Netcat (or nc in short) is a simple yet powerful networking command-line tool used for performing any operation in Linux related to TCP, UDP, or UNIX-domain sockets.
Netcat can be used for port scanning, port redirection, as a port listener (for incoming connections); it can also be used to open remote connections and so many other things. Besides, you can use it as a backdoor to gain access to a target server.
In this article, we will explain Netcat usage commands with examples.
How to Install and Use Netcat in Linux
To install the netcat package on your system, use the default package manager for your Linux distribution.
$ yum install nc [On CentOS/RHEL] $ dnf install nc [On Fedora 22+ and RHEL 8] $ sudo apt-get install Netcat [On Debian/Ubuntu]
Once netcat package installed, you can proceed further to learn the usage of netcat command in the following examples.
Port Scanning
Netcat can be used for port scanning: to know which ports are open and running services on a target machine. It can scan a single or multiple or a range of open ports.
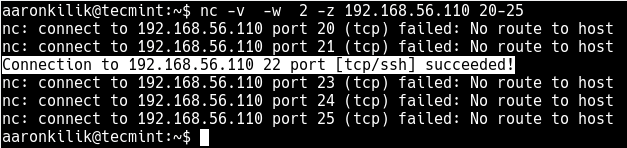
Here is an example, the -z option sets nc to simply scan for listening daemons, without actually sending any data to them. The -v option enables verbose mode and -w specifies a timeout for connection that can not be established.
$ nc -v -w 2 z 192.168.56.1 22 #scan a single port OR $ nc -v -w 2 z 192.168.56.1 22 80 #scan multiple ports OR $ nc -v -w 2 z 192.168.56.1 20-25 #scan range of ports
Transfer Files Between Linux Servers
Netcat allows you to transfer files between two Linux computers or servers and both these systems must have nc installed.
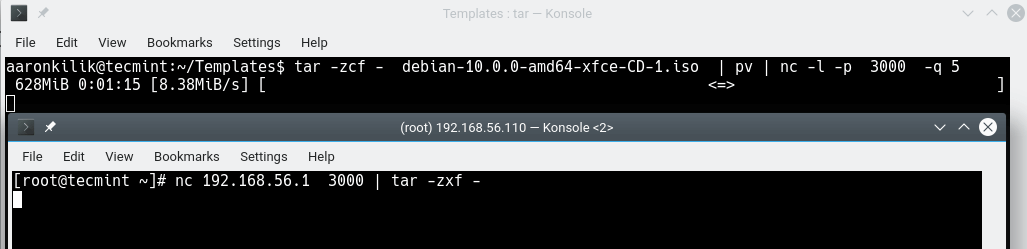
For example, to copy an ISO image file from one computer to another and monitor the transfer progress (using the pv utility), run the following command on the sender/server computer (where the ISO file exists).
This will run nc in listening mode (-l flag) on port 3000.
$ tar -zcf - debian-10.0.0-amd64-xfce-CD-1.iso | pv | nc -l -p 3000 -q 5
And on the receiver/client computer, run the following command to obtain the file.
$ nc 192.168.1.4 3000 | pv | tar -zxf -
Create a Command Line Chat Server
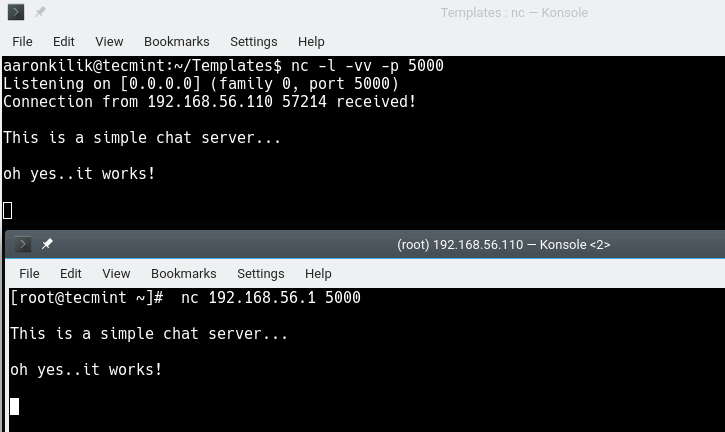
You can also use Netcat to create a simple command-line messaging server instantly. As in the previous usage example, nc must be installed on both systems used for the chat room.
On one system, run the following command to create the chat server listening on port 5000.
$ nc -l -vv -p 5000
On the other system, run the following command to launch a chat session to a machine where the messaging server is running.
$ nc 192.168.56.1 5000
Create a Basic Web Server
Wit the -l option of nc command used to create a basic, insecure web server to serve static web files for learning purposes. To demonstrate this, create a .html file as shown.
$ vim index.html
Add the following HTML lines in the file.
<html>
<head>
<title>Test Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Serving this file using Netcat Basic HTTP server!</p>
</body>
</html>
Save changes in the file and exit.
