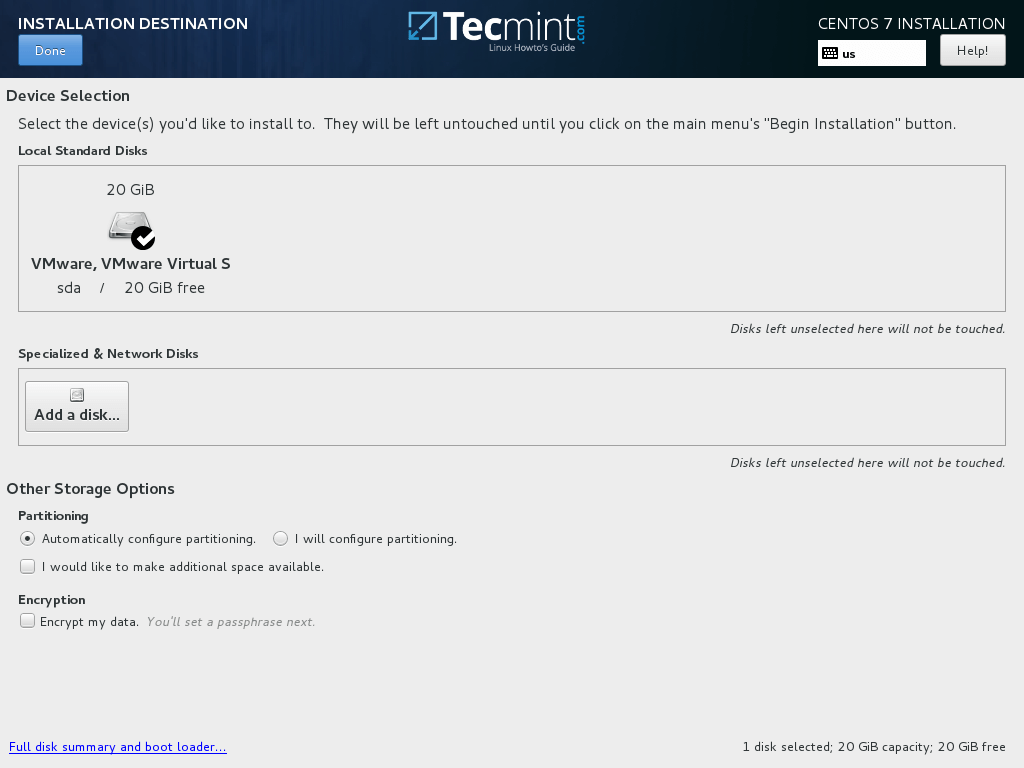
9. Leave the Installation Source as default in case you’re not using other specific network locations such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP or NFS protocols as additional repositories and hit on Installation Destination in order to create hard disk partitions.
On the Device selection screen make sure your local machine hard disk is checked. Also, on Other Storage Options assure that Automatically configure partitioning is selected.
This option ensures that your hard disk will be properly partitioned according to your disk size and Linux file system hierarchy. It will automatically create /(root), /home and swap partitions on your behalf. Hit on Done to apply the hard drive partition scheme and go back to the main installer screen.
Important: If you want to create custom layout with custom partition sizes, you can select “I will configure partitioning” option to create custom partitions.
