Red Hat has announced the release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.0, which comes with GNOME 3.28 as the default desktop environment and runs on Wayland.
This article describes instructions on how to upgrade from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 using the Leapp utility.
If you’re looking for a fresh RHEL 8 installation, head over to our article: Installation of RHEL 8 with Screenshots
Requirements
An in-place upgrade to RHEL 8 is presently supported only on systems meeting the following requirements:
- RHEL 7.6 installed
- The Server variant
- The Intel 64 architecture
- At least 100MB of free space available on the boot partition (mounted at /boot).
Preparing an RHEL 7 For The Upgrade
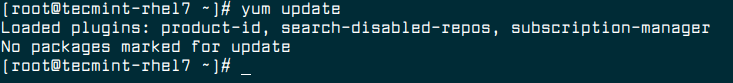
1. Make sure you are using RHEL 7.6 version, if you’re using RHEL version older than RHEL 7.6, you need to update your RHEL system to RHEL 7.6 version using following yum command.
# yum update
Note: Make sure your RHEL 7 system has been successfully registered using the Red Hat Subscription Manager to enable system repositories and perform a full system update.
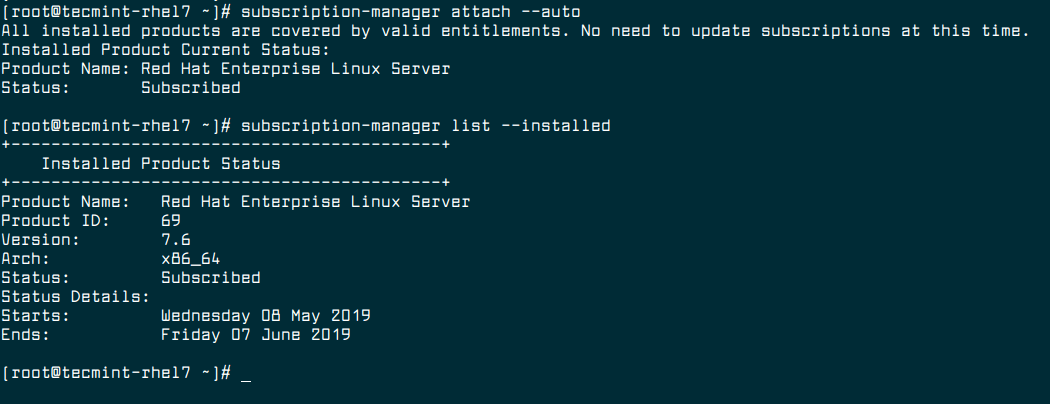
2. Make sure your RHEL 7 system has the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server subscription attached. If not, run the following commands to automatically assign the subscription to the system and verify the subscription.
# subscription-manager attach --auto # subscription-manager list --installed
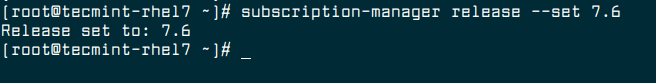
3. Now set the RHEL 7.6 version as a beginning point for the upgrade using the following command.
# subscription-manager release --set 7.6
4. If you have used yum-plugin-versionlock plug-in to lock packages to a specific version, make sure to remove the lock by running the following command.
# yum versionlock clear
5. Update all software packages to the latest version and reboot the system.
# yum update # reboot
6. Once system booted, make sure to enable the Extras repository for software package dependencies.
# subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-extras-rpms