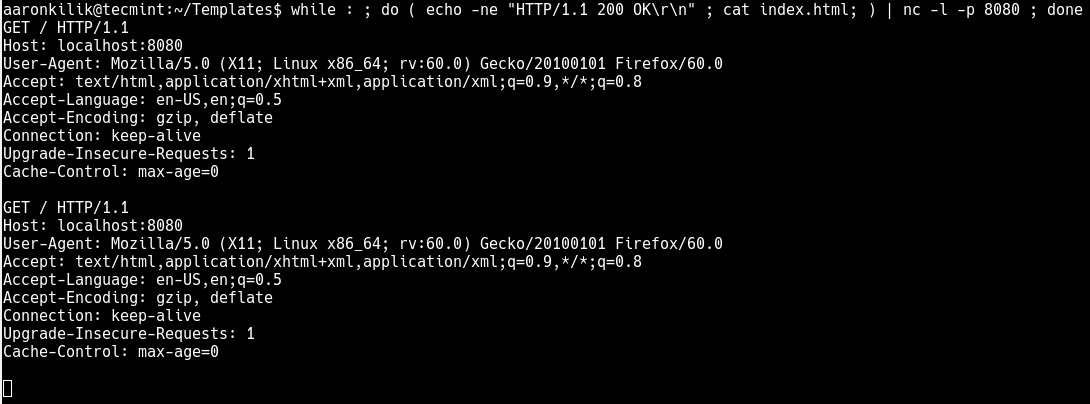
Then serve the above file over HTTP by running the following command, which will enables the HTTP server to run continuously.
$ while : ; do ( echo -ne "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" ; cat index.html; ) | nc -l -p 8080 ; done
Then open a web browser and can access the content using the following address.
http://localhost:8080 OR http://SERVER_IP:8080
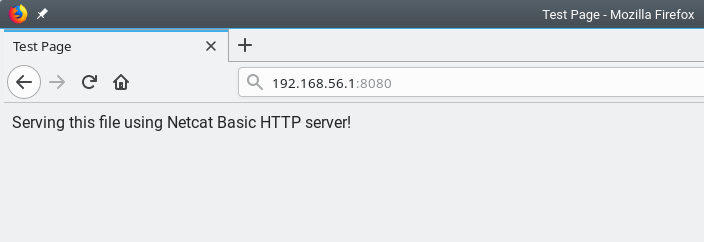
Note that you can to stop the Netcat HTTP server by pressing [Ctrl+ C].
Troubleshoot Linux Server Connection
Another useful usage of Netcat is to troubleshoot server connection issues. Here, you can use Netcat to verify what data a server is sending in response to commands issued by the client.
The following command retrieves the home page of example.com.
$ printf "GET / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n" | nc text.example.com 80
The output of the above command includes the headers sent by the web-server which can be used for troubleshooting purposes.
Find a Service Running on Port
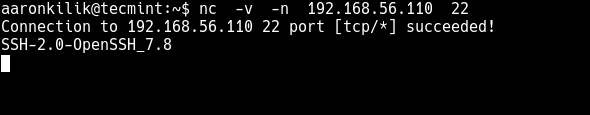
You can also use Netcat to obtain port banners. In this case, it will tell you what service is running behind a certain port. For example to know what type of service is running behind port 22 on a specific server, run the following command (replace 192.168.56.110 with the target server’s IP address). The -n flag means to disable DNS or service lookups.
$ nc -v -n 192.168.56.110 80
Create a Stream Sockets
Netcat also supports creation of UNIX-domain stream sockets. The following command will create and listen on a UNIX-domain stream socket.
$ nc -lU /var/tmp/mysocket & $ ss -lpn | grep "/var/tmp/"
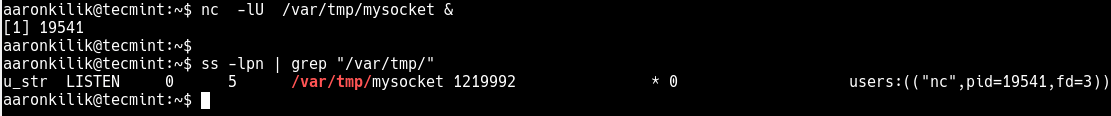
Create a Backdoor
You can as well run Netcat as a backdoor. However, this calls for more work. If Netcat is installed on a target server, you can use it to create a backdoor, to get a remote command prompt.
To act a backdoor you need Netcat to listen on a chosen port (e.g port 3001) on the target server and then you can connect to this port from your machine as follows.
This is the command intended to run on the remote server where the -d option disables reading from stdin, and -e specifies the command to run on the target system.
$ nc -L -p 3001 -d -e cmd.exe
Last but not least, Netcat can be used as a proxy for different services/protocols including HTTP, SSH, and many more. For more information, see its man page.
$ man nc
In this article, we have explained 8 practical Netcat command usage examples. If you know any other practical use case(s), share with us via the feedback form below. You can ask a question as well.




The package name is not `Netcat`, its `netcat`.
nc is failing for multiple ports & range
In the first example, you should make it
-zrather than z.Thanks
You can pair netcat with tcpdump to stream a packet capture to another host. This is useful for capturing in real time traffic on busybox or other small Linux distributions.
I have had luck using tcpdump for android on busybox running a security camera.
@Jared
Great, I will do more research on this and practically test it. Many thanks for sharing.