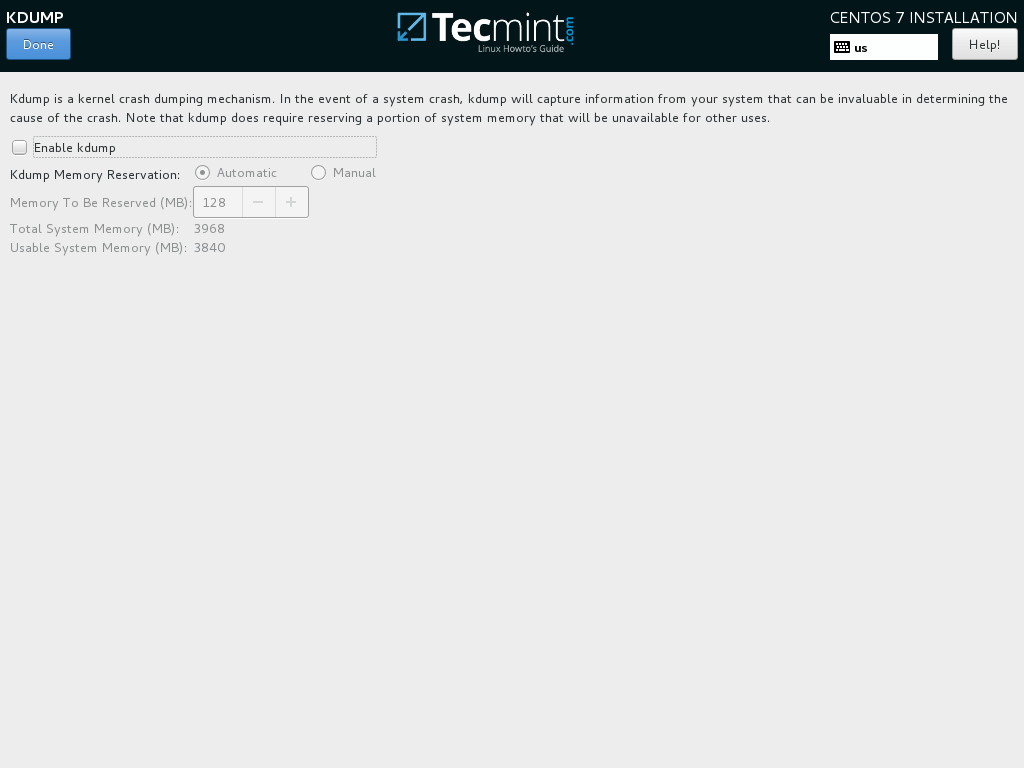
10. Next, hit on KDUMP option and disable it if you want to free RAM in your system. Hit Done to apply changes and go back to main installation screen.
11. In the next step set-up your machine hostname and enable network service. Hit on Network & Hostname, type your system Fully Qualified Domain Name on Host name and activate the network interface by switching the Ethernet button from OFF to ON in case you have a DHCP server in your LAN.
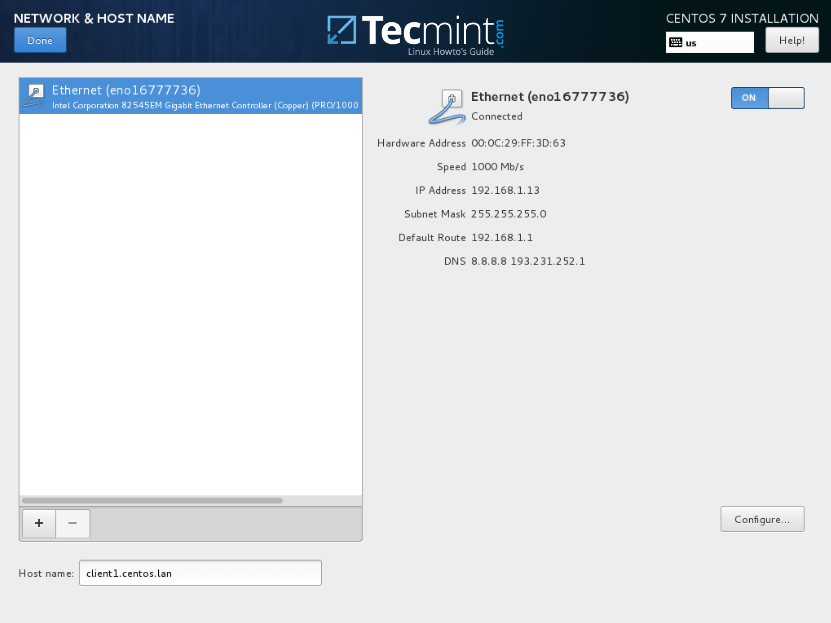