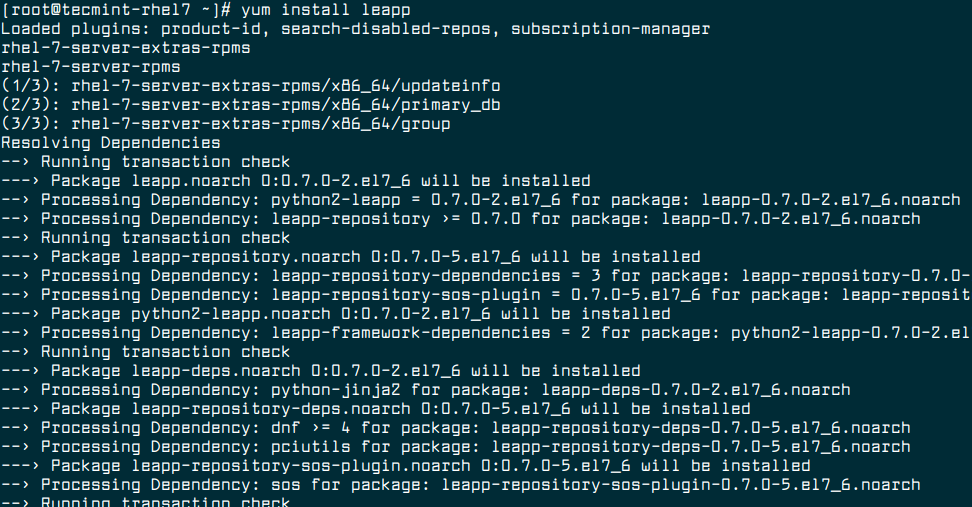
7. Install the Leapp utility.
# yum install leapp
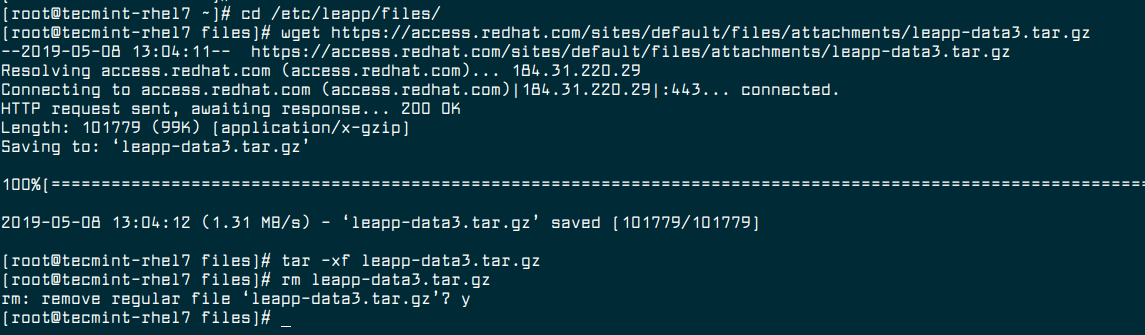
8. Now download additional required data files, which is required by the Leapp utility for a successful upgrade from RHEL 7 to RHEL 8 and place them in the /etc/leapp/files/ directory.
# cd /etc/leapp/files/ # wget https://access.redhat.com/sites/default/files/attachments/leapp-data3.tar.gz # tar -xf leapp-data3.tar.gz # rm leapp-data3.tar.gz
9. Make sure to take a full RHEL 7.6 system backup, before performing the upgrade using this article: backup and restore RHEL system with the dump/restore commands.
If the upgrade fails, you should able to get your system to the pre-upgrade state if you follow the standard backup instructions provides in the above article.
Upgrading from RHEL 7 TO RHEL 8
10. Now start the RHEL 7 system upgrade process using the following command.
# leapp upgrade
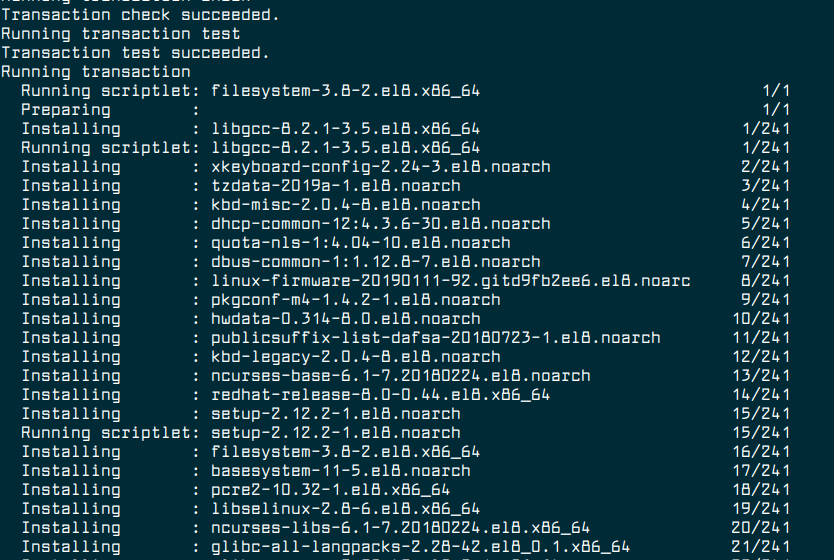
Once you run the upgrade process, the Leapp utility gathers data about your system, tests the upgradability, and creates a pre-upgrade report in the /var/log/leapp/leapp-report.txt file.
