To a little surprise this time we are not presenting Interview question on any specific subject but on random topics. These question will surely help you in cracking Interviews beside adding to your Knowledge.

1. Let’s say you maintains a backup on regular basis for the company you are working. The backups are maintained in Compressed file format. You need to examine a log, two months old. What would you suggest without decompressing the compressed file?
# zcat f phpshell2.4.tar.gz
2. You need to track events on your system. What will you do?
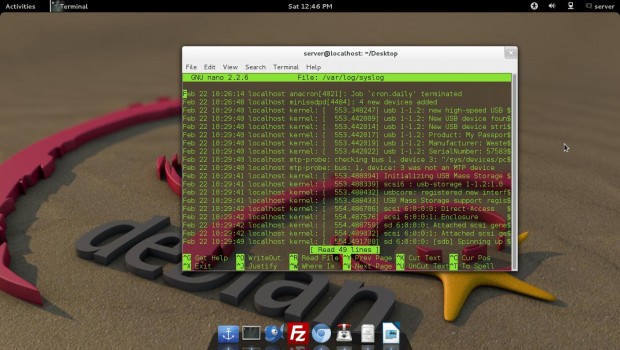
Running ‘syslogd‘ application in terminal generates log file at the location ‘/var/log/syslog‘. The syslogd application is very useful in troubleshooting Linux sytems. A sample log file looks similar to below.
3. How will you restrict IP so that the restricted IP’s may not use the FTP Server?
Block IP Address
Open ‘/etc/hosts.deny’ file.
# vi /etc/hosts.deny
Add the IP address that you want to block at the bottom of the file.
# # hosts.deny This file contains access rules which are used to # deny connections to network services that either use # the tcp_wrappers library or that have been # started through a tcp_wrappers-enabled xinetd. # # The rules in this file can also be set up in # /etc/hosts.allow with a 'deny' option instead. # # See 'man 5 hosts_options' and 'man 5 hosts_access' # for information on rule syntax. # See 'man tcpd' for information on tcp_wrappers # vsftpd:172.16.16.1
4. Tell us the difference between Telnet and SSH?
6. You need to stop your X server. When you tries to kill your X server, You got an error message that you cannot quit X server. What will you do?
6. What is the difference between command ‘ping’ and ‘ping6’?
7. You want to search for all the *.tar files in your Home directory and wants to delete all at once. How will you do it?
# find /home/ name '*.tar' | xargs rm rf
8. What is the difference between locate and slocate command?
9. You need to search for the string “Tecmint” in all the “.txt” files in the current directory. How will you do it?
# find -name “*.txt” | xargs grep “Tecmint”
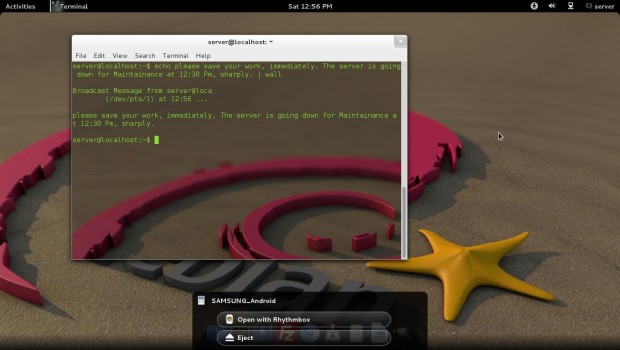
10. You want to send a message to all connected users as “Server is going down for maintenance”, what will you do?
# echo please save your work, immediately. The server is going down for Maintenance at 12:30 Pm, sharply. | wall
That’s all for now. I will be here again, with an interesting article very soon. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t Forget to give your valuable feedback in comment section below.






I need all the linux interview questions & answers so that i can prepare for the interview by this december i need to crack job.
@Niharika,
Please check out our Interview Questions section, where you will find all Linux related questions, which will help you to prepare for your Job interview..
Awesome! thanks for the valuable information, awaiting for further questions!!
Good questions posted by tecmint, thanks a lot
lesspipe will be helpful for viewing backup which is compressed.
*.a
*.arj
*.tar.bz2
*.bz
*.bz2
*.deb, *.udeb, *.ddeb
*.doc
*.gif, *.jpeg, *.jpg, *.pcd, *.png, *.tga, *.tiff, *.tif
*.iso, *.raw, *.bin
*.lha, *.lzh
*.tar.lz, *.tlz
*.lz
*.7z
*.pdf
*.rar, *.r[0-9][0-9]
*.rpm
*.tar.gz, *.tgz, *.tar.z, *.tar.dz
*.gz, *.z, *.dz
*.tar
*.tar.xz, *.xz
*.jar, *.war, *.xpi, *.zip
*.zoo