Arpwatch is an open-source computer software program that helps you to monitor Ethernet traffic activity (like Changing IP and MAC Addresses) on your network and maintains a database of ethernet/ip address pairings.
It produces a log of the noticed pairing of IP and MAC address information along with a timestamp, so you can carefully watch when the pairing activity appeared on the network. It also has the option to send reports via email to a network administrator when a pairing is added or changed.
The Arpwatch tool is especially useful for Network administrators to keep a watch on ARP activity to detect ARP spoofing or unexpected IP/MAC address modifications.
Installing Arpwatch in Linux
The Arpwatch tool is not installed on Linux distributions, you need to use your default package manager to install it from the system repositories as shown.
$ sudo apt install arpwatch [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install arpwatch [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a net-analyzer/arpwatch [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add arpwatch [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S arpwatch [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install arpwatch [On OpenSUSE]
Once installed, you can view the most important arpwatch files, the locations of the files are slightly different based on your operating system.
- /usr/lib/systemd/system/arpwatch – The arpwatch service for starting or stopping the daemon.
- /etc/sysconfig/arpwatch – This is the main arpwatch configuration file.
- /usr/sbin/arpwatch – Binary command to starting and stopping tool via the terminal.
- /var/lib/arpwatch/arp.dat – This is the main database file where IP/MAC addresses are recorded.
- /var/log/messages – The log file, where arpwatch writes any changes or unusual activity to IP/MAC.
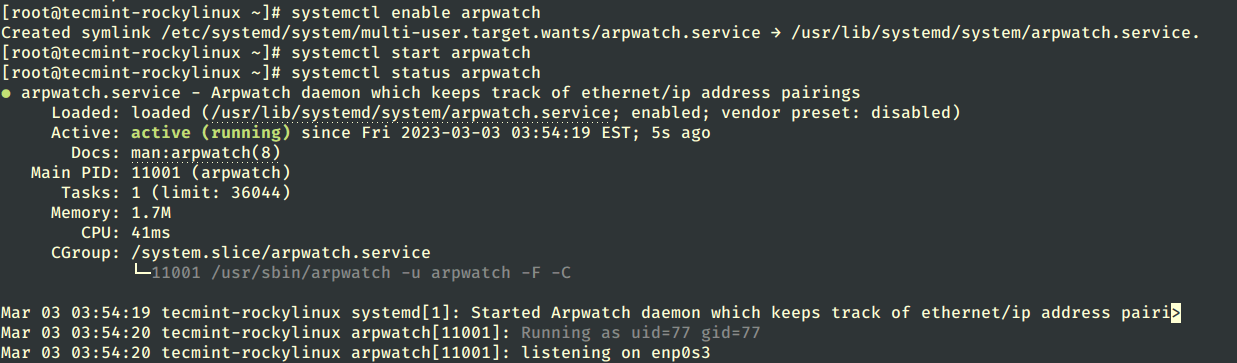
Now run the following command to start the arpwatch service.
# systemctl enable arpwatch # systemctl start arpwatch # systemctl status arpwatch
How to Use Arpwatch Commands in Linux
To watch a specific interface, type the following command with -i and device name.
# arpwatch -i eth0
So, whenever a new MAC is plugged in or a particular IP is changing his MAC address on the network, you will notice syslog entries in the ‘/var/log/syslog‘ or ‘/var/log/message‘ file using the tail command.
# tail -f /var/log/messages
Sample Output
Apr 15 12:45:17 tecmint arpwatch: new station 172.16.16.64 d0:67:e5:c:9:67 Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: new station 172.16.25.86 0:d0:b7:23:72:45 Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: new station 172.16.25.86 0:d0:b7:23:72:45 Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: new station 172.16.25.86 0:d0:b7:23:72:45 Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: new station 172.16.25.86 0:d0:b7:23:72:45
The above output displays a new workstation. If any changes are made, you will get the following output.
Apr 15 12:45:17 tecmint arpwatch: changed station 172.16.16.64 0:f0:b8:26:82:56 (d0:67:e5:c:9:67) Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: changed station 172.16.25.86 0:f0:b8:26:82:56 (0:d0:b7:23:72:45) Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: changed station 172.16.25.86 0:f0:b8:26:82:56 (0:d0:b7:23:72:45) Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: changed station 172.16.25.86 0:f0:b8:26:82:56 (0:d0:b7:23:72:45) Apr 15 12:45:19 tecmint arpwatch: changed station 172.16.25.86 0:f0:b8:26:82:56 (0:d0:b7:23:72:45)
You can also check the current ARP table, by using the following command.
# arp -a
Sample Output
tecmint.com (172.16.16.94) at 00:14:5e:67:26:1d [ether] on eth0 ? (172.16.25.125) at b8:ac:6f:2e:57:b3 [ether] on eth0
If you want to send alerts to your custom email id, then open the main configuration file ‘/etc/sysconfig/arpwatch‘ and add the email as shown below.
# -u <username> : defines with what user id arpwatch should run # -e <email> : the <email> where to send the reports # -s <from> : the <from>-address OPTIONS="-u arpwatch -e [email protected] -s 'root (Arpwatch)'"
Here is an example of an email report, when a new MAC is connected on.
hostname: centos
ip address: 172.16.16.25
interface: eth0
ethernet address: 00:24:1d:76:e4:1d
ethernet vendor: GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.
timestamp: Monday, April 15, 2022 15:32:29
Here is an example of an email report, when an IP changes his MAC address.
hostname: centos
ip address: 172.16.16.25
interface: eth0
ethernet address: 00:56:1d:36:e6:fd
ethernet vendor: GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.
old ethernet address: 00:24:1d:76:e4:1d
timestamp: Monday, April 15, 2022 15:43:45
previous timestamp: Monday, April 15, 2022 15:32:29
delta: 9 minutes
As you can see above, it records, Hostname, IP address, MAC address, Vendor name, and timestamps.
For more information, see the arpwatch man page by hitting ‘man arpwatch’ on the terminal.
# man arpwatch


Not happy with the tutorial. It is not explaining much for Linux bionic. I have installed ARPwatch on my ubuntu system (sudo apt install arpwatch) I cannot see any config file in /etc, not any sysconfig file in /etc. Am I doing anything wrong?
not recommend to use arpwatch on VPS or shared network because it opens the promiscuous mode by default which lets attacker sniff all packets.
Then what do you recommend on VPS?