If the system is upgradable, Leapp downloads required data and create an RPM transaction for the upgrade.
If the system is not upgradeable, Leapp closes the upgrade operation and creates a record explaining the issue and a solution in the /var/log/leapp/leapp-report.txt file.
11. Once upgrades finish, manually reboot the system.
# reboot
At this stage, the system boots into an RHEL 8-based initial RAM disk image, initramfs. Leapp upgrades all software packages and automatically reboots to the RHEL 8 system.
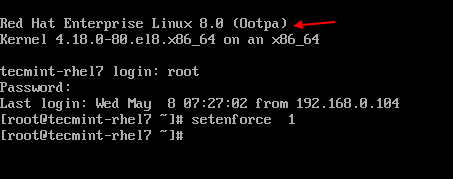
12. Now Log in to the RHEL 8 system and change the SELinux mode to enforcing.
# setenforce 1
13. Enable the firewall.
# systemctl start firewalld # systemctl enable firewalld
For more information, see how to configure firewall using firewalld.
Verifying RHEL 8 Upgrade
14. After the upgrade completes, verify that the current OS version is Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
# cat /etc/redhat-release Red Hat Enterprise Linux release 8.0 (Ootpa)
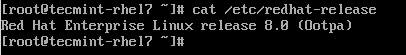
15. Check the OS kernel version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
# uname -r 4.18.0-80.el8.x86_64
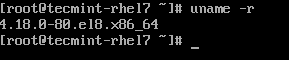
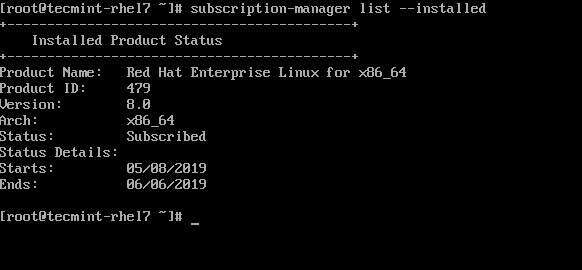
16. Verify that the correct Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 is installed.
# subscription-manager list --installed
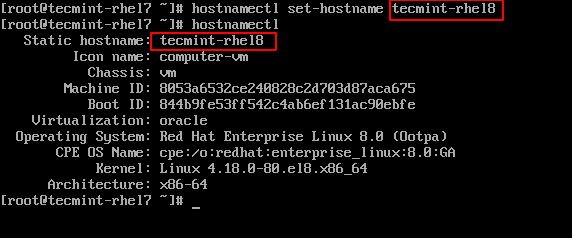
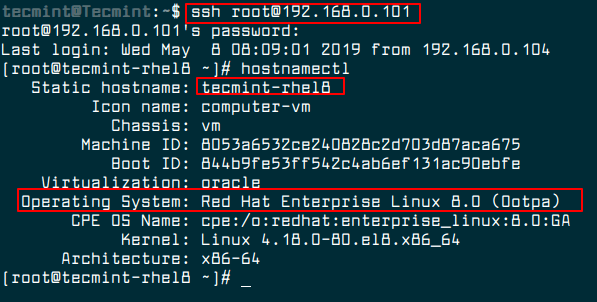
17. Optionally, set the hostname in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 using hostnamectl command.
# hostnamectl set-hostname tecmint-rhel8 # hostnamectl
18. Finally, verify that network services are functional by connecting to a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 server using SSH.
# ssh [email protected] # hostnamectl

A lot of big companies feel the Leapp tool has too many shortcomings to be practical for the migration to 8. We created Project78, a tool to address those issues and enable swift and practical in-place upgrades.
Aside from automatically addressing hundreds of ‘inhibitors’, and filesystems, and working around leapp bugs, third-party application migrations are performed.
We just launched for this the Project78 website:
https://www.project78.comWhich also includes a Cloud version, to preview our technology without needing to install the upgrade server.
Is it possible to migrate using trail subscription to migrate rhel 7.6 to 8?
Hello,
Great article and it give me an idea of how to proceed.
Also, can you make the same article but for Oracle Linux?
Thank you.
@Lee
Check this article – How to Migrate from CentOS to Oracle Linux