In this article, we will describe how to change a user’s shell in Linux. The shell is a program that accepts and interprets commands; there are several shells such as bash, sh, ksh, zsh, fish and many other lesser known shells available on Linux.
Bash (/bin/bash) is a popular shell on most if not all Linux systems, and it’s normally the default shell for user accounts.
Read Also: 5 Most Frequently Used Open Source Shells for Linux
There are several reasons for changing a user’s shell in Linux including the following:
- To block or disable normal user logins in Linux using a nologin shell.
- Use a shell wrapper script or program to login user commands before they are sent to a shell for execution. Here, you specify the shell wrapper as a user’s login shell.
- To meet a user’s demands (wants to use a specific shell), especially those with administrative rights.
When creating user accounts with the useradd or adduser utilities, the --shell flag can be used to specify the name of a user’s login shell other than that specified in the respective configuration files.
A login shell can be accessed from a text based interface or via a SSH from remote Linux machine. However, if you login via a graphical user interface (GUI), you can access the shell from a terminal emulators like xterm, konsole and many more.
Let’s first list all available shells on your Linux system, type.
# cat /etc/shells /bin/sh /bin/bash /sbin/nologin /bin/tcsh /bin/csh /bin/dash
Before you proceed any further, note that:
- A user can change their own shell to any thing: which, however must be listed in the /etc/shells file.
- Only root can run a shell not listed in /etc/shells file.
- If an account has a restricted login shell, then only root can change that user’s shell.
Now let’s discuss three different ways to change Linux user shell.
1. usermod Utility
usermod is a utility for modifying a user’s account details, stored in the /etc/passwd file and the -s or --shell option is used to change the user’s login shell.
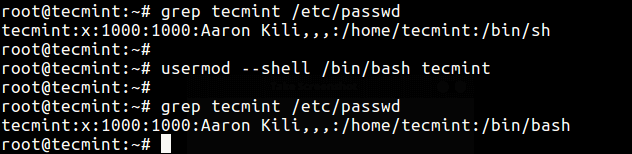
In this example, we’ll first check user tecmint’s account information to view his default login shell and then change its login shell from /bin/sh to /bin/bash as follows.
# grep tecmint /etc/passwd # usermod --shell /bin/bash tecmint # grep tecmint /etc/passwd
2. chsh Utility
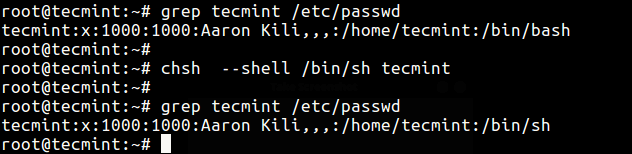
chsh is a command line utility for changing a login shell with the -s or –shell option like this.
# grep tecmint /etc/passwd # chsh --shell /bin/sh tecmint # grep tecmint /etc/passwd
The two methods above all modify the shell specified in /etc/passwd file which you can edit manually as in the third method below.
3. Change User Shell in /etc/passwd File
In this method, simply open the /etc/passwd file using any of your favorite command line text editors and change a specific users shell.
# vi /etc/passwd
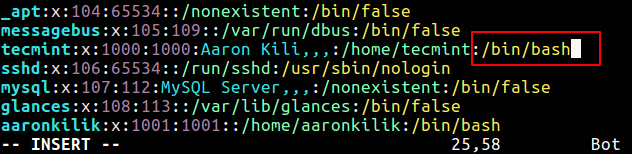
When your done editing, save and close the file.
Do not forget to read these related topics:
- Understanding Shell Initialization Files and User Profiles in Linux
- Understand Linux Shell and Basic Shell Scripting Tips – Part I
- How To Write and Use Custom Shell Functions and Libraries
- Understanding Different Classifications of Shell Commands and Their Usage
In this article, we described various ways of changing a user’s shell in Linux. To share any thoughts with us, use the comment section below.




On some Linux distributions, some shells like tcsh aren’t installed by default, but you can probably install them.
For instance on Fedora 31,
It is all you need to do (as root) to install tcsh.