The apt-get command was the primary package management command used in Debian-based Linux distributions prior to the introduction of the apt command.
With the apt-get command, you could install, remove, upgrade, search, and manage packages on your system. However, starting from Ubuntu 16.04 and Debian 9, the apt command became the recommended command-line tool for package management, although apt-get is still available and functional.
What is apt-get Command?
The apt-get command is a powerful and free package management command line program, that is used to work with Ubuntu’s APT (Advanced Packaging Tool) library to perform the installation of new software packages, removing existing software packages, upgrading of existing software packages, and even used to upgrading the entire operating system.
The syntax for the apt-get command is as follows:
$ sudo apt-get <options> <command>
Here, <options> represent any additional flags or modifiers you can use with the command, and <command> specifies the action you want to perform, such as installing, upgrading, removing, or searching for packages.
1. Update Ubuntu System Packages
The ‘update‘ command is used to resynchronize the package index files from the sources specified in /etc/apt/sources.list file. The update command fetched the packages from their locations and update the packages to newer versions.
$ sudo apt-get update
2. Upgrade Ubuntu System Packages
The ‘upgrade‘ command is used to upgrade all the currently installed software packages on the system. Under any circumstances currently installed packages are not removed or packages that are not already installed neither retrieved nor installed to satisfy upgrade dependencies.
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
3. Install Package in Ubuntu
The ‘install‘ sub command is tracked by one or more packages wishing for installation or upgrading from the repositories. For example, to install or update the package named wget, you can run:
$ sudo apt-get install wget
Alternatively, you can also use the apt-cache command to search for a package before installing in the system package cache based on a given search term such as name or description.
4. Install Multiple Packages in Ubuntu
You can add more than one package name along with the command in order to install multiple packages at the same time. For example, the following command will install packages ‘nethogs‘ and ‘goaccess‘.
$ sudo apt-get install nethogs goaccess
5. Install Several Packages Using Wildcard
With the help of regular expression, you can add several packages with one string. For example, we use * wildcard to install several packages that contain the ‘*name*‘ string, the name would be ‘package-name‘.
$ sudo apt-get install '*name*'
6. Install Package Without Upgrading
Using sub ‘--no-upgrade‘ command will prevent already installed packages from upgrading.
$ sudo apt-get install packageName --no-upgrade
7. Update a Single Package
The ‘--only-upgrade‘ command does not install new packages but it only upgrades the already installed packages and disables new installation of packages.
$ sudo apt-get install packageName --only-upgrade
8. Install Specific Package Version on Ubuntu
Let’s say you wish to install only specific versions of packages, simply use the ‘=‘ with the package name and append desired version.
$ sudo apt-get install vsftpd=3.0.5-0ubuntu1
9. Uninstall Package Without Configuration
To uninstall software packages without removing their configuration files (for later re-use of the same configuration), use the remove command as shown.
$ sudo apt-get remove vsftpd
10. Completely Remove Package with Configuration
To remove software packages including their configuration files, use the ‘purge‘ sub-command as shown below.
$ sudo apt-get purge vsftpd
Alternatively, you can combine both commands together as shown below.
$ sudo apt-get remove --purge vsftpd
11. Clear Apt Cache to Save Disk Space
The ‘clean‘ command is used to free up the disk space by cleaning retrieved (downloaded) .deb files (packages) from the local repository.
$ sudo apt-get clean OR $ sudo apt-get autoclean
12. Download Source Code of a Package in Ubuntu
To download only the source code of a particular package, use the option ‘--download-only source‘ with ‘package-name‘ as shown.
