Linux command line attracts most of the Linux Enthusiastic. A normal Linux user generally posses a vocabulary of roughly 50-60 commands to carry out their day-to-day task. Linux commands and their switches remains the most valuable treasure for a Linux-user, Shell-script programmer and Administrator. There are some Linux Commands which are lesser Known, yet very useful and handy irrespective of the fact whether you are a Novice or an Advanced User.

This very article aims at throwing light on some of the lesser known Linux commands which surely will help you to handle your Desktop/Server more efficiently.
1. sudo !! command
Running the command without specifying sudo command will give you permission denied error. So, you don’t need to rewrite the whole command again just put ‘!!‘ will grab the last command.
$ apt-get update E: Could not open lock file /var/lib/apt/lists/lock - open (13: Permission denied) E: Unable to lock directory /var/lib/apt/lists/ E: Could not open lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (13: Permission denied) E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), are you root?
$ sudo !! sudo apt-get update [sudo] password for server: … .. Fetched 474 kB in 16s (28.0 kB/s) Reading package lists... Done server@localhost:~$
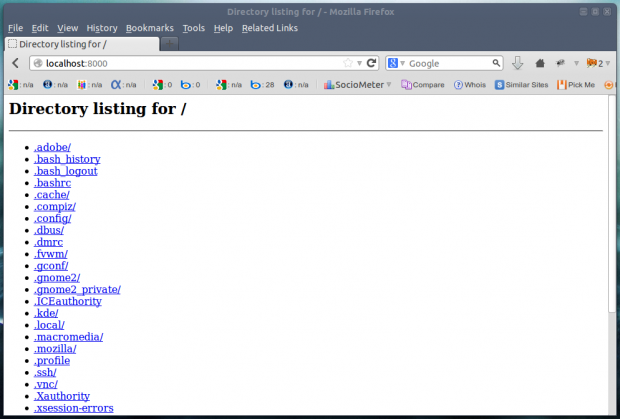
2. python command
The below command generates a simple web page over HTTP for the directory structure tree and can be accessed at port 8000 in browser till interrupt signal is sent.
# python -m SimpleHTTPServer
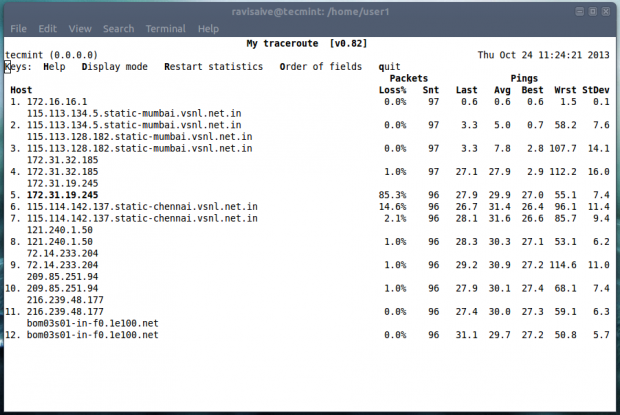
3. mtr Command
Most of us are familiar with ping and traceroute. How about combining the functionality of both the command into one with mtr command. In case mtr is not installed into your machine, apt or yum the required package.
$ sudo apt-get install mtr (On Debian based Systems)
# yum install mtr (On Red Hat based Systems)
Now run mtr command to start investigating the network connection between the host mtr runs on and google.com.
# mtr google.com
4. Ctrl+x+e Command
This command is very much useful for administrator and developers. To Automate day-to-day task an administrator needs to open editor by typing vi, vim, nano, etc. How about firing instant editor (from terminal).
Just Press “Ctrl-x-e” from the terminal prompt and start working in editor.
Download Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet

5. nl Command
The “nl command” number the lines of a file. Number the lines of a file say ‘one.txt‘ with lines say (Fedora, Debian, Arch, Slack and Suse). First list the content of a file “one.txt” using cat command.
# cat one.txt fedora debian arch slack suse
Now run “nl command” to list them in a numbered fashion.
# nl one.txt 1 fedora 2 debian 3 arch 4 slack 5 suse
6. shuf Command
The “shuf” command randomly select lines/files/folder from a file/folder. First list the contents of a folder using ls command.
# ls Desktop Documents Downloads Music Pictures Public Templates Videos
# ls | shuf (shuffle Input) Music Documents Templates Pictures Public Desktop Downloads Videos
# ls | shuf -n1 (pick on random selection) Public
# ls | shuf -n1 Videos
# ls | shuf -n1 Templates
# ls | shuf -n1 Downloads
Note: You can always replace ‘n1‘ with ‘n2‘ to pick two random selection or any other number of random selection using n3, n4.…
7. ss Command
The “ss” stands for socket statistics. The command investigates the socket and shows information similar to netstat command. It can display more TCP and state informations than other tools.
# ss State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.198:41250 *.*.*.*:http CLOSE-WAIT 1 0 127.0.0.1:8000 127.0.0.1:41393 ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.198:36239 *.*.*.*:http ESTAB 310 0 127.0.0.1:8000 127.0.0.1:41384 ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.198:41002 *.*.*.*:http ESTAB 0 0 127.0.0.1:41384 127.0.0.1:8000
8. last Command
The “last” command show the history of last logged in users. This command searches through the file “/var/log/wtmp” and shows a list of logged-in and logged-out users along with tty’s.
# last server pts/0 :0 Tue Oct 22 12:03 still logged in server tty8 :0 Tue Oct 22 12:02 still logged in … ... (unknown tty8 :0 Tue Oct 22 12:02 - 12:02 (00:00) server pts/0 :0 Tue Oct 22 10:33 - 12:02 (01:29) server tty7 :0 Tue Oct 22 10:05 - 12:02 (01:56) (unknown tty7 :0 Tue Oct 22 10:04 - 10:05 (00:00) reboot system boot 3.2.0-4-686-pae Tue Oct 22 10:04 - 12:44 (02:39) wtmp begins Fri Oct 4 14:43:17 2007
9. curl ifconfig.me
So how do you obtain your External IP address? Using google?. Well the command output your external IP address right into your terminal.
# curl ifconfig.me
Note: You might don’t have curl package installed, you have to apt/yum to install package.
10. tree command
Get the current directory structure in tree like format.
# tree
. |-- Desktop |-- Documents | `-- 37.odt |-- Downloads | |-- attachments.zip | |-- ttf-indic-fonts_0.5.11_all.deb | |-- ttf-indic-fonts_1.1_all.deb | `-- wheezy-nv-install.sh |-- Music |-- Pictures | |-- Screenshot from 2013-10-22 12:03:49.png | `-- Screenshot from 2013-10-22 12:12:38.png |-- Public |-- Templates `-- Videos 10 directories, 23 files
11. pstree
This commands shows all the processes running currently along with associated child process, in a tree like format similar to ‘tree‘ command output.
# pstree
init─┬─NetworkManager───{NetworkManager}
├─accounts-daemon───{accounts-daemon}
├─acpi_fakekeyd
├─acpid
├─apache2───10*[apache2]
├─at-spi-bus-laun───2*[{at-spi-bus-laun}]
├─atd
├─avahi-daemon───avahi-daemon
├─bluetoothd
├─colord───{colord}
├─colord-sane───2*[{colord-sane}]
├─console-kit-dae───64*[{console-kit-dae}]
├─cron
├─cupsd
├─2*[dbus-daemon]
├─dbus-launch
├─dconf-service───2*[{dconf-service}]
├─dovecot─┬─anvil
│ ├─config
│ └─log
├─exim4
├─gconfd-2
├─gdm3─┬─gdm-simple-slav─┬─Xorg
│ │ ├─gdm-session-wor─┬─x-session-manag─┬─evolution-a+
│ │ │ │ ├─gdu-notific+
│ │ │ │ ├─gnome-scree+
│ │ │ │ ├─gnome-setti+
│ │ │ │ ├─gnome-shell+++
│ │ │ │ ├─nm-applet──+++
│ │ │ │ ├─ssh-agent
│ │ │ │ ├─tracker-min+
│ │ │ │ ├─tracker-sto+
│ │ │ │ └─3*[{x-sessi+
│ │ │ └─2*[{gdm-session-wor}]
│ │ └─{gdm-simple-slav}
│ └─{gdm3}
├─6*[getty]
├─gnome-keyring-d───9*[{gnome-keyring-d}]
├─gnome-shell-cal───2*[{gnome-shell-cal}]
├─goa-daemon───{goa-daemon}
├─gsd-printer───{gsd-printer}
├─gvfs-afc-volume───{gvfs-afc-volume}
That’s all for now. In the next article of mine I would cover certain other lesser known Linux commands which would be fun. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Like and share us and help us get spread.
Read Also:




Excellent article. Some commands I had once known and then forgotten and some new ones. Thanks!
Very useful – despite working with Linux for years, there is always new/surpising stuff hidden there.
Tecmint team is happy knowing this and will keep coming with such stuffs in future. Keep connected!
Thank you very much, sir.
Can I point out that #9 is not really a linux command, as such, but is making use of the website called “http://ifconfig.me”. Your readers should be made clearly aware of that. Many newbie linux users will not be aware, and many come to linux for privacy concerns.
As for the rest, nice work…
and ifconfig.me doesn’t answer anymore either :(
Very informative!!! Thanks a lot Avishek.
@ Long Cao, welcome. Comment of This kind Encourages us (as writer).
python -m http.server
? @ ovi did u faced any problem in executing this python script. well the command is python -m SimpleHTTPServer.
Avishek, I think what @ ovi is referring to is that in python 3 SimpleHTTPServer has been merged into the http.server module.
Thus his command is correct in python 3 and yours in python 2.
This is described in detail in the following stackoverflow discussion:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/7943751/what-is-the-python3-equivalent-of-python-m-simplehttpserver