Nodejs is a free open source, lightweight, scalable and efficient JavaScript framework built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine, and uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. Nodejs is now everywhere, and has become so popular for developing software from websites, web apps to network apps and more.
Nginx is an open source, high-performance HTTP server, load balancer and reverse proxy software. It has a straightforward configuration language making it easy to configure. In this article, we will show how to configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for Nodejs applications.
Read Also: The Ultimate Guide to Secure, Harden and Improve Performance of Nginx Web Server
Note: If your system already running with Nodejs and NPM, and have your app running on a certain port, go straight to Step 4.
Step 1: Installing Nodejs and NPM in Linux
The latest version of Node.js and NPM is available to install from the official NodeSource Enterprise Linux, Fedora, Debian and Ubuntu binary distributions repository, which is maintained by the Nodejs website and you will need to add it to your system to be able to install the latest Nodejs and NPM packages as shown.
On Debian/Ubuntu
---------- Install Node.js v11.x ---------- $ curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_11.x | sudo -E bash - $ sudo apt-get install -y nodejs ---------- Install Node.js v10.x ---------- $ curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_10.x | sudo -E bash - $ sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
On CentOS/RHEL and Fedora
---------- Install Node.js v11.x ---------- $ curl -sL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_11.x | bash - ---------- Install Node.js v10.x ---------- $ curl -sL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_10.x | bash -
Step 2: Creating a Nodejs Application
For demonstration purpose, we will be creating a sample application called “sysmon”, which will run on port 5000 as shown.
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/sysmon $ sudo vim /var/www/html/sysmon/server.js
Copy and paste the following code in the server.js file (replace 192.168.43.31 with your server IP).
const http = require('http');
const hostname = '192.168.43.31';
const port = 5000;
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.statusCode = 200;
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.end('Sysmon App is Up and Running!\n');
});
server.listen(port, hostname, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`);
});
Save the file and exit.
Now start your node application using the following command (press Ctrl+x to terminate it).
$ sudo node /var/www/html/sysmon/server.js OR $ sudo node /var/www/html/sysmon/server.js & #start it in the background to free up your terminal
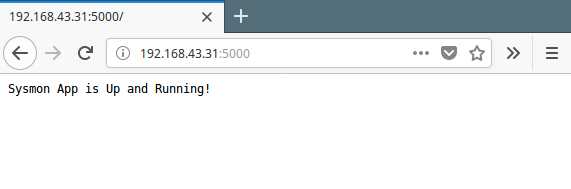
Now open a browser and access your application at the URL http://198.168.43.31:5000.
Step 3: Install Nginx Reverse Proxy in Linux
We will install the latest version of Nginx from the official repository, as shown below.
On Debian/Ubuntu
Create a file called /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list and add the following lines to it.
deb http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ bionic nginx deb-src http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ bionic nginx
Next, add the repository signing key, update your system package index and install the nginx package as follows.
$ wget --quiet http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key && sudo apt-key add nginx_signing.key $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install nginx
On CentOS/RHEL and Fedora
Create a file named /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo and paste one of the configurations below.
CentOS
[nginx]
name=nginx repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
RHEL
[nginx]
name=nginx repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/rhel/$releasever/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
Note: Due to differences between how CentOS and RHEL, it is necessary to replace $releasever with either 6 (for 6.x) or 7 (for 7.x), depending upon your OS version.
Next, add the repository signing key and install the nginx package as shown.
# wget --quiet http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key && rpm --import nginx_signing.key # yum install nginx
After successfully installing Nginx, start it, enable it to auto-start at system boot and check if it is up and running.
---------- On Debian/Ubuntu ---------- $ sudo systemctl status nginx $ sudo systemctl enable nginx $ sudo systemctl status nginx ---------- On CentOS/RHEL ---------- # systemctl status nginx # systemctl enable nginx # systemctl status nginx
If you are running a system firewall, you need to open port 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS) and 5000 (Node app), which the web server listens on for client connection requests.
---------- On Debian/Ubuntu ---------- $ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp $ sudo ufw allow 443/tcp $ sudo ufw allow 5000/tcp $ sudo ufw reload ---------- On CentOS/RHEL ---------- # firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp # firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcp # firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5000/tcp # firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4: Configure Nginx as Reverse Proxy For Nodejs Application
Now create a server block configuration file for your Node app under /etc/nginx/conf.d/ as shown.
$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/sysmon.conf
Copy and paste the following configuration (change 192.168.43.31 with your server IP and tecmint.lan with your domain name).
server {
listen 80;
server_name sysmon.tecmint.lan;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_pass http://192.168.43.31:5000;
}
}
Save the changes and exit the file.
Finally, restart the Nginx service to effect the recent changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx OR # systemctl restart nginx
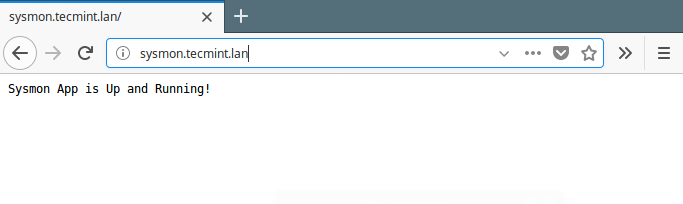
Step 5: Access Nodejs Application via Web Browser
Now you should be able to access your Node app without providing the port it is listening on, in the URL: this is a much convenient way for users to access it.
http://sysmon.tecmint.lan
For your test domain name to work, you need to setup local DNS using the /etc/hosts file, open it and add the line below in it (remember to change 192.168.43.31 with your server IP and tecmint.lan with your doamin name as before).
192.168.43.31 sysmon.tecmint.lan
That’s all! In this article, we showed how to configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for Nodejs applications. Use the feedback form below to ask any questions or share your thoughts about this article.





After updating the server.js file inside the sysmon folder and then running the node command line, I get nothing when trying to reach port 5000 on my browser. I tried using ‘sudo ufw allow 5000/tcp‘, but to no avail. What should I do?
Gabriel,
I hope Nginx already installed on the system to get this work, if not first install Nginx and then try the instructions given in the article…
The config of site have wrong extra
}Please remove it
@Abubakr,
Removed the extra
}string in the article…