$ sudo apt-get --download-only source vsftpd
13. Download and Extract Source Package in Ubuntu
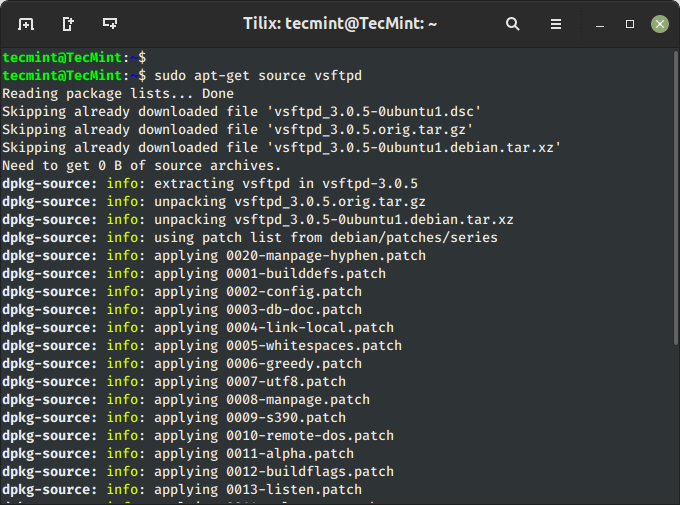
To download and unpack the source code of a package to a specific directory, type the following command.
$ sudo apt-get source vsftpd
You may encounter one common error “E: You must put some ‘deb-src’ URIs in your sources.list” when attempting to download the source code of a package from the repositories.
14. Compile Ubuntu Package from Source
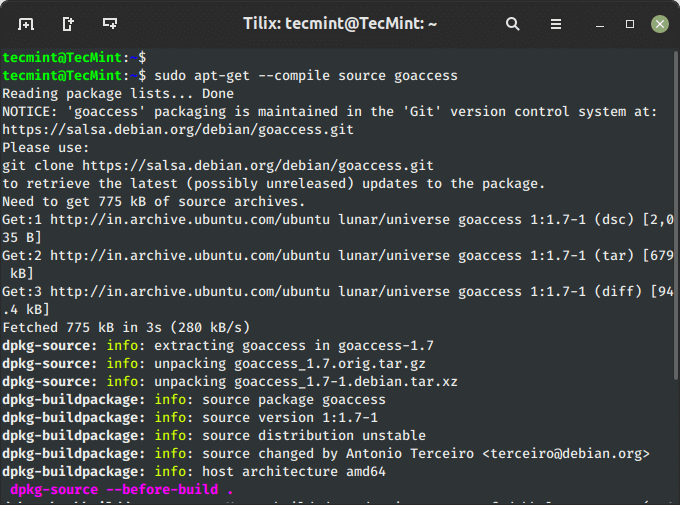
You can also download, unpack and compile the source code at the same time, using the option ‘--compile‘ as shown below.
$ sudo apt-get --compile source goaccess
15. Download Package Without Installing
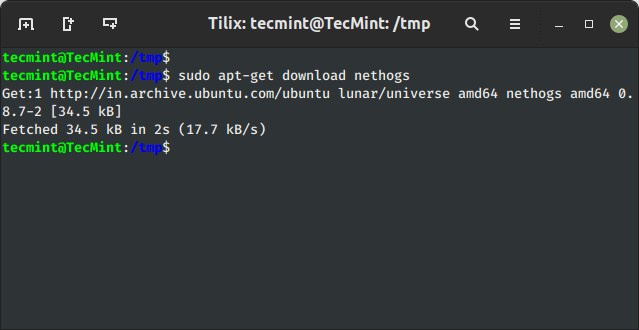
Using the ‘download‘ option, you can download any given package without installing it. For example, the following command will only download the ‘nethogs‘ package to the current working directory.
$ sudo apt-get download nethogs
16. View Package Changelog in Ubuntu
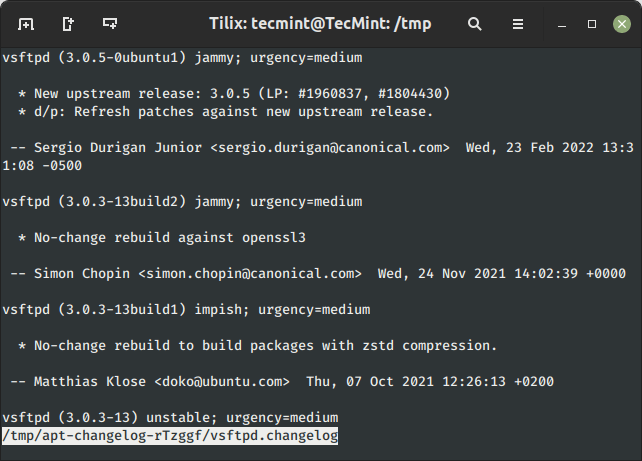
The ‘changelog‘ flag downloads a package change-log and shows the package version that is installed.