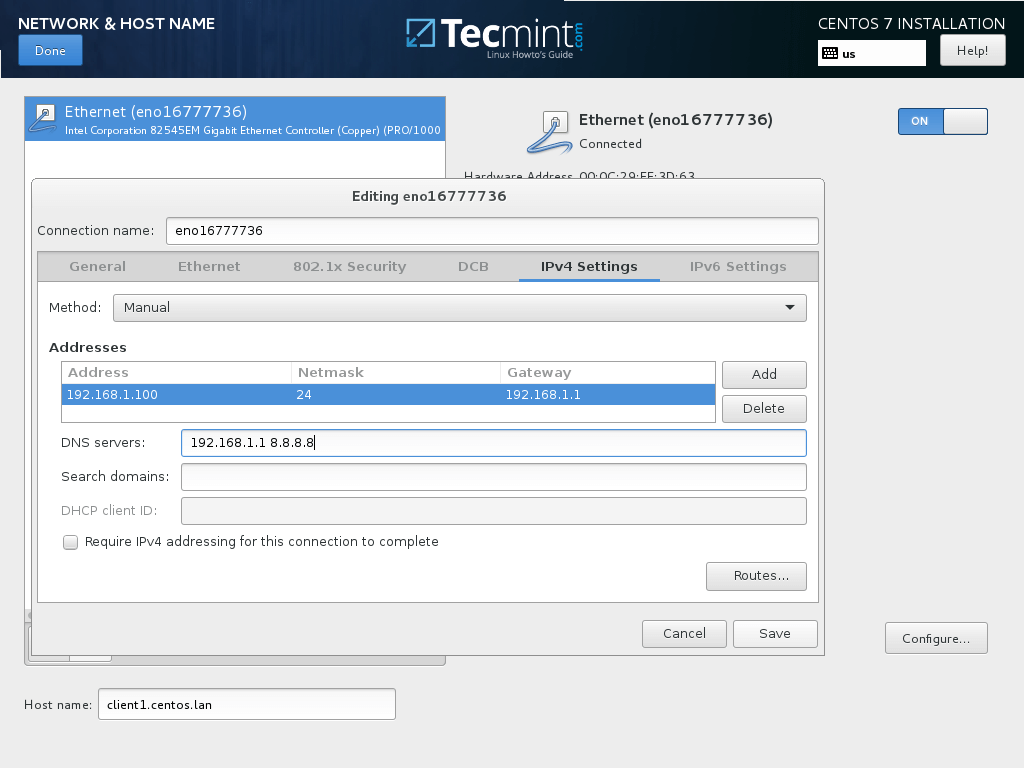
12. In order to statically configure your network interface hit on Configure button, manually add your IP settings as illustrated in the below screenshot and hit on Save button to apply changes. When you finish, hit on Done button to return to main installer menu.
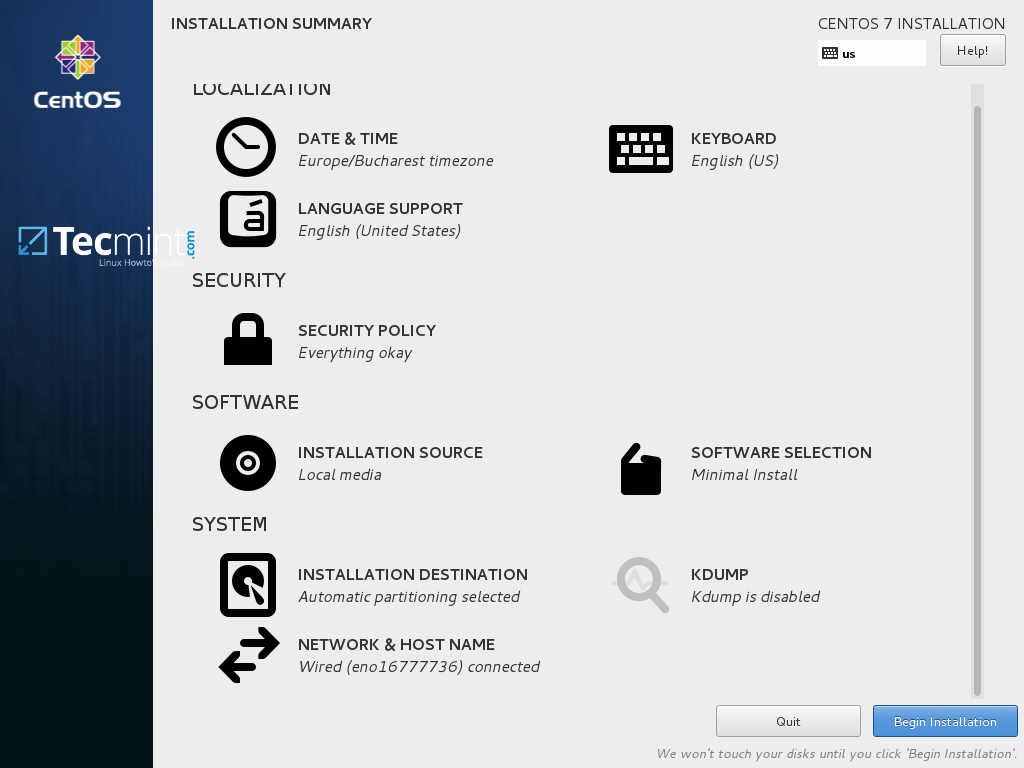
13. Finally, review all configurations so far and if everything seems in place, hit on Begin Installation button to start the installation process.
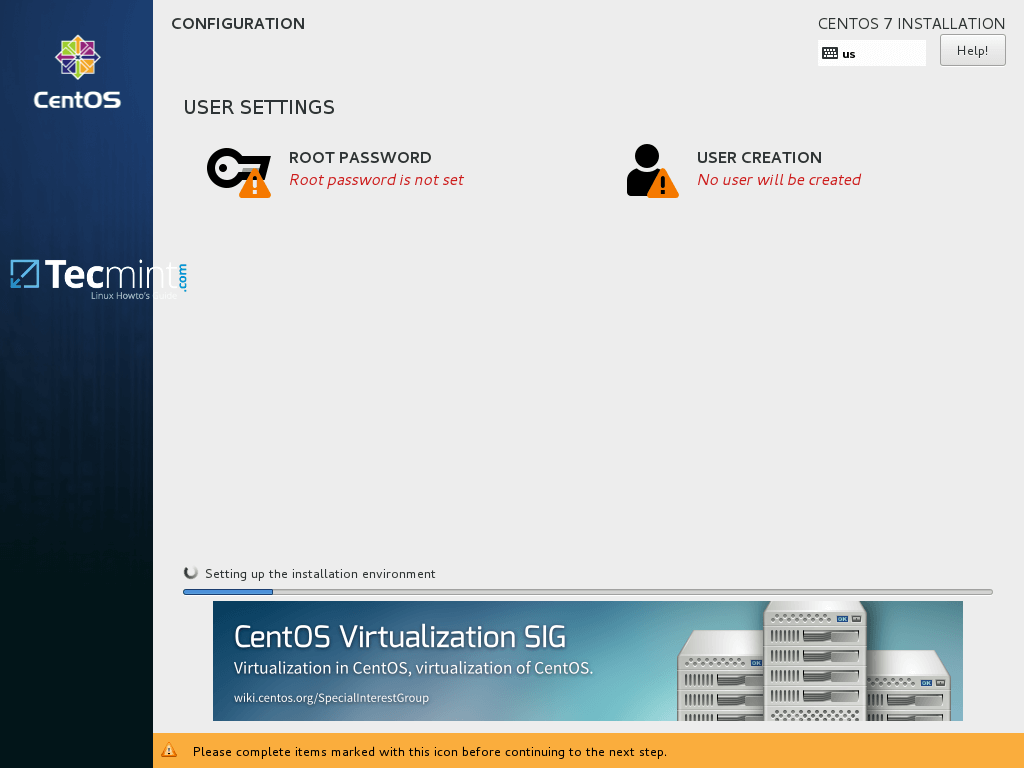
14. After the installation process starts, a new configuration screen for setting-up users will appear. First, hit on ROOT PASSWORD and add a strong password for root account.
The root account is the highest administrative account in every Linux system and has full privileges. After you finish hit on Done button to return to user settings screen.
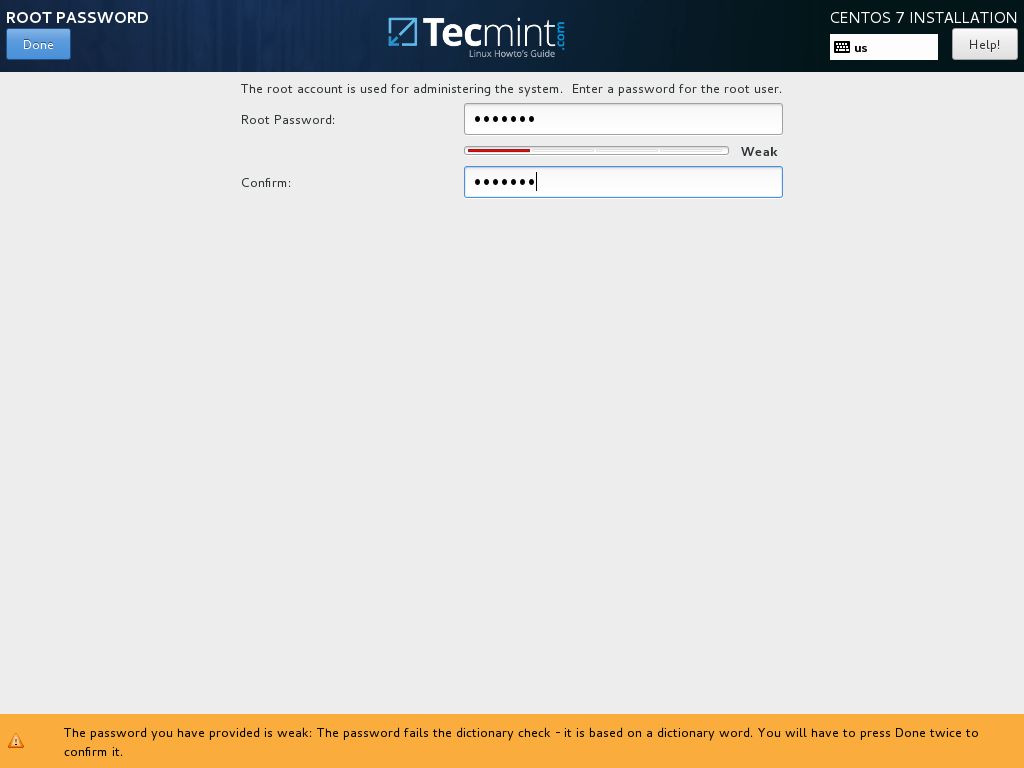
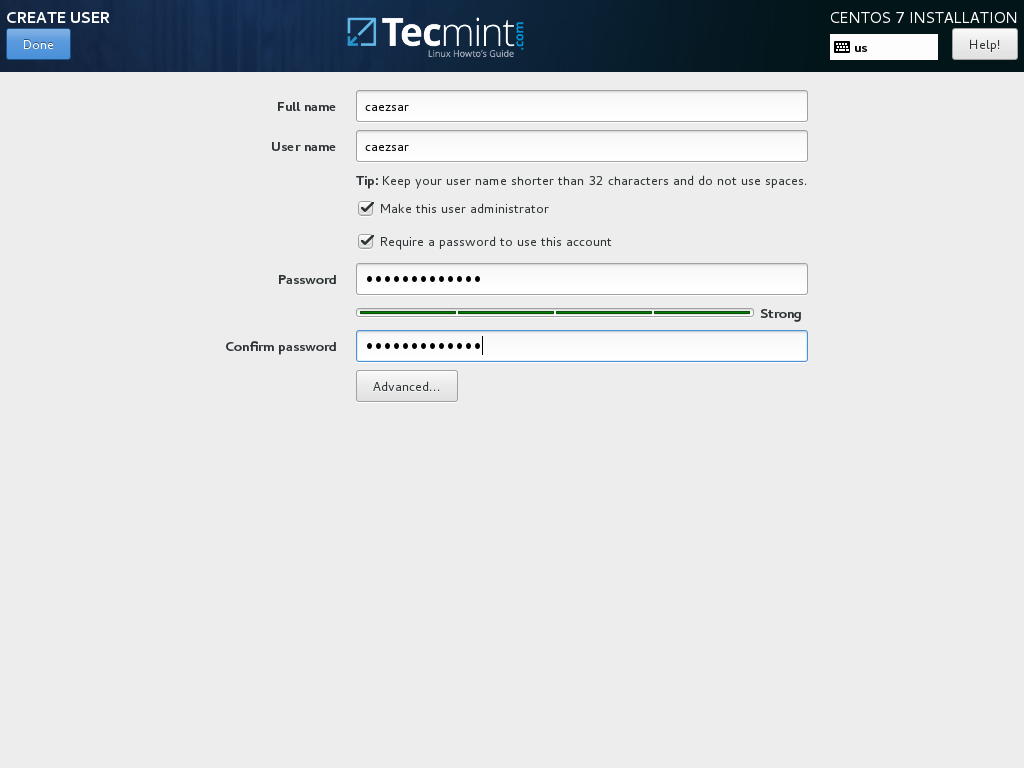
15. Running the system from root account is extremely unsecure and dangerous so it’s advisable to create a new system account in order to perform day-to-day system tasks by hitting on User Creation button.
Add your new user credentials and check both options in order to grant this user with root privileges and manually enter the password each time you log in to the system.
When you finish this last section hit on Done button and wait for the installation process to finish.
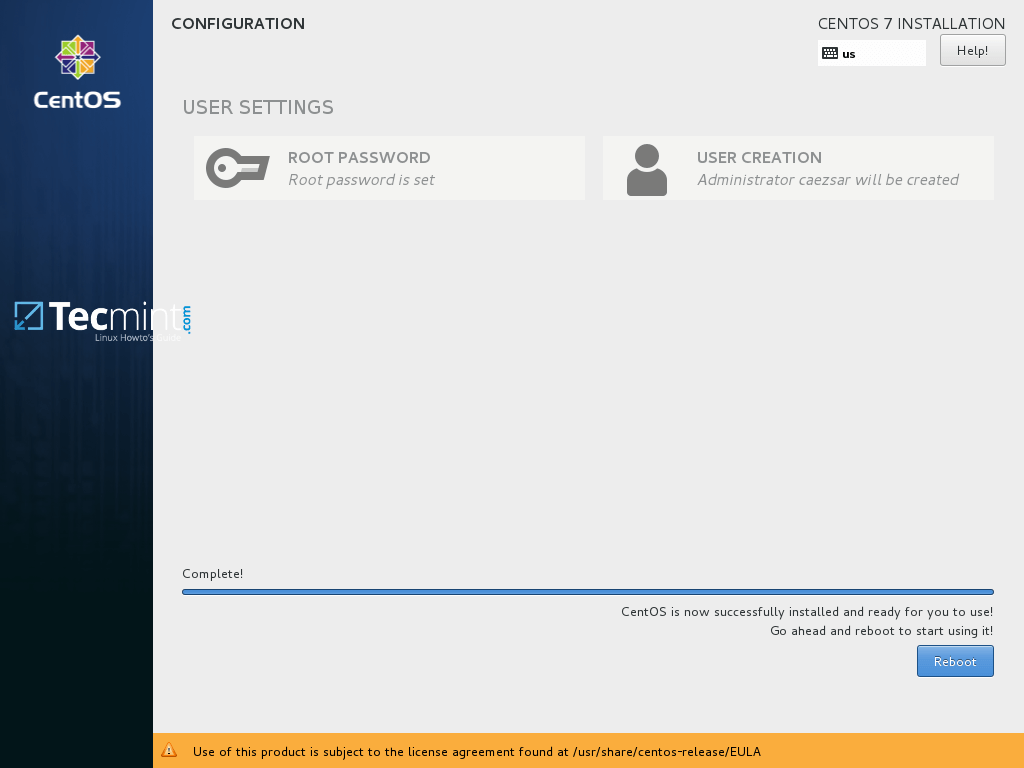
16. After a few minutes the installer will report that CentOS has been successfully installed on your machine. In order to use the system you just have to remove the installation media and reboot the machine.
17. After reboot, log in to the system using the credentials created during the installation process and make sure perform a full system update by issuing the below command with root privileges.
$ sudo yum update

Answer with yes to all questions asked by yum package manager and finally, reboot the machine again (use sudo init 6) in order to apply new kernel upgrade.
$ sudo init 6
That’s all! Enjoy the latest release of CentOS 7.5 on your machine.




How can we install the same using a bootable iso on a serial console?
Hello Matei,
I want to install a severe web in an HP ProLiant g8 microserver (4gb Ram, INTEL CELERON-G1610T, 2 HDD, 1Terra each). I will have around 5 domains and only one user (s) with ssh open only in the internal network. What options in the centos installation list do you recommend? Thank you.
Perform a minimal installation for security reasons.
After the minimal installation centos 7.0 using proxmox virtual machine.,qemu..What are the important packages that needed to installed..Can YOU PLEASE TELL THE STEP BY STEP PROCEDURE TO BE DONE NEXT
@Roshna,
After minimal CentOS 7 installation, you can go through the following article and do things which are needed as per your requirements..
30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL/CentOS 7 Installation
Thank You so much, It was very helpful. Is there any other article which gives detailed information about Linux commands, packages and repository?..
@Roshna,
Thanks for finding those CentOS articles useful, yes there are many articles on Linux commands, security, etc. Just use our search form to search for articles at TecMint.com.
There are no important packages you need to install…it all depends on how and for what you need to use that machine, what services you what to advertise to network, for what purposes…and the list goes on. There are no standards,.it all depends on you.
Using it as a test server to gain knowledge about the packages and the repositories. Even to check certain commands..
I just wanted to say something, if you are running centos 7.2 like I was and you want to go to centos 7.3 you don’t need to do a clean install or upgrade. I did a “yum update” and in about 15 or so minutes it finished downloading and installing about 210 packages (this is a server box) and then I just rebooted the box and I was up and running in no time.
the download link is incorrect, it leads you to version 1511 (which is 7.2) version 7.3 is 1611.
this is the correct link:
http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1611.iso
@Gadi,
Sorry for that incorrect link, yes the latest CentOS 7.3 actual build is 1611.. Thanks for updating us, we’ve corrected the link in the article to point CentOS 7.3 download mirrors..