OpenStack is a free and open-source software platform which provides IAAS (infrastructure-as-a-service) for public and private clouds.
OpenStack platform consists of several inter-related projects that control hardware, storage, networking resources of a datacenter, such as: Compute, Image Service, Block Storage, Identity Service, Networking, Object Storage, Telemetry, Orchestration and Database.
The administration of those components can be managed through the web-based interface or with the help of OpenStack command line.

This tutorial will guide you on how you can deploy your own private cloud infrastructure with OpenStack installed on a single node in CentOS 7 or RHEL 7 or Fedora distributions by using rdo repositories, although the deployment can be achieved on multiple nodes.
Requirements
Step 1: Initial System Configurations
1. Before you begin preparing the node in order to deploy your own virtual cloud infrastructure, first login with root account and assure that the system is up to date.
2. Next, issue the ss -tulpn command to list all running services.
# ss -tulpn
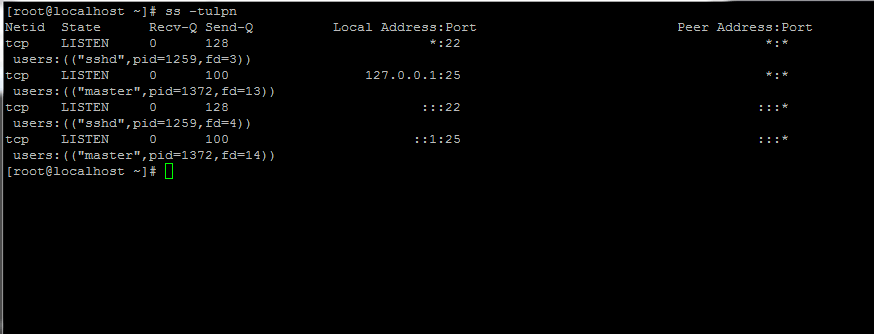
3. Next, identify, stop, disable and remove unneeded services, mainly postfix, NetworkManager and firewalld. At the end the only daemon that would be running on your machine should be sshd.
# systemctl stop postfix firewalld NetworkManager # systemctl disable postfix firewalld NetworkManager # systemctl mask NetworkManager # yum remove postfix NetworkManager NetworkManager-libnm
4. Completely disable Selinux policy on the machine by issuing the below commands. Also edit /etc/selinux/config file and set SELINUX line from enforcing to disabled as illustrated on the below screenshot.
# setenforce 0 # getenforce # vi /etc/selinux/config

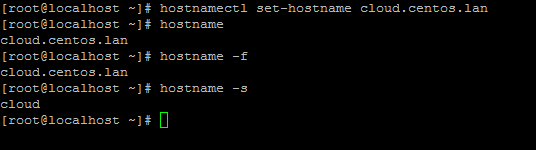
5. On the next step using the hostnamectl command to set your Linux system hostname. Replace the FQDN variable accordingly.
# hostnamectl set-hostname cloud.centos.lan
6. Finally, install ntpdate command in order to synchronize time with a NTP server on your premises near your physical proximity.
# yum install ntpdate
Step 2: Install OpenStack in CentOS and RHEL
7. OpenStack will be deployed on your Node with the help of PackStack package provided by rdo repository (RPM Distribution of OpenStack).
In order to enable rdo repositories on RHEL 7 run the below command.
# yum install https://www.rdoproject.org/repos/rdo-release.rpm
On CentOS 7, the Extras repository includes the RPM that actives the OpenStack repository. Extras is already enabled, so you can easily install the RPM to setup the OpenStack repository:
# yum install -y centos-release-openstack-mitaka # yum update -y
8. Now it’s time to install PackStack package. Packstack represents a utility which facilitates the deployment on multiple nodes for different components of OpenStack via SSH connections and Puppet modules.
Install Packstat package in Linux with the following command:
# yum install openstack-packstack
9. On the next step generate an answer file for Packstack with the default configurations which will be later edited with the required parameters in order to deploy a standalone installation of Openstack (single node).
The file will be named after the current day timestamp when generated (day, month and year).
# packstack --gen-answer-file='date +"%d.%m.%y"'.conf # ls
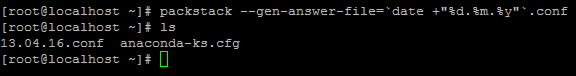
10. Now edit the generated answer configuration file with a text editor.
# vi 13.04.16.conf
and replace the following parameters to match the below values. In order to be safe replace the passwords fields accordingly.
CONFIG_NTP_SERVERS=0.ro.pool.ntp.org
Please consult http://www.pool.ntp.org/en/ server list in order to use a public NTP server near your physical location.

CONFIG_PROVISION_DEMO=n

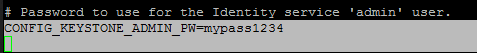
CONFIG_KEYSTONE_ADMIN_PW=your_password for Admin user
Access OpenStack dashboard via HTTP with SSL enabled.
CONFIG_HORIZON_SSL=y

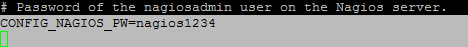
The root password for MySQL server.
CONFIG_MARIADB_PW=mypassword1234
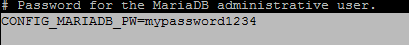
Setup a password for nagiosadmin user in order to access Nagios web panel.
CONFIG_NAGIOS_PW=nagios1234
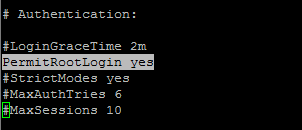
11. After you finished editing save and close the file. Also, open SSH server configuration file and uncomment PermitRootLogin line by removing the front hashtag as illustrated on the below screenshot.
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Then restart SSH service to reflect changes.
# systemctl restart sshd
Step 3: Start Openstack Installation Using Packstack Answer File
12. Finally start Openstack installation process via the answer file edited above by running the below command syntax:
# packstack --answer-file 13.04.16.conf
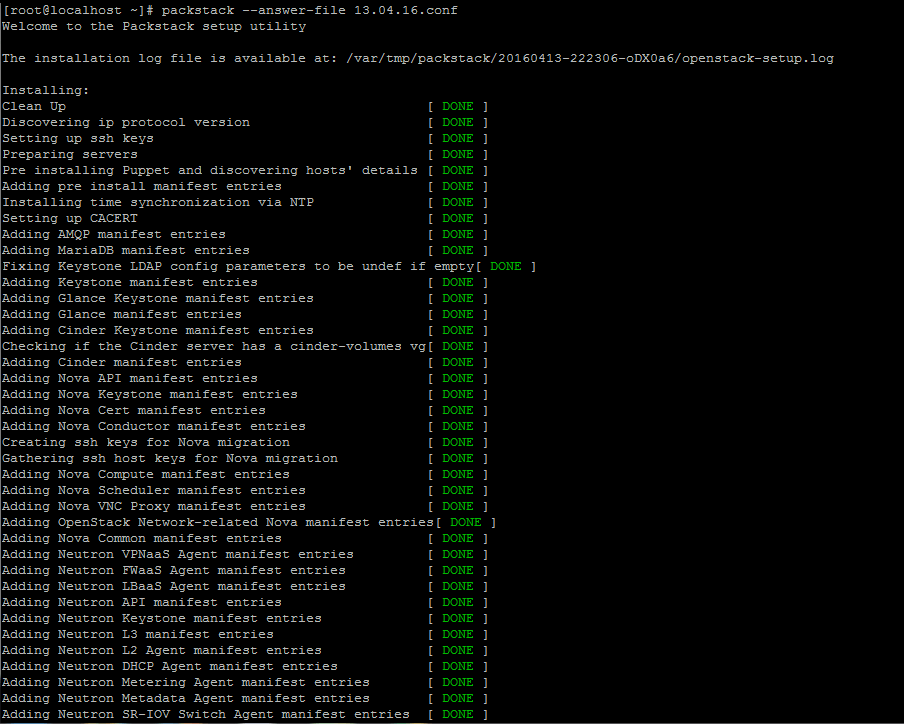
13. Once the installation of OpenStack components is successfully completed, the installer will display a few lines with the local dashboard links for OpenStack and Nagios and the required credentials already configured above in order to login on both panels.
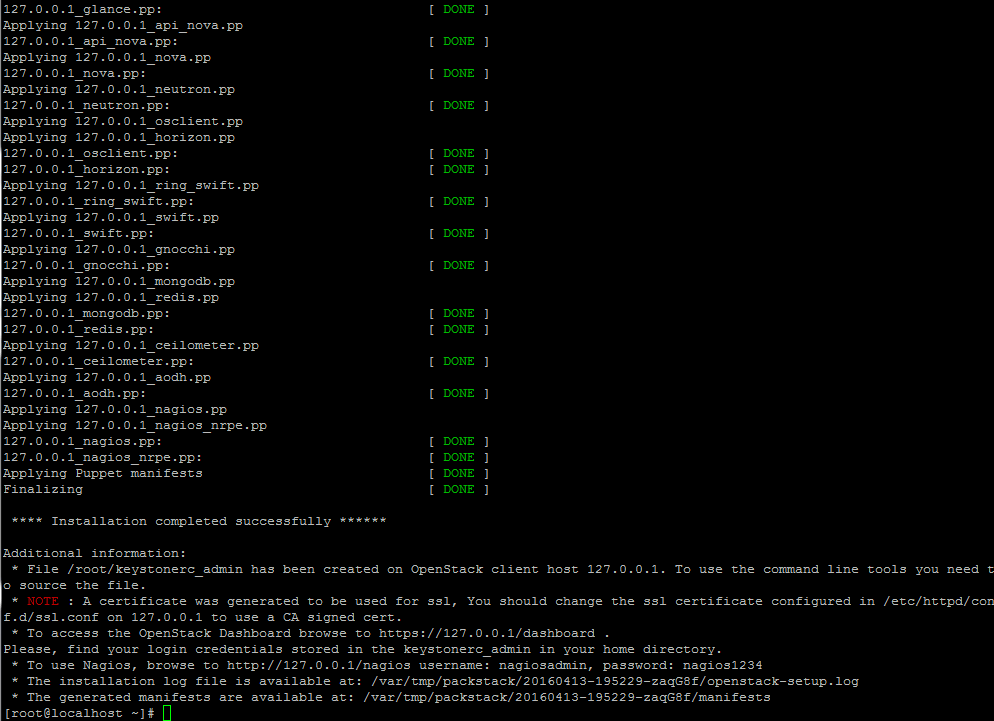
The credentials are also stored under your home directory in keystonerc_admin file.
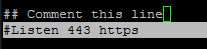
14. If for some reasons the installation process ends with an error regarding httpd service, open /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf file and make sure you comment the following line as illustrated below.
#Listen 443 https
Then restart Apache daemon to apply changes.
# systemctl restart httpd.service
Note: In case you still can’t browse Openstack web panel on port 443 restart the installation process from beginning with the same command issued for the initial deployment.
# packstack --answer-file /root/13.04.16.conf
Step 4: Remotely Access OpenStack Dashboard
15. In order to access OpenStack web panel from a remote host in your LAN navigate to your machine IP Address or FQDN/dashboard via HTTPS protocol.
Due to the fact that you’re using a Self-Signed Certificate issued by an untrusted Certificate Authority an error should be displayed on your browser.
Accept the error and login to the dashboard with the user admin and the password set on CONFIG_KEYSTONE_ADMIN_PW parameter from answer file set above.
https://192.168.1.40/dashboard

16. Alternatively, if you opted to install Nagios component for OpenStack, you can browse Nagios web panel at the following URI and login with the credentials setup in answer file.
https://192.168.1.40/nagios
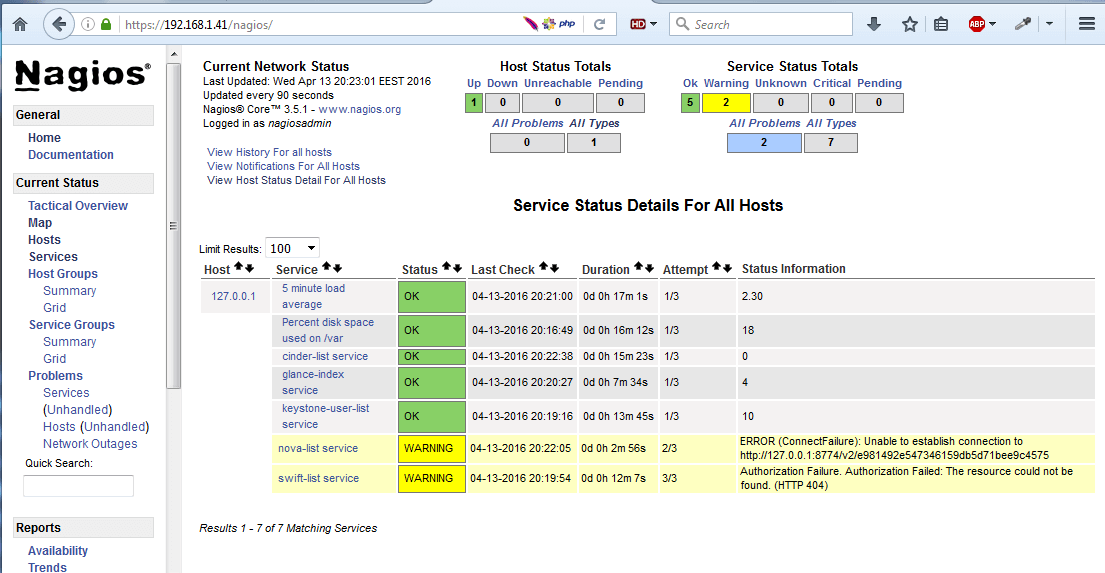
That’s all! Now you can start setup your own internal cloud environment. Now follow the next tutorial that will explain how to link the server physical NIC to openstack bridge interface and manage Openstack from web panel.



Not able to find #Listen 443 https port ssl.conf file.
Thanks
mahesh madudhula
No package centos-release-openstack-mitaka available.
Kindly suggest
Type below command:
and then the available series will be printed.
It works for me, thanks a lot for your contribution!!!