$ sudo apt-get changelog vsftpd
17. View Broken Dependencies in Ubuntu
The ‘check‘ command is a diagnostic tool, which is used to update the package cache and check for broken dependencies.
$ sudo apt-get check
18. Install Build Dependencies of Package
The ‘build-dep‘ command searches the local repositories in the system and installs the build dependencies for the curl package. If the package does not exist in the local repository it will return an error code.
$ sudo apt-get build-dep curl
19. Auto Remove Installed Packages
The ‘autoremove‘ sub-command is used to auto-remove packages that were certainly installed to satisfy dependencies for other packages but were now no longer required. For example, the following command will remove an installed package with its dependencies.
$ sudo apt-get autoremove vsftpd
20. apt-get Command Help
The apt-get help command displays the built-in help documentation with the available options to use with the apt-get command.
$ sudo apt-get help
I’ve covered most of the available options with the apt-get command, but still, there are more options available, you can check them out using ‘man apt-get‘ from the terminal.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article, If I’ve missed anything and you would like me to add to the list. Please feel free to mention this in the comment below.
Read Also : 20 Useful Linux YUM Commands for Package Management




I installed a package by compiling it and using checkinstall. The package name is different from the Ubuntu packages. It is actually an all-in-one package.
Other packages depend on those other named packages. I want to set those packages as being installed, but not actually install any files.
(They are already there) So I am wondering if there is a way to just change the package database to say that a given package is installed.
What’s the command for getting apt-utils it is telling me that I need to install it can someone please help me?
@Heather,
You can install apt-utils on your Debian system using the following command.
How can I see the installed package in my system?
@Rahul,
Run the following command to list all installed packages on the Ubuntu system
this is my “daily” check and upgrade command:
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade && sudo apt-get full-upgrade && sudo apt-get check && sudo apt-get -f install && sudo apt-get -y clean && sudo apt-get -y autoclean && sudo apt-get autoremove && sudo dpkg --configure -a && sudo apt --fix-broken install
Try these commands to update and fix Ubuntu…
$ sudo apt update$ sudo apt upgrade
$ sudo apt full-upgrade
$ sudo apt dist-upgrade
$ sudo apt-get check
$ sudo apt -f install
$ sudo apt -y clean
$ sudo apt -y autoclean
$ sudo apt autoremove
$ sudo dpkg --configure -a
$ sudo apt --fix-broken install --fix-missing
Can you share some information about apt-cache implementation? I couldn’t find anywhere.
How the cache is created, refreshed (is it periodic, once a day or manual). As far as I read, the cache is refreshed manually.
Assuming there is one package that has the new version, how does apt-cache updates its cache? Does the apt-cache send the current cache information ( like the list of pkg names and it’s version) to server then the server sends what has changed?
Hi, How can i search through installed applications ? In particular I want to search with a keyword in both package name and description for installed package?
apt-cache search --installedkeyword does not work.@Sansu,
You can use the following command to search for a particular packages, for example apache in this case.
Sorry if I was not clear. I specifically need to look into list of packages that are installed in my system.
will list all the packages available but i need only those which are installed in my system.
Instead of using the CLI tool ‘apt-cache’. use the GUI tool, Synaptic. When you search for ‘apache’, Synaptic will display on one screen all packages with ‘apache’ in the name or the description, and whether they are installed or not.
I work in many places offline (no Internet access). I had to use apt clean to fix a bad installation issue, and don’t know how to download again all the
.debfiles again, which I used in my installation, since I usually need to reinstall packages that I need from offline places.So how do I re-download all
.debfiles that were installed on my system (official and ppa repositories) ?If there a apt-cache –only-download “all-installed” type of command ?
I am still using trusty 14.04.5 (64 bits) here.
@John,
This following command will download all installed packages to directory /var/cache/apt/archives.
$ sudo dpkg -l | grep "^ii"| awk ' {print $2} ' | xargs sudo apt-get -y install --reinstall --download-only