In this article, you will learn how to install and enable the EPEL repository on RHEL-based Linux distributions to install additional standard open-source software packages by using YUM and DNF package manager.
What is EPEL
EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) is an open-source and free community-based repository project from the Fedora team which provides 100% high-quality add-on software packages for Linux distribution including RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux), CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux.
EPEL project is not a part of RHEL/CentOS but it is designed for major Linux distributions by providing lots of open-source packages like networking tools, sysadmin tools, programming, monitoring, and so on. Most of the EPEL packages are maintained by the Fedora repo.
Why Do We Use the EPEL Repository?
- Provides lots of open-source packages to install via Yum and DNF.
- Epel repo is 100% open source and free to use.
- It does not provide any core duplicate packages and has no compatibility issues.
- All EPEL packages are maintained by the Fedora repo.
How to Install EPEL Repository on RHEL 9 Systems
To install the EPEL repository on any RHEL-based distributions, log in to your server instance as a root user and run the commands as explained below as per your release version.
Install EPEL Repo on RHEL 9
# subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-9-$(arch)-rpms # dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
Install EPEL Repo on CentOS Stream 9
# dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb # dnf install epel-release epel-next-release
Install EPEL Repo on AlmaLinux 9
# dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb # dnf install epel-release
How to Install EPEL Repository on RHEL 8 Systems
To install the EPEL repository on RHEL 8-based release systems, use:
Install EPEL Repo on RHEL 8
# subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-$(arch)-rpms # dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
Install EPEL Repo on CentOS Stream 8
# dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools # dnf install epel-release
Install EPEL Repo on Rocky/AlmaLinux 8
# dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools # dnf install epel-release
How to Install EPEL Repository on RHEL 7 Systems
Install EPEL Repo on RHEL 7
# subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-*-optional-rpms \
--enable rhel-*-extras-rpms \
--enable rhel-ha-for-rhel-*-server-rpms
# yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
Install EPEL Repo on CentOS 7
# yum install epel-release
Install EPEL Repo on CentOS 6.x
# yum install epel-release
How Do I Verify EPEL Repo?
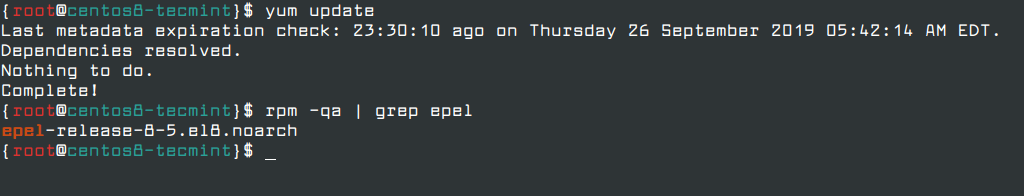
Now update the software packages and verify the installation of the EPEL repository using the following commands.
# yum update # rpm -qa | grep epel
You can also verify that the EPEL repository is enabled on the system by listing all active repositories using the following command.
# yum repolist

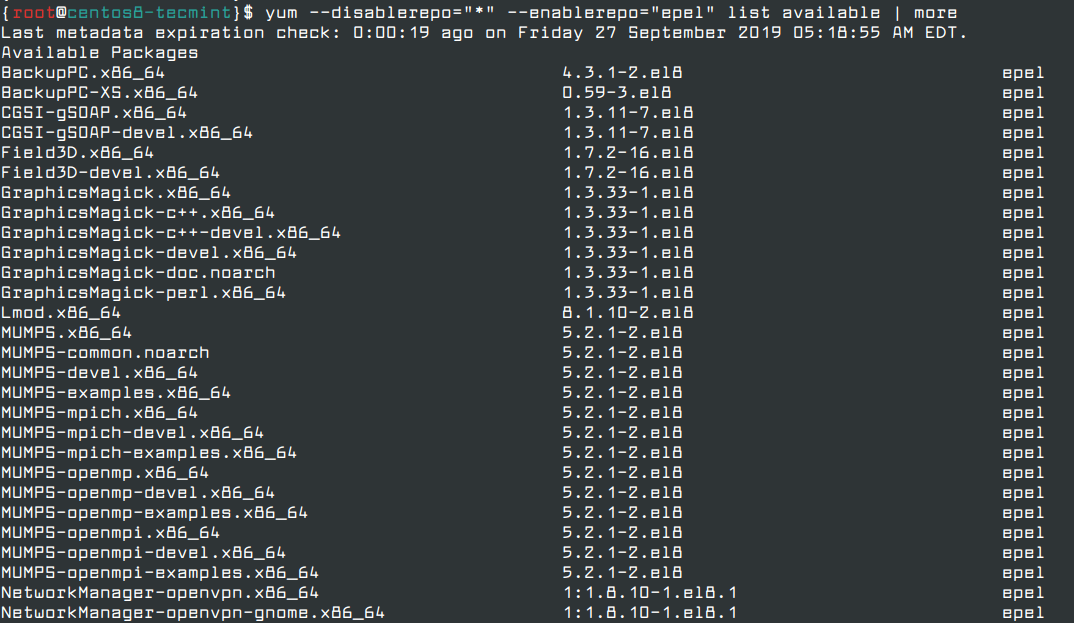
To list the software packages that constitute the EPEL repository, run the command.
# dnf --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="epel" list available OR # yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="epel" list available
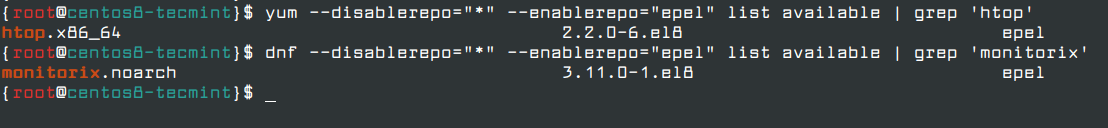
Alternatively, you can use the following grep command to search for individual package names as shown.
# yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="epel" list available | grep 'htop' OR # dnf --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="epel" list available | grep 'monitorix'
How Do I Use EPEL Repo to Install Packages?
Once the EPEL repository has been successfully installed, a package can be installed using the command.
# dnf --enablerepo="epel" install <package_name> OR # yum --enablerepo="epel" install <package_name>
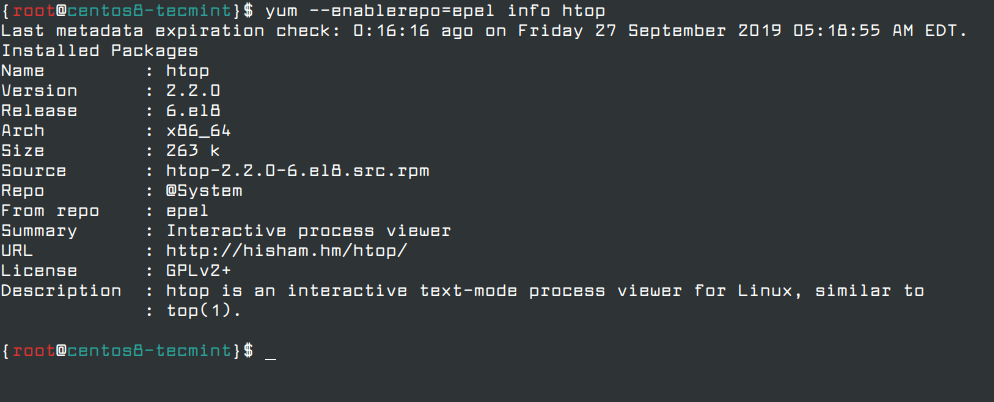
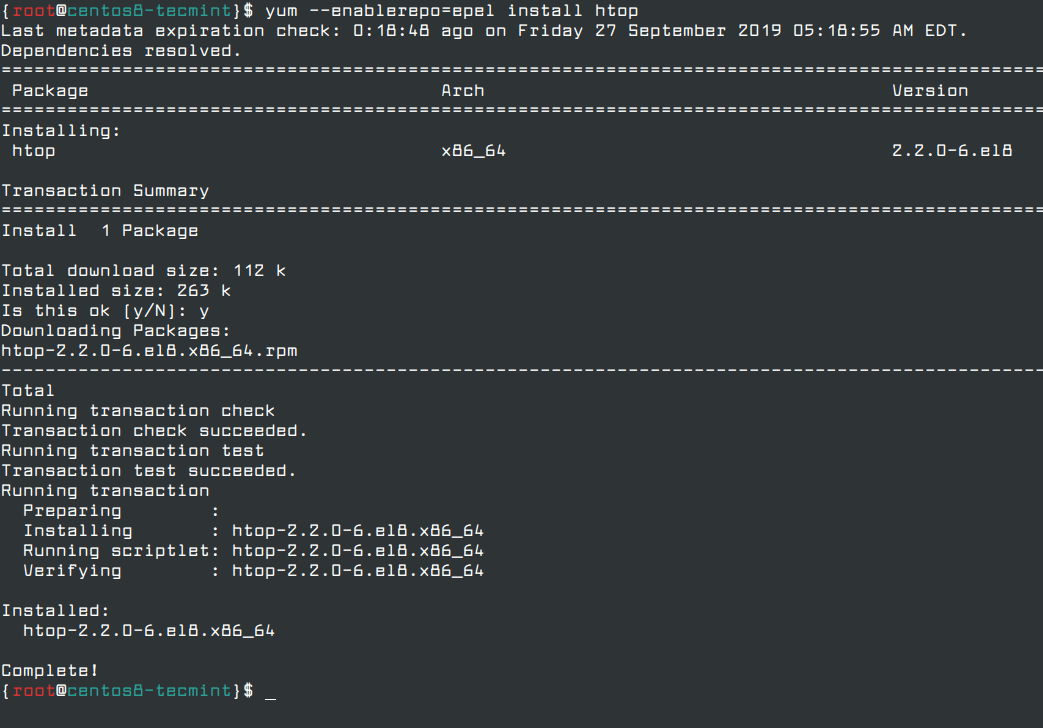
For example, to search and install a package called htop – an interactive Linux process-viewer, run the following command.
# yum --enablerepo=epel info htop
Now, to install the Htop package, the command will be.
# yum --enablerepo=epel install htop
Note: The EPEL configuration file is located under /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.
Conclusion
In this article, you learned how to install the EPEL repository on RHEL-based distributions. We welcome you to try it out and share your feedback in the comment section below.





Does the EPEL Repository stay around after the YUM Repository has reached EOL ??
I am tired of depending on YUM and being left hanging after YUM reaches EOL, and then being forced to upgrade just to use Yum. Is EPEL a stable alternative to YUM?
I use my server to solve problems. I’m not into computer systems development.
I like using Centos, but I don’t like the frequency that new versions come out.
Thanks,
Jim
Trouble installing gdl on Centos 7 with epel-release, conflict with Python installed library. I updated Centos 7. Installed epel-release 7. when I run gdl is